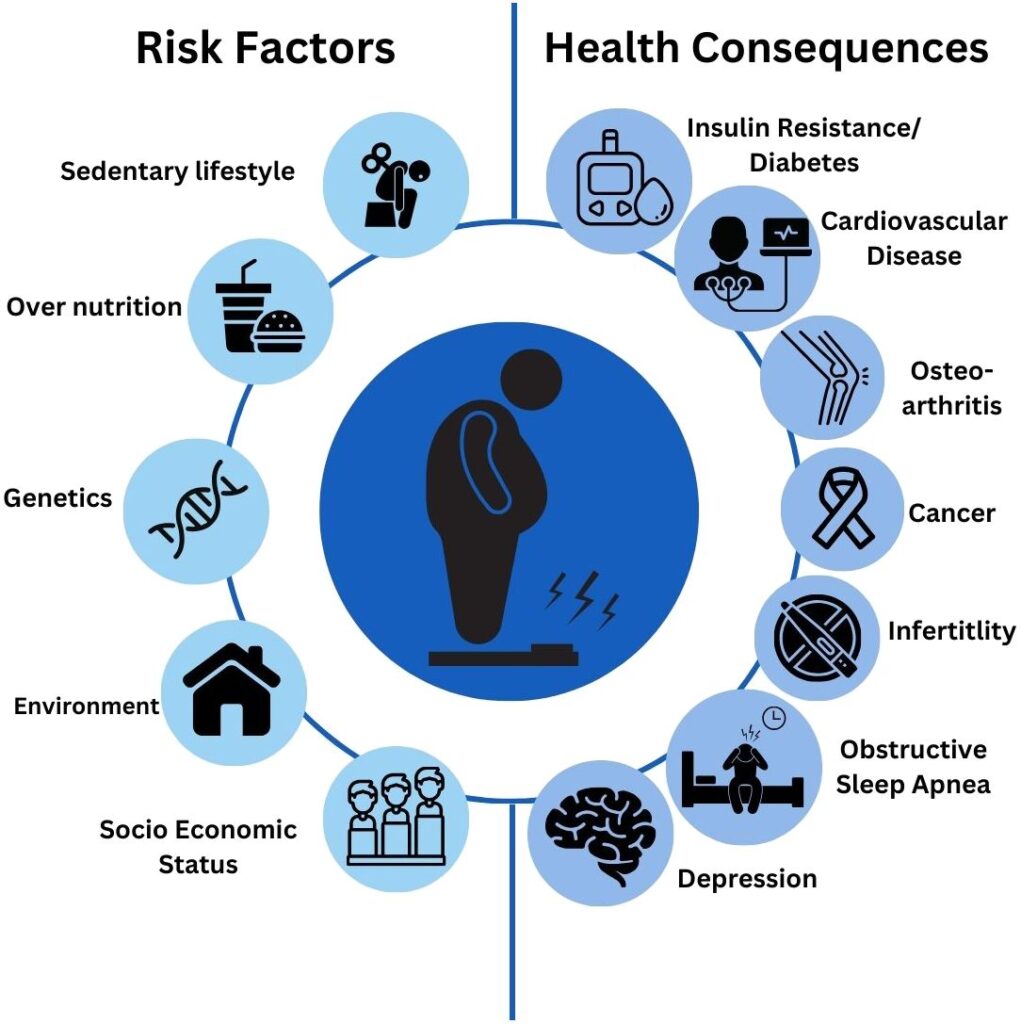
Patients with body mass index (BMI) ranging from 27 to 29.9 kg/m² fall within the overweight category. While this does not meet the obesity threshold (BMI ≥30), the presence of weight-related comorbidities—such as type 2 diabetes, hypertension, dyslipidemia, or obstructive sleep apnea—justifies active clinical intervention. Early weight loss management reduces the risk of progression to obesity and mitigates associated health complications.
Comprehensive Clinical Assessment and Diagnosis
Identifying Candidates for Intervention
Patients with BMI 27–29.9 and at least one obesity-related comorbidity are candidates for structured treatment. Evaluation includes:
- Anthropometric Measurements:
- BMI, waist circumference (>102 cm for men; >88 cm for women)
- Body fat analysis via bioelectrical impedance or DEXA when available
- Comorbidity Screening:
- Fasting blood glucose, lipid profile, HbA1c, blood pressure
- Sleep studies or echocardiogram if indicated
- Lifestyle and Behavioral History:
- Physical activity level
- Sleep duration and quality
- Psychological factors: stress, eating behavior, mood disorders
Lifestyle Modification: Core Strategy for Weight Management
Caloric Control and Dietary Strategies
Weight reduction begins with a consistent caloric deficit, personalized to patient preference and medical conditions.
- Target Deficit:
- 500–750 kcal/day deficit leads to 0.5–1 kg/week of weight loss
- Recommended intake:
- Women: 1200–1500 kcal/day
- Men: 1500–1800 kcal/day
- Effective Diet Types:
- Mediterranean Diet: anti-inflammatory, heart-healthy
- DASH Diet: ideal for hypertension and cardiovascular disease
- Low-Carbohydrate Diet: suitable for insulin resistance and diabetes
- Meal Replacements:
- High-protein, low-glycemic shakes to replace 1–2 meals/day can enhance adherence
Structured Physical Activity
Exercise improves insulin sensitivity, cardiovascular function, and helps maintain lean mass during weight loss.
- Aerobic Activity:
- 150–300 minutes/week of moderate-intensity exercise (e.g., walking, swimming)
- Resistance Training:
- Minimum 2 sessions per week focusing on large muscle groups
- NEAT (Non-Exercise Activity Thermogenesis):
- Encourage standing desks, walking meetings, stair use
Behavioral Therapy Integration
- Goal Setting & Monitoring:
- SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound) goals
- Daily tracking using digital or paper logs
- Motivational Interviewing:
- Helps resolve ambivalence and enhance patient engagement
- CBT (Cognitive Behavioral Therapy):
- Useful for patients with emotional or disordered eating patterns
Pharmacologic Therapy for Overweight with Comorbidities
When lifestyle modification alone does not result in ≥5% weight loss in 3–6 months, pharmacotherapy may be initiated for patients with BMI ≥27 and comorbidities.
Approved Anti-Obesity Agents
| Drug | Mechanism | Indications |
|---|---|---|
| Orlistat | Inhibits GI lipases | Fat absorption control |
| Phentermine/Topiramate ER | Appetite suppression | Long-term weight control |
| Naltrexone/Bupropion SR | Modulates hunger & reward pathways | Food addiction, binge control |
| Liraglutide (Saxenda) | GLP-1 receptor agonist | Cardio-metabolic risk patients |
| Semaglutide (Wegovy) | GLP-1 receptor agonist | High-efficacy weekly injections |
Clinical Monitoring
- Initial response monitored after 12 weeks
- Discontinue or switch if <5% body weight loss
- Regular checks for blood pressure, glycemic control, and mental health status
Long-Term Weight Maintenance and Relapse Prevention
Continued Patient Engagement
- Monthly to quarterly follow-ups
- Ongoing coaching and support groups improve adherence
- Modify interventions to prevent plateau or regain
Tools for Success
- Use of mobile apps for calorie and activity tracking
- Text message interventions and telehealth check-ins
- Family or peer involvement to enhance accountability
Addressing Psychosocial, Environmental, and Cultural Factors
Effective care extends beyond clinical protocols:
- Mental Health Management:
- Depression, anxiety, and trauma can hinder progress
- Cultural Adaptation:
- Respect dietary preferences, language, and belief systems
- Environment Modification:
- Improve access to healthy foods, safe activity spaces, and weight-neutral support
Expected Outcomes and Clinical Goals
- 5–10% reduction in body weight over 6–12 months
- Improved markers: HbA1c, LDL cholesterol, blood pressure, sleep quality
- Reduced medication burden and improved quality of life
Frequently Asked Questions:
Can patients with BMI 27 to 29 benefit from weight loss?
Yes. Even a modest weight loss of 5–10% significantly reduces the risk of diabetes, heart disease, and other comorbidities.
When should medications be used for overweight patients?
If a patient with BMI 27–29 and weight-related conditions fails to lose weight through lifestyle changes alone, pharmacotherapy is appropriate.
How fast should weight be lost safely?
A goal of 0.5 to 1 kg per week is considered safe and effective for sustained long-term weight management.
Is bariatric surgery an option for BMI 27–29?
No. Bariatric surgery is typically indicated for BMI ≥35 with comorbidities or BMI ≥40 without.
Are anti-obesity medications safe for long-term use?
Many approved agents, particularly GLP-1 receptor agonists, are proven safe and effective when used under medical supervision.
Weight loss management in overweight patients with BMI 27 to 29 and weight-related comorbidities requires an evidence-based, patient-centric approach. Through lifestyle modification, behavioral support, and appropriate pharmacotherapy, clinicians can help patients achieve meaningful health outcomes. Early intervention in this population is crucial for preventing disease progression and improving long-term well-being.