Post-menopause begins 12 consecutive months after a woman’s last menstrual period. It marks the end of natural reproductive years, generally occurring between ages 45 and 55. This phase is driven by a significant decline in estrogen and progesterone levels, leading to physiological and psychological changes that can impact quality of life.
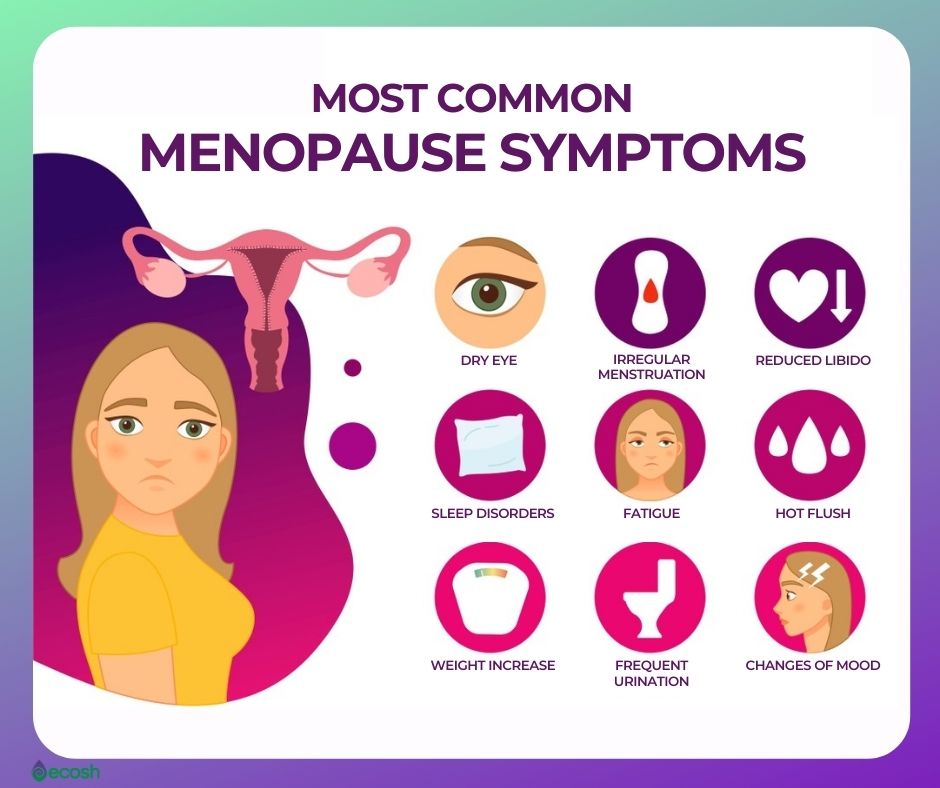
Common Post-Menopausal Symptoms
1. Hot Flashes and Night Sweats
Hot flashes are sudden, intense episodes of heat usually centered on the upper body, often accompanied by sweating and flushed skin. Night sweats are their nocturnal counterpart, frequently disrupting sleep.
Causes:
- Estrogen withdrawal disrupts the hypothalamus, the body’s thermostat.
Management:
- Hormone replacement therapy (HRT)
- SSRIs/SNRIs (e.g., venlafaxine)
- Lifestyle modifications (cool rooms, breathable clothing)
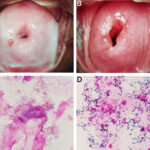
2. Vaginal Dryness and Genitourinary Syndrome of Menopause (GSM)
Reduced estrogen thins the vaginal lining and decreases natural lubrication, leading to vaginal dryness, discomfort during intercourse, and urinary symptoms like urgency or recurrent infections.
Treatments:
- Local estrogen therapy (creams, tablets, rings)
- Non-hormonal lubricants and moisturizers
- Vaginal DHEA and laser therapy in select cases
3. Mood Swings and Mental Health Changes
Fluctuating hormone levels can contribute to mood instability, irritability, anxiety, and depression.
Risk Enhancers:
- History of mood disorders
- Poor sleep
- Chronic stress or isolation
Interventions:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
- Antidepressants
- Physical activity and social engagement
4. Sleep Disturbances
Post-menopausal women often experience insomnia, frequent night awakenings, or non-restorative sleep.
Contributors:
- Hormonal shifts
- Night sweats
- Mood disorders
- Sleep apnea risk increases with age
Solutions:
- Sleep hygiene practices
- Melatonin supplements
- Medical evaluation for sleep apnea if symptoms persist
5. Weight Gain and Metabolic Changes
Declining estrogen contributes to altered fat distribution (more abdominal fat) and a reduction in metabolic rate.
Consequences:
- Increased risk of cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes
Strategies:
- Mediterranean-style diet
- Strength training and aerobic exercise
- Monitoring blood glucose and lipid profiles
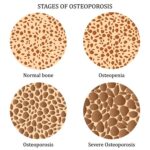
6. Osteoporosis and Joint Pain
Bone loss accelerates due to estrogen deficiency, increasing fracture risk. Joint stiffness and pain are also commonly reported.
Preventive Measures:
- Calcium (1,200 mg/day) and Vitamin D (800–1,000 IU/day)
- Weight-bearing and resistance exercises
- Bone density screening and pharmacotherapy when indicated
7. Sexual Dysfunction and Low Libido
Reduced estrogen and testosterone levels may lead to diminished sexual desire, arousal difficulties, and discomfort during intimacy.
Management Options:
- Counseling or sex therapy
- Topical estrogen or testosterone (under supervision)
- Use of vaginal moisturizers and dilators
8. Cognitive Changes
Memory lapses and difficulty concentrating, sometimes referred to as “menopause brain,” can persist post-menopause.
Supporting Brain Health:
- Adequate sleep
- Omega-3 fatty acids
- Cognitive stimulation through mental tasks and social interaction
9. Skin, Hair, and Eye Changes
Estrogen deficiency affects collagen, leading to drier skin, thinning hair, brittle nails, and dry eyes.
Care Tips:
- Use of emollients and retinoids
- Hydration and sun protection
- Artificial tears for eye discomfort
Medical Treatments for Post-Menopausal Symptoms
Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT)
HRT remains the most effective option for managing vasomotor and genitourinary symptoms.
Types:
- Systemic estrogen (with or without progestogen)
- Local estrogen for vaginal symptoms
Risks & Monitoring:
- Increased risk of thromboembolism and breast cancer in some cases
- Not suitable for women with hormone-sensitive cancers
Non-Hormonal Options
- SSRIs/SNRIs (for hot flashes and mood)
- Gabapentin (night sweats)
- Clonidine (vasomotor relief)
- Ospemifene (dyspareunia treatment)
Natural and Lifestyle Approaches
Dietary Adjustments
- Incorporate phytoestrogens (soy, flaxseed)
- Limit caffeine and alcohol
- Prioritize fruits, vegetables, and lean protein
Exercise Regimen
- At least 150 minutes/week of moderate activity
- Include strength training 2x/week
- Improves mood, bone health, and metabolism
Mind-Body Techniques
- Yoga, tai chi, and meditation help reduce stress and enhance flexibility
- Acupuncture may offer relief from hot flashes and mood swings
Long-Term Health Considerations
Cardiovascular Disease
Post-menopausal women are at elevated risk due to lipid changes and endothelial dysfunction. Regular monitoring of blood pressure, cholesterol, and glucose is essential.
Cancer Screening
Routine mammograms, Pap smears, and colonoscopies should continue. Any abnormal vaginal bleeding warrants immediate evaluation.
Cognitive Decline and Alzheimer’s Risk
Estrogen has neuroprotective properties; however, HRT is not routinely recommended for cognitive prevention. Instead, focus on:
- Brain-active lifestyle
- Blood pressure and cholesterol control
- Smoking cessation
FAQs
How long do post-menopausal symptoms last?
Symptoms may persist for 4–10 years, though some, like vaginal dryness or joint pain, can last indefinitely.
What is the most effective treatment for hot flashes?
HRT is most effective. Non-hormonal therapies like SSRIs or lifestyle modifications are alternatives.
Is weight gain inevitable after menopause?
No. With diet and exercise, weight gain can be controlled or prevented.
Can post-menopausal symptoms return years later?
Certain symptoms like vaginal dryness and joint pain may reappear or worsen with age.
Should I take supplements after menopause?
Calcium, vitamin D, and omega-3s are commonly recommended, but consult a healthcare provider for personalized guidance.
Post-menopausal symptoms can profoundly affect daily life, but with a proactive, informed approach, women can maintain optimal health and well-being. Through the right balance of medical therapies, lifestyle changes, and regular monitoring, it is entirely possible to navigate the post-menopausal years with resilience and vitality.