Often described as a persistent discomfort or burning sensation in the pelvic area, can significantly impact one’s quality of life. Understanding its causes, recognizing the symptoms, and seeking appropriate treatment are vital steps toward alleviation. This comprehensive guide delves into the root causes of bladder pain, associated symptoms, diagnostic approaches, and effective treatments.
Common Causes
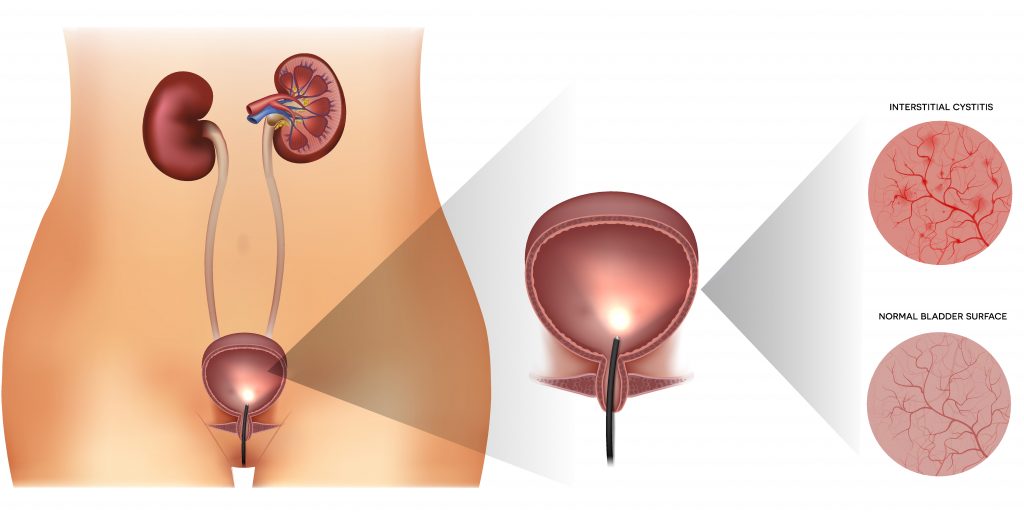
1. Interstitial Cystitis (IC)
Also known as painful bladder syndrome, IC is a chronic condition characterized by bladder pressure, pain, and occasional pelvic discomfort. Its exact cause remains unclear, though potential triggers include:
- Bladder lining damage
- Autoimmune reactions
- Nervous system disorders
2. Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
Bacterial infections of the urinary tract can result in inflammation and pain in the bladder. Symptoms typically include:
- Frequent urination
- Burning sensation during urination
- Cloudy or foul-smelling urine
3. Bladder Stones
Mineral deposits in the bladder can cause irritation, blockage, and pain. Contributing factors include dehydration, urinary tract infections, and enlarged prostate in men.
4. Overactive Bladder (OAB)
An overactive bladder causes involuntary bladder contractions, often leading to pain and urgency. Potential causes are:
- Nerve damage
- Hormonal changes
- Muscle dysfunction
5. Bladder Cancer
Although rare, bladder cancer can present as persistent pain, blood in urine (hematuria), and frequent urination. Early diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment.
Symptoms
symptoms may vary depending on the underlying cause. Common indicators include:
- Persistent pelvic discomfort
- Frequent urination with little output
- Urgency to urinate
- Pain during or after urination
- Blood in the urine
Diagnostic Approaches
Accurate diagnosis is essential for identifying the cause of bladder pain. Common diagnostic methods include:
Medical History and Physical Examination
Doctors assess medical history and conduct physical exams to identify symptoms and potential risk factors.
Urinalysis and Urine Culture
Laboratory tests analyze urine for bacteria, blood, or other abnormalities.
Cystoscopy
A thin tube with a camera is inserted into the bladder to examine its lining and detect abnormalities.
Imaging Tests
Techniques like ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI can provide detailed visuals of the bladder and surrounding structures.
Biopsy
A tissue sample may be taken during a cystoscopy to test for cancer or other conditions.
Treatment Options
Treatment varies based on the cause of bladder pain. Below are common approaches:
1. Medications
- Antibiotics: For bacterial infections like UTIs
- Pain Relievers: To manage discomfort
- Antispasmodics: To reduce bladder spasms
- Antihistamines: For interstitial cystitis relief
2. Bladder Training
A behavioral therapy that involves scheduled urination to improve bladder control.
3. Physical Therapy
Pelvic floor therapy can strengthen muscles and reduce pain.
4. Surgical Interventions
In severe cases, surgery might be necessary, such as bladder augmentation or removal of bladder stones.
5. Lifestyle Adjustments
- Avoiding bladder irritants like caffeine, alcohol, and spicy foods
- Staying hydrated
- Stress management
Preventive Measures
Involves adopting a proactive approach:
- Maintain proper hygiene
- Drink plenty of water
- Avoid holding urine for long periods
- Practice safe sexual habits
Common Causes of Bladder Pain
Its a complex issue requiring careful evaluation and treatment. By understanding the potential causes and symptoms, individuals can seek timely medical intervention and improve their quality of life. If you experience persistent bladder pain, consult a healthcare professional for a tailored approach.
myhealthmag