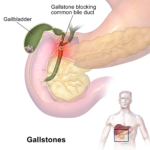
Biliary obstruction with pruritus is a complex condition involving the blockage of bile flow and the subsequent onset of itching. This article aims to provide an in-depth understanding of the condition, from its causes and symptoms to the diagnosis and treatment options. We will explore the mechanisms behind this disorder and offer expert insights into the management of biliary obstruction and associated pruritus.
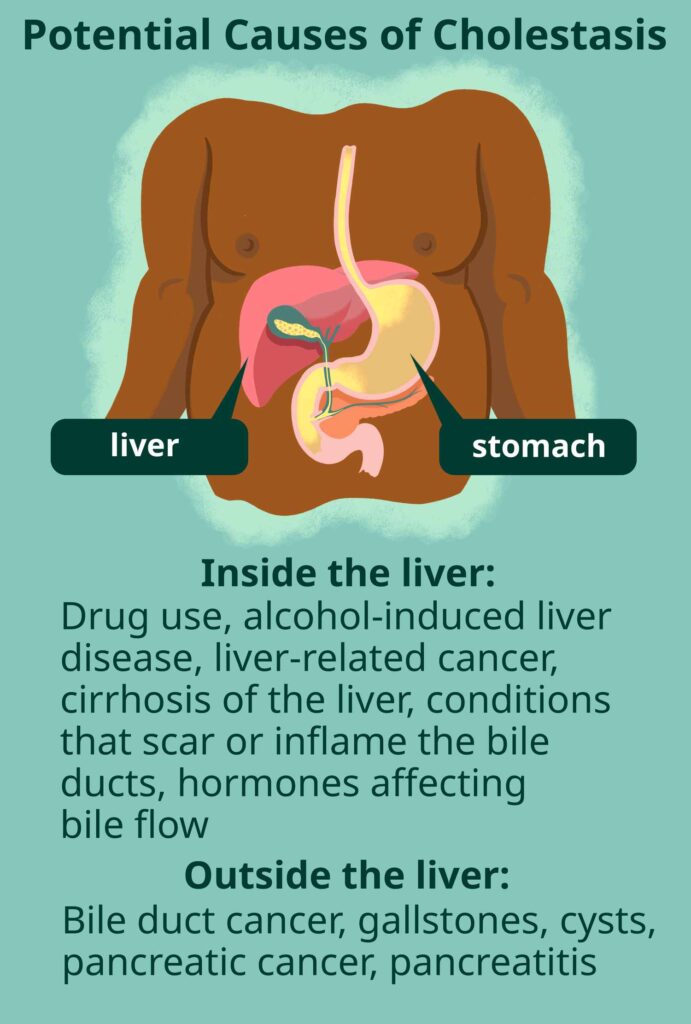
Understanding Biliary Obstruction and Pruritus
Biliary obstruction occurs when there is a blockage in the bile ducts, which hinders the flow of bile from the liver to the intestines. This blockage can result from various causes, such as gallstones, tumors, or strictures in the bile duct. As bile builds up in the liver, it leads to a condition known as cholestasis, which refers to the reduced or halted flow of bile. One of the hallmark symptoms of biliary obstruction is pruritus, a form of intense itching.
Mechanism of Pruritus in Biliary Obstruction
The exact cause of pruritus in biliary obstruction is still not fully understood. However, it is believed that the accumulation of bile acids in the bloodstream plays a central role in triggering the itching sensation. In a healthy liver, bile acids are excreted into the bile and later enter the intestines. When bile flow is obstructed, bile acids can accumulate in the liver and spill into the bloodstream, where they interact with the skin and nerve receptors, causing pruritus.
Causes of Biliary Obstruction
Biliary obstruction can result from several underlying conditions, including:
Gallstones
Gallstones are the most common cause of bile duct obstruction. When these stones block the bile ducts, they prevent the normal flow of bile, leading to cholestasis and associated pruritus.
Malignancies
Cancerous growths in the liver, pancreas, or bile ducts can lead to partial or complete obstruction of the bile ducts. Pancreatic cancer, in particular, is notorious for causing biliary obstruction.
Biliary Strictures
Biliary strictures, which are narrowings of the bile ducts due to scarring, often occur after surgery, inflammation, or injury. These strictures can obstruct bile flow and result in pruritus.
Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis (PSC)
PSC is a chronic liver disease characterized by inflammation and scarring of the bile ducts. This condition can lead to progressive bile duct narrowing and eventual obstruction, causing cholestasis and pruritus.
Choledochal Cysts
Choledochal cysts are rare, congenital malformations of the bile ducts. When these cysts become enlarged or infected, they can obstruct bile flow, leading to biliary obstruction and pruritus.
Symptoms of Biliary Obstruction
The most prominent symptom of biliary obstruction is pruritus. However, other symptoms commonly associated with this condition include:
- Jaundice: The yellowing of the skin and eyes caused by elevated bilirubin levels.
- Abdominal pain: Pain, particularly in the upper right quadrant of the abdomen, due to bile buildup.
- Dark urine: Urine may appear darker than usual due to excess bilirubin being excreted through the kidneys.
- Clay-colored stools: The absence of bile in the intestines can cause stool discoloration.
- Fatigue and weight loss: These can occur due to the effects of the underlying disease or the reduced absorption of fat-soluble vitamins.
Diagnosis of Biliary Obstruction
Diagnosing biliary obstruction requires a combination of clinical evaluation and diagnostic tests. The following methods are commonly used:
Blood Tests
Liver function tests (LFTs) are typically elevated in patients with biliary obstruction, especially alkaline phosphatase (ALP) and bilirubin levels. Elevated levels of bilirubin indicate cholestasis.
Imaging Studies
Imaging techniques such as ultrasound, CT scans, or MRCP (magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography) help visualize the bile ducts and identify any obstructions or abnormalities.
Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP)
ERCP is a procedure used to directly visualize the bile ducts and remove or treat obstructions. It can also be used for diagnostic purposes.
Biopsy
In certain cases, a liver biopsy may be performed to assess the extent of liver damage or to identify the underlying cause of the obstruction.
Treatment of Biliary Obstruction and Pruritus
The treatment approach for biliary obstruction depends on the underlying cause and the severity of the obstruction.
Endoscopic Intervention
For bile duct obstructions caused by gallstones or tumors, endoscopic procedures such as ERCP may be used to remove stones, place stents, or perform a biopsy.
Surgery
In some cases, surgery may be required to remove obstructions, repair bile duct strictures, or address tumors.
Medications for Pruritus
Managing pruritus in biliary obstruction is a critical component of treatment. Several medications are available to alleviate itching:
- Cholestyramine: A bile acid sequestrant that binds bile acids in the intestines and reduces their reabsorption, helping to decrease pruritus.
- Ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA): This medication helps improve bile flow in some cases of cholestasis, reducing itching.
- Antihistamines: These can be used to provide temporary relief from itching.
- Naltrexone: An opioid antagonist that can reduce pruritus by acting on the central nervous system.
Phototherapy
Ultraviolet (UV) light therapy may also be used to treat pruritus, especially in cases where other treatments have been ineffective.
Liver Transplantation
In severe cases, where liver function is significantly compromised, liver transplantation may be necessary.
Preventing Biliary Obstruction and Managing Pruritus
While not all cases of biliary obstruction are preventable, there are steps that can be taken to reduce the risk of developing conditions that lead to obstruction, such as:
- Maintaining a healthy weight: Reduces the risk of gallstones, which are a major cause of biliary obstruction.
- Avoiding excessive alcohol consumption: Helps prevent liver damage that may lead to biliary obstruction.
- Regular screening: Individuals with a history of liver disease or bile duct disorders should undergo regular screening to detect any early signs of obstruction.
Biliary obstruction with pruritus is a serious condition that can have significant effects on a person’s quality of life. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for effective management. Early diagnosis and intervention are essential to alleviate symptoms and prevent complications. Through appropriate medical care, including medication and surgical interventions, individuals affected by this condition can find relief from pruritus and improve their overall health.