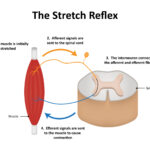
Musculoskeletal pain affects millions worldwide, impacting bones, muscles, joints, ligaments, and tendons. It can result from injury, disease, or overuse, leading to chronic discomfort and restricted mobility. Effective management requires a thorough understanding of its causes, symptoms, and treatment strategies.
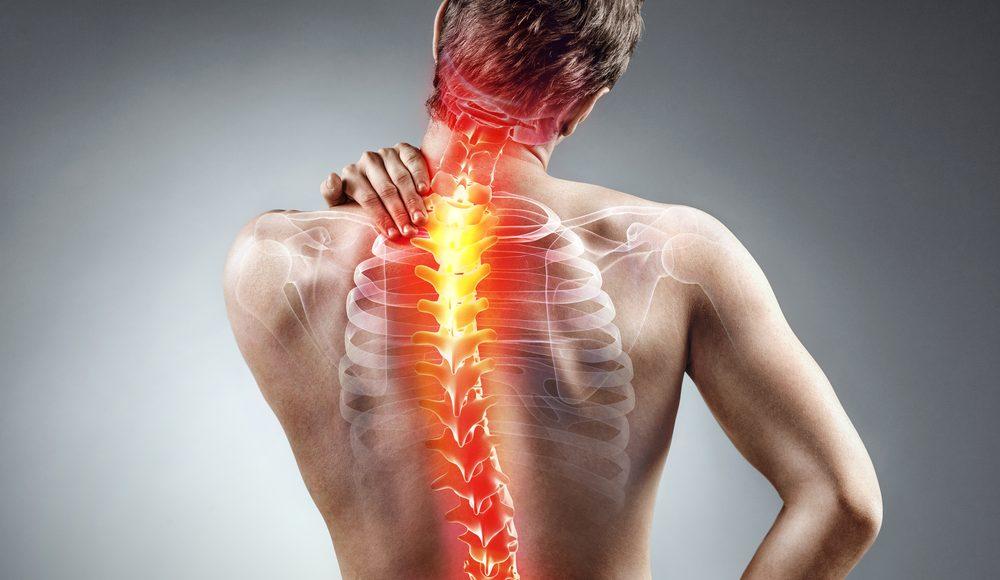
What Is Musculoskeletal Pain?
Musculoskeletal pain refers to discomfort arising from the body’s musculoskeletal system, including muscles, bones, tendons, ligaments, and nerves. It can be localized or widespread and may vary in intensity from mild to debilitating. The pain may develop suddenly due to trauma or gradually due to degenerative conditions.
Types of Musculoskeletal Pain
Musculoskeletal pain can be classified based on its origin:
- Bone Pain: Often deep, dull, or sharp, linked to fractures, infections, or tumors.
- Muscle Pain: Common in strains, cramps, or fibromyalgia, often causing stiffness.
- Joint Pain: Associated with arthritis, injuries, or inflammatory conditions.
- Tendon and Ligament Pain: Resulting from sprains, tendonitis, or overuse injuries.
- Nerve Pain: Caused by conditions like sciatica or neuropathy, leading to burning sensations.
Common Causes of Musculoskeletal Pain
1. Injury and Trauma
- Fractures and Sprains: Sudden impacts or falls can cause fractures and ligament sprains.
- Repetitive Motion Injuries: Overuse can lead to tendonitis and stress fractures.
- Whiplash and Strains: Sudden movements can strain muscles and ligaments.
2. Degenerative and Inflammatory Disorders
- Osteoarthritis: Cartilage wear leads to joint pain and stiffness.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: Autoimmune attack on joints causing inflammation.
- Fibromyalgia: Chronic widespread pain with fatigue and tenderness.
3. Postural and Occupational Factors
- Poor Posture: Misalignment places stress on muscles and joints.
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of movement weakens muscles and increases stiffness.
- Repetitive Work Movements: Jobs requiring repetitive actions may lead to strain injuries.
4. Systemic Conditions
- Lupus: An autoimmune disease that affects joints and muscles.
- Osteoporosis: Weak bones leading to fractures and chronic pain.
- Infections and Cancer: Bone infections and tumors can contribute to musculoskeletal pain.
Symptoms of Musculoskeletal Pain
The symptoms depend on the underlying cause but commonly include:
- Pain and Tenderness: Ranges from dull aches to sharp, localized pain.
- Stiffness and Reduced Range of Motion: Common in arthritis and fibromyalgia.
- Swelling and Inflammation: Sign of an injury or autoimmune disease.
- Fatigue and Weakness: Often seen in chronic pain conditions.
- Tingling or Numbness: Associated with nerve-related musculoskeletal issues.
Diagnosis of Musculoskeletal Pain
Accurate diagnosis is key to effective treatment. Methods include:
- Physical Examination: Assessing movement, swelling, and tenderness.
- X-rays and MRI: Identifying fractures, arthritis, or soft tissue injuries.
- Blood Tests: Checking for inflammatory markers in conditions like rheumatoid arthritis.
- Electromyography (EMG): Evaluating nerve and muscle function in neuropathic conditions.
Treatment Options for Musculoskeletal Pain
1. Medications
- Pain Relievers: NSAIDs like ibuprofen help reduce inflammation.
- Muscle Relaxants: Alleviate muscle spasms and tension.
- Corticosteroids: Used in severe inflammatory conditions like arthritis.
2. Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation
- Stretching and Strengthening Exercises: Improve flexibility and muscle strength.
- Manual Therapy: Chiropractic adjustments and massage therapy relieve tension.
- Heat and Cold Therapy: Reduces inflammation and soothes sore muscles.
3. Lifestyle and Home Remedies
- Regular Exercise: Low-impact activities like swimming and yoga help maintain mobility.
- Healthy Diet: Anti-inflammatory foods support joint and muscle health.
- Ergonomic Adjustments: Proper posture and supportive furniture prevent strain.
4. Alternative Therapies
- Acupuncture: Helps reduce chronic pain symptoms.
- Mind-Body Techniques: Meditation and relaxation methods alleviate pain perception.
- Electrical Stimulation (TENS): Provides relief by interrupting pain signals.
5. Surgical Interventions
For severe cases, surgery may be necessary:
- Joint Replacement: Treats advanced arthritis.
- Spinal Surgery: Used in cases of herniated discs or spinal stenosis.
- Tendon and Ligament Repair: Fixes severe sprains or ruptures.
Preventing Musculoskeletal Pain
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Reduces stress on joints.
- Stay Active: Regular movement prevents stiffness.
- Use Proper Lifting Techniques: Avoids strain injuries.
- Manage Stress: Reduces tension-related muscle pain.
Musculoskeletal pain is a widespread condition that significantly affects daily life. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options enables individuals to take proactive steps toward pain management and improved mobility. Early intervention, lifestyle modifications, and medical treatments can help prevent chronic pain and enhance overall well-being.