Posted inH
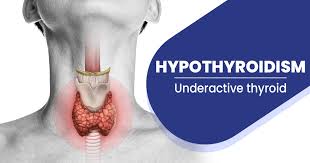
Hypothyroidism: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Treatments
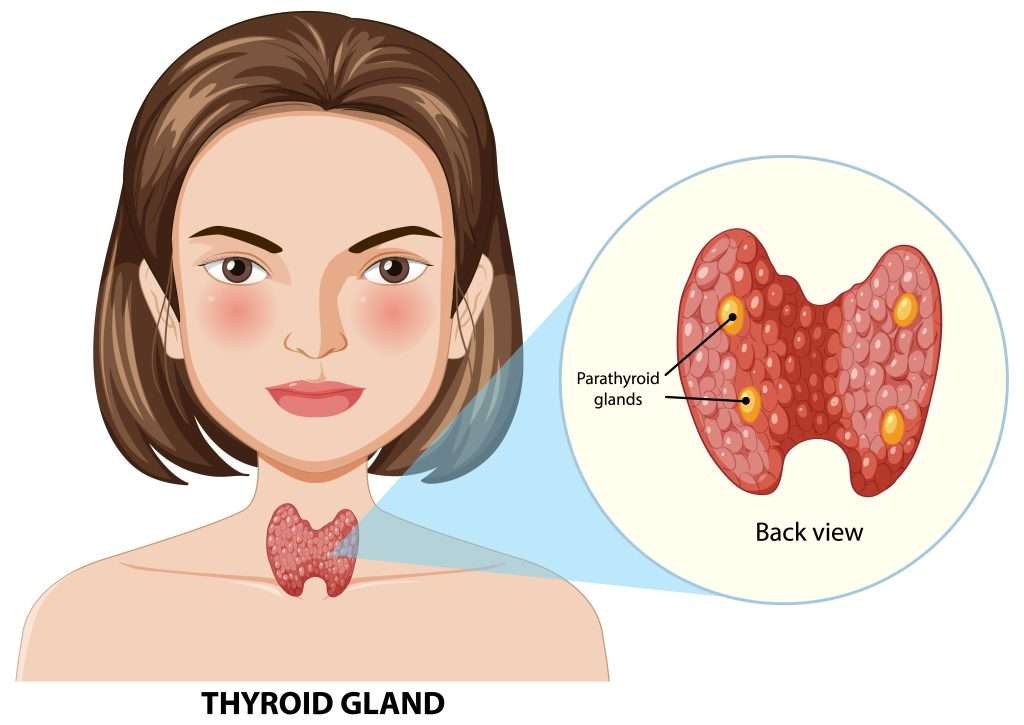
Hypothyroidism, commonly referred to as an underactive thyroid, is a medical condition in which the thyroid gland fails to produce sufficient thyroid hormones. These hormones…