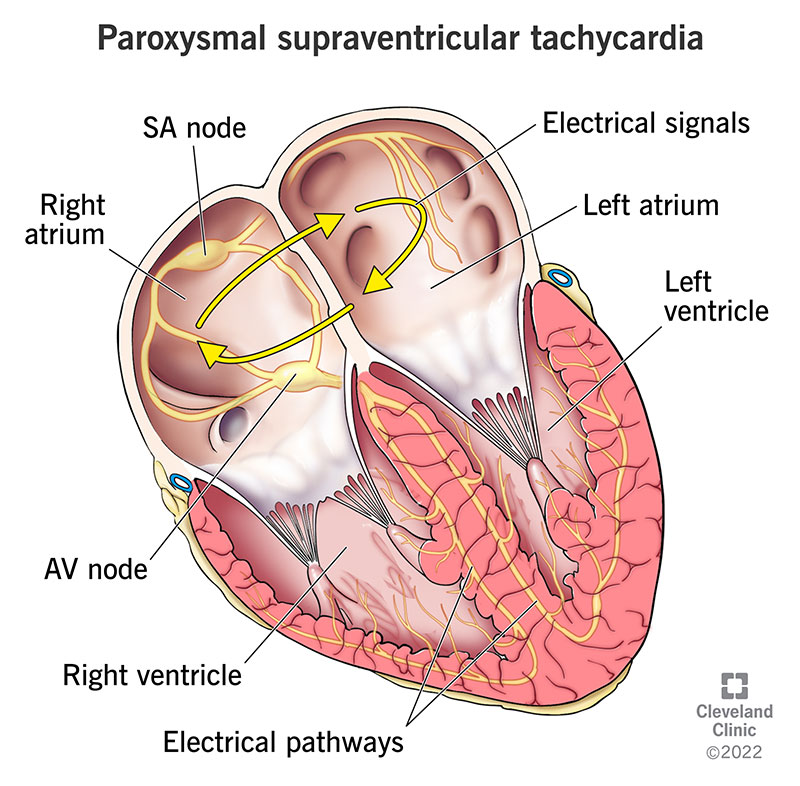
Paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (PSVT) is a condition characterized by sudden, rapid heartbeats originating from the upper chambers of the heart. This arrhythmia can occur without warning and cause significant symptoms such as palpitations, dizziness, and shortness of breath. Although PSVT can often be treated effectively, preventing its onset is key to improving quality of life for individuals at risk. In this article, we will explore various methods of preventing paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia through lifestyle changes, medications, and medical interventions.
Understanding Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardia (PSVT)
What is PSVT?
PSVT refers to a group of arrhythmias where the heart beats unusually fast due to electrical impulses originating above the ventricles. The condition is often episodic, meaning that the abnormal heart rate starts and stops abruptly. These episodes can last anywhere from a few seconds to several hours and can cause symptoms ranging from mild to severe.
Causes and Risk Factors
PSVT can be triggered by a variety of factors, including:
- Structural heart abnormalities: Conditions such as Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome or atrial septal defects can predispose individuals to PSVT.
- Excessive caffeine or alcohol intake: Stimulants can increase the likelihood of arrhythmic episodes.
- Stress and anxiety: Emotional stress and anxiety can trigger PSVT episodes.
- Medications: Certain medications, particularly those that affect heart rhythm or blood pressure, may contribute to arrhythmias.
- Underlying heart disease: Conditions like coronary artery disease or heart failure may increase the risk.
Prevention Strategies for Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardia
1. Lifestyle Modifications
Reducing Triggers: Dietary and Behavioral Changes
One of the first lines of defense against PSVT is to avoid known triggers. This includes:
- Limiting caffeine: Caffeine is a stimulant that can increase the risk of PSVT episodes. Reducing or eliminating caffeine intake from coffee, tea, soda, and energy drinks can help minimize the frequency of episodes.
- Avoiding alcohol: Excessive alcohol consumption is a well-known trigger for arrhythmias, including PSVT. Limiting alcohol intake can prevent episodes.
- Stress management: Stress and anxiety are significant triggers for PSVT. Adopting relaxation techniques such as yoga, meditation, deep breathing exercises, or mindfulness can help reduce the frequency of episodes.
- Adequate sleep: Poor sleep can exacerbate heart arrhythmias. Ensuring sufficient rest and establishing a consistent sleep schedule is critical for maintaining heart health and reducing PSVT risks.
Regular Exercise
Regular physical activity can help maintain a healthy heart and prevent the development of arrhythmias. However, high-intensity exercise may exacerbate PSVT in some individuals. It is advisable to engage in moderate-intensity aerobic activities like walking, cycling, and swimming, and consult a healthcare provider before starting an exercise program.
2. Medication for PSVT Prevention
For individuals who experience frequent or severe PSVT episodes, pharmacologic treatments may be recommended. These medications aim to either prevent the episodes or reduce their severity. Common medications include:
- Beta-blockers: These medications slow the heart rate and can help prevent the onset of PSVT by blocking the effects of stress hormones like adrenaline.
- Calcium channel blockers: These drugs work by relaxing the blood vessels and reducing the workload on the heart, thereby preventing the onset of arrhythmias.
- Antiarrhythmic drugs: Certain antiarrhythmic medications, such as flecainide or propafenone, can help control the electrical impulses in the heart and reduce the frequency of PSVT episodes.
A healthcare provider will evaluate the appropriate medications based on the individual’s health status and the frequency and severity of their episodes.
3. Catheter Ablation Therapy
In cases where medication is ineffective or not well-tolerated, catheter ablation may be considered. This procedure involves threading a catheter through the blood vessels to the heart, where it delivers radiofrequency energy to the area of the heart responsible for the abnormal electrical impulses. By destroying this tissue, ablation can significantly reduce the occurrence of PSVT episodes.
4. Vagal Maneuvers
For some individuals, vagal maneuvers can help terminate a PSVT episode. These techniques stimulate the vagus nerve and can slow the heart rate. Common maneuvers include:
- Valsalva maneuver: Involves exhaling forcefully with the mouth closed and nose pinched.
- Carotid sinus massage: A technique performed by a healthcare provider in which pressure is applied to the carotid artery in the neck.
- Coughing: In some cases, coughing forcefully can help interrupt the abnormal rhythm.
These maneuvers can be especially useful for those experiencing mild or occasional episodes of PSVT.
Medical Interventions for Persistent PSVT
1. Electrophysiological Study (EPS)
An electrophysiological study may be conducted to identify the specific electrical pathways that are causing PSVT. During the EPS, doctors use catheters to map the heart’s electrical activity. This test helps guide treatment decisions, particularly when ablation is considered.
2. Implantable Devices
For individuals with frequent or high-risk PSVT episodes, an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) may be recommended. This device monitors the heart’s rhythm and delivers shocks if it detects a life-threatening arrhythmia. While ICDs are more commonly used for other arrhythmias like ventricular fibrillation, they can also provide protection against PSVT in severe cases.
Ongoing Management and Follow-Up Care
Regular Monitoring
Ongoing monitoring of heart health is essential for individuals with PSVT. Routine follow-up visits to a cardiologist will ensure that any changes in the frequency or severity of PSVT episodes are addressed promptly. Additionally, any adjustments to medications or lifestyle recommendations can be made as necessary.
Symptom Tracking
Keeping a record of PSVT episodes, including potential triggers, duration, and severity, can help both patients and healthcare providers track patterns and adjust treatment plans accordingly.
Preventing paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia requires a multifaceted approach that includes lifestyle adjustments, pharmacologic treatments, and sometimes invasive interventions. By recognizing triggers, managing risk factors, and adhering to medical recommendations, individuals with PSVT can effectively reduce the frequency and severity of episodes. Early intervention and personalized care are key to maintaining a healthy heart and preventing the complications associated with this arrhythmia. Regular monitoring and follow-up care ensure long-term success in managing PSVT and improving overall quality of life.