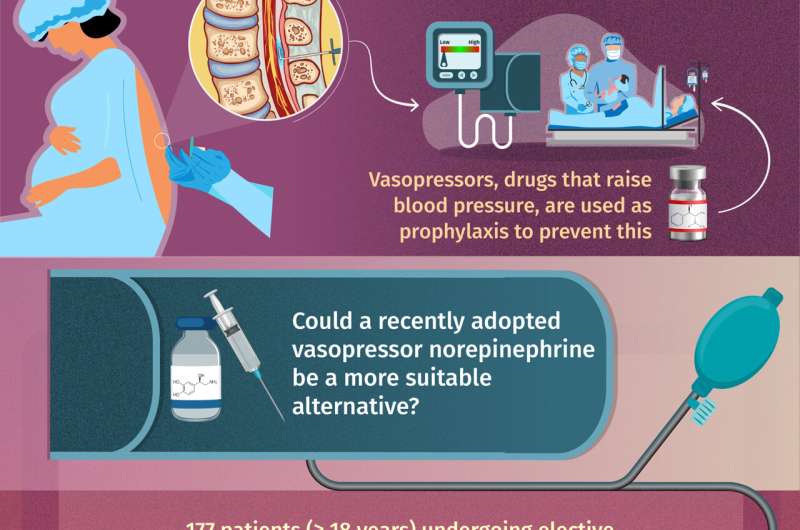
Prevention of Ischemic Complications of Non-Q Wave
Non-Q wave myocardial infarction (non-Q wave MI), often categorized under non-ST elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI), poses significant risk for recurrent ischemic events, including reinfarction, heart…