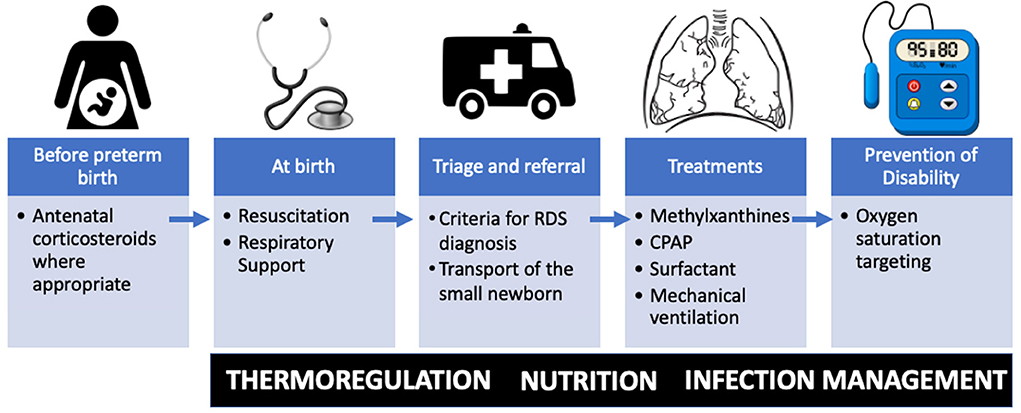
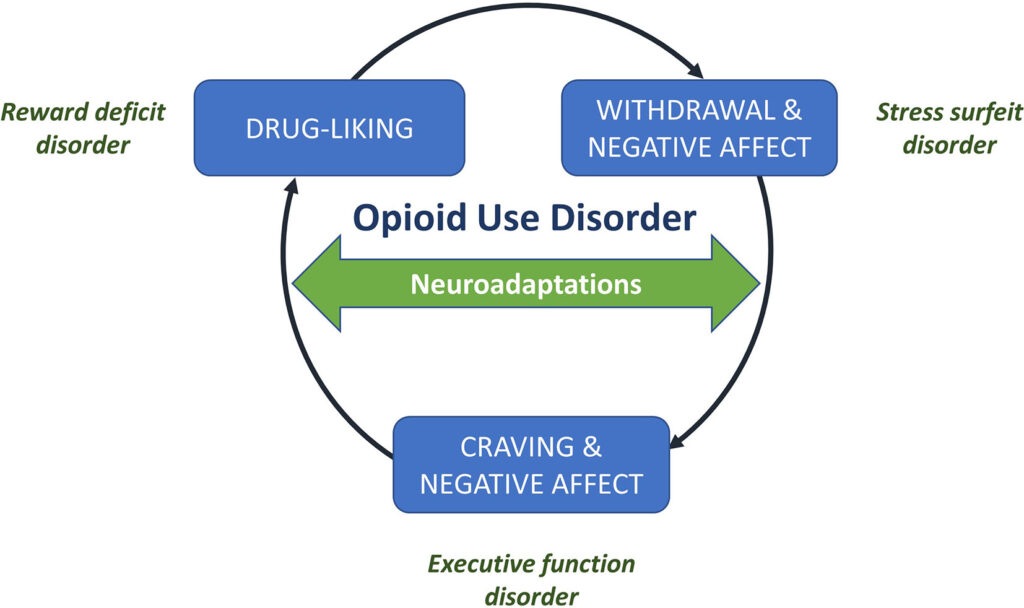
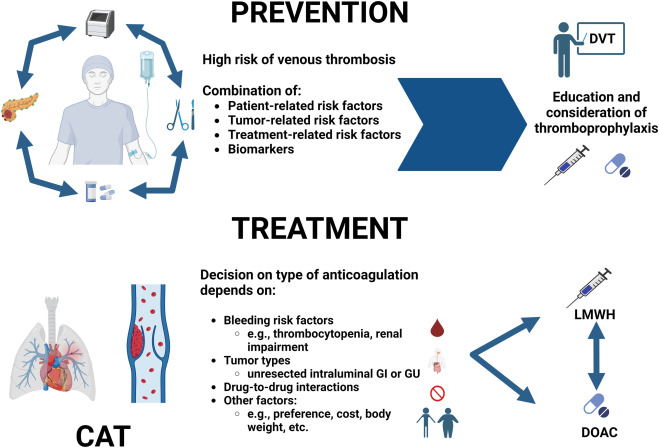
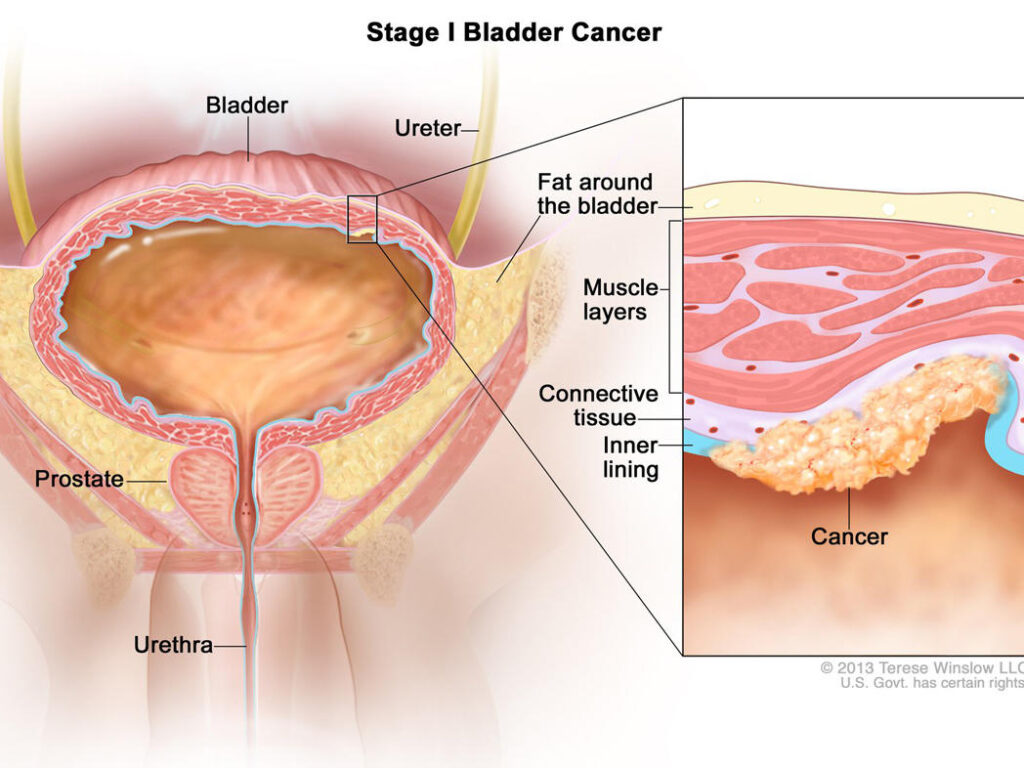
Prevention of Seizures Following Cranial Trauma or Surgery
Seizures following cranial trauma or neurosurgical interventions represent a serious neurological complication with implications for recovery, long-term outcomes, and patient safety. These seizures can be…