Mania is a key characteristic of bipolar disorder, a severe mood disorder that affects millions worldwide. It is marked by periods of extreme excitement, impulsivity, and elevated mood. Understanding the symptoms, triggers, and treatment options is crucial for managing this condition effectively.
What is Mania in Bipolar Disorder?
Mania is a mental state characterized by excessive energy, euphoria, or irritability. It occurs in bipolar disorder as part of alternating mood episodes, which can range from severe depression to full-blown manic episodes.
Types of Mania
- Mania: Severe symptoms lasting at least a week, often requiring hospitalization.
- Hypomania: A milder form of mania with similar symptoms but less impairment.
Symptoms of Mania
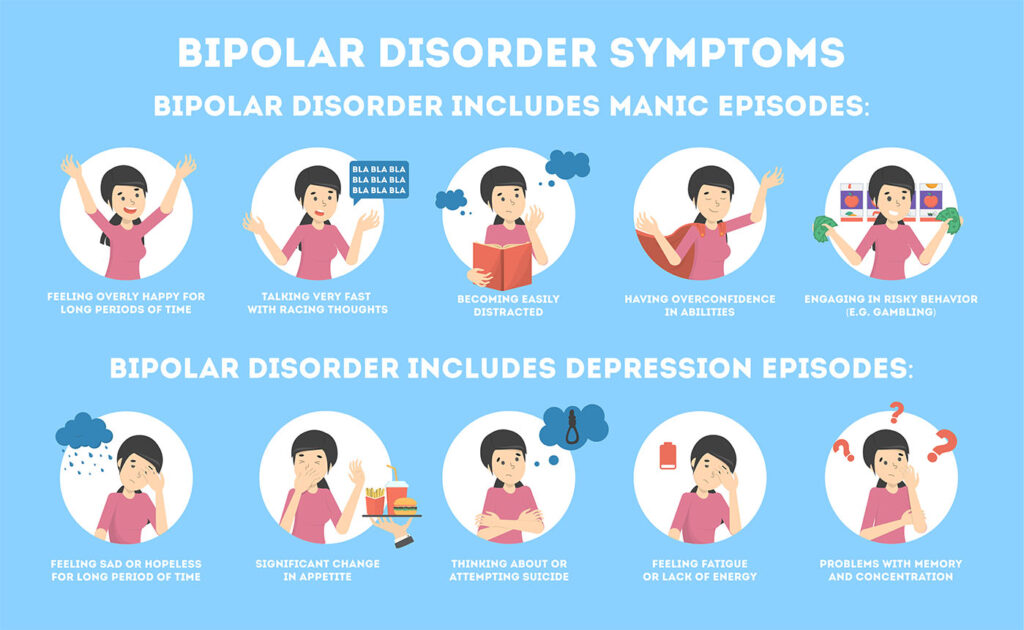
Manic episodes significantly impact daily life, leading to impaired judgment and risky behavior. Symptoms include:
- Elevated or irritable mood
- Increased energy and decreased need for sleep
- Racing thoughts and rapid speech
- Grandiosity and inflated self-esteem
- Impulsivity and reckless behavior (e.g., excessive spending, risky sexual activity)
- Delusions or hallucinations (in severe cases)
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors contribute to manic episodes in bipolar disorder:
- Genetic predisposition: Family history of bipolar disorder increases the risk.
- Neurochemical imbalances: Dysregulation of neurotransmitters like dopamine and serotonin plays a role.
- Environmental triggers: Stressful life events, substance abuse, or sleep deprivation can trigger mania.
- Medical conditions: Thyroid disorders and neurological diseases may contribute.
Diagnosis of Bipolar Mania
Diagnosing mania involves clinical assessment and medical history evaluation. Key diagnostic criteria include:
- Manic symptoms lasting at least one week (or requiring hospitalization)
- Significant impairment in social or occupational functioning
- Ruling out substance-induced mood disturbances
Treatment for Mania in Bipolar Disorder
Managing mania requires a combination of medications, therapy, and lifestyle adjustments.
Medications
- Mood stabilizers: Lithium, valproate, and carbamazepine
- Antipsychotics: Olanzapine, risperidone, and quetiapine for acute manic episodes
- Benzodiazepines: Used for short-term control of agitation and insomnia
Psychotherapy
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Helps patients identify and manage triggers
- Psychoeducation: Informs patients and families about symptom management
- Interpersonal Therapy: Addresses relationship issues caused by mood instability
Lifestyle and Preventive Strategies
- Regular sleep schedule: Helps regulate mood swings
- Stress management techniques: Meditation, yoga, and exercise reduce triggers
- Avoiding stimulants: Caffeine, drugs, and alcohol can exacerbate mania
Mania is a serious condition associated with bipolar disorder, requiring timely diagnosis and comprehensive treatment. With the right combination of medications, therapy, and lifestyle adjustments, individuals with bipolar disorder can lead stable and fulfilling lives.