Cesarean section (C-section) is a critical surgical procedure often performed to ensure the safety of the mother and baby during childbirth. However, like any surgical intervention, it carries a risk of postoperative infections. Effective infection prevention strategies are essential to minimize these risks, improve patient outcomes, and reduce healthcare costs.
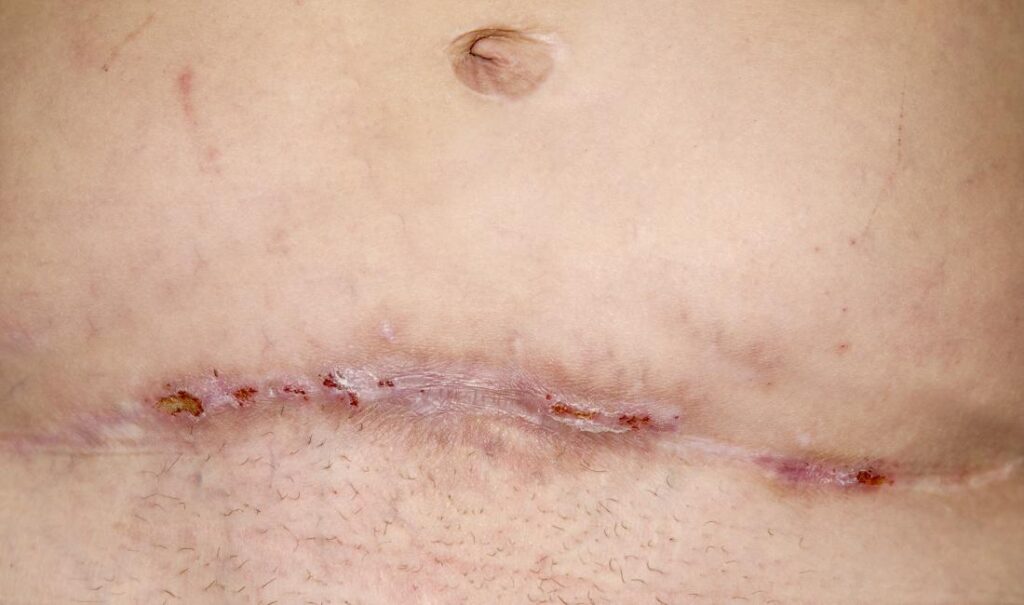
Common Types of Infections After a Cesarean Section
- Surgical Site Infection (SSI):
- SSIs involve infection of the incision site and are among the most frequent postoperative complications.
- Symptoms include redness, swelling, pain, and discharge from the surgical wound.
- Endometritis:
- Infection of the uterine lining can occur post-surgery, characterized by fever, uterine tenderness, and abnormal vaginal discharge.
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs):
- Often linked to catheter use during the procedure, UTIs can cause discomfort, frequent urination, and fever.
- Sepsis:
- In rare cases, infections may lead to sepsis, a life-threatening condition requiring immediate medical attention.
Preoperative Infection Prevention Measures
1. Patient Preparation
- Screening and Treatment:
- Identify and treat maternal infections such as bacterial vaginosis before surgery.
- Skin Preparation:
- Ensure proper cleansing of the surgical site using antiseptic solutions like chlorhexidine or iodine.
- Preoperative Bathing:
- Encourage patients to bathe or shower with antiseptic soap before the procedure.
2. Antibiotic Prophylaxis
- Administer a single dose of prophylactic antibiotics, such as cefazolin, 30-60 minutes before incision to reduce SSI risk.
3. Staff Hygiene and Preparation
- Hand Hygiene:
- Strict adherence to handwashing protocols by surgical staff.
- Sterile Techniques:
- Use of sterile gloves, gowns, and equipment.
Intraoperative Measures
1. Surgical Techniques
- Minimizing Tissue Trauma:
- Employ careful and precise surgical techniques to reduce tissue damage and inflammation.
- Maintaining Hemostasis:
- Control bleeding effectively to prevent hematoma formation, which can increase infection risk.
2. Operating Room Environment
- Maintain a sterile and controlled environment with regulated air quality.
- Limit traffic and movement within the operating room to reduce contamination.
3. Wound Closure
- Suture Selection:
- Use absorbable sutures to minimize foreign body reaction.
- Layered Closure:
- Ensure proper closure of each layer to promote healing and prevent infection.
Postoperative Infection Prevention Strategies
1. Wound Care
- Keep the incision site clean and dry.
- Educate patients on proper wound care and signs of infection.
2. Early Ambulation
- Encourage patients to move as soon as possible to improve circulation and reduce complications like deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
3. Monitoring and Follow-Up
- Schedule regular follow-ups to assess healing and address any early signs of infection.
4. Nutritional Support
- Promote a balanced diet rich in protein, vitamins, and minerals to support immune function and wound healing.
Emerging Trends in Cesarean Section Infection Prevention
- Antimicrobial Dressings:
- Use of advanced dressings impregnated with silver or iodine to reduce SSI risk.
- Enhanced Recovery After Surgery (ERAS) Protocols:
- Comprehensive perioperative care pathways to improve outcomes and reduce complications.
- Microbiome Research:
- Exploring maternal and neonatal microbiomes to develop personalized infection prevention strategies.