Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) is a progressive condition characterized by the accumulation of plaque in the arteries, leading to narrowed or blocked vessels. This condition significantly increases the risk of heart attack, stroke, and other cardiovascular events.
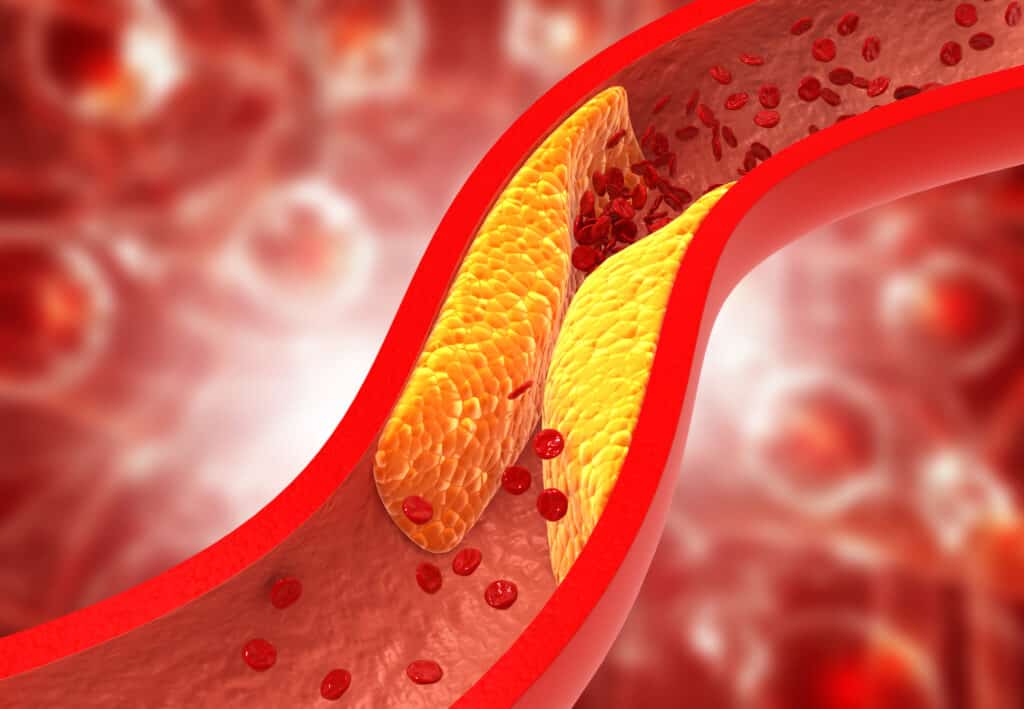
Key Risk Factors for ASCVD
Several factors contribute to the heightened risk of ASCVD:
1. High Cholesterol Levels
- Elevated low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol is a primary contributor to atherosclerosis.
- HDL (high-density lipoprotein) cholesterol helps protect against plaque buildup but may decline with poor lifestyle choices.
2. Hypertension (High Blood Pressure)
- Chronic high blood pressure exerts pressure on artery walls, damaging blood vessels and accelerating plaque formation.
3. Diabetes Mellitus
- Diabetes can lead to increased blood sugar levels, damaging arteries and promoting plaque formation.
4. Obesity and Sedentary Lifestyle
- Excess body weight, particularly around the abdomen, raises the risk of hypertension, diabetes, and abnormal cholesterol levels.
5. Smoking and Tobacco Use
- Tobacco chemicals damage blood vessels, promoting inflammation and plaque accumulation.
6. Poor Diet
- Diets high in saturated fats, trans fats, and refined sugars elevate LDL cholesterol and triglyceride levels.
7. Genetic Predisposition
- Family history of cardiovascular disease can increase susceptibility to atherosclerosis.
Symptoms of ASCVD
Early stages of ASCVD are often asymptomatic. As the condition progresses, individuals may experience:
- Chest pain (angina)
- Shortness of breath
- Numbness or weakness in limbs
- Dizziness or fainting
- Irregular heartbeat
Diagnostic Methods for ASCVD
Effective diagnosis involves a combination of the following:
- Blood Tests: Evaluating cholesterol, glucose, and lipid profiles.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): Identifying abnormal heart rhythms or past heart attacks.
- Coronary Angiography: Visualizing blood flow in coronary arteries.
- Carotid Ultrasound: Assessing plaque buildup in the neck arteries.
Prevention Strategies for ASCVD
1. Adopt a Heart-Healthy Diet
- Increase intake of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Limit saturated fats, trans fats, and sodium.
2. Regular Exercise
- Engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise weekly.
3. Weight Management
- Maintaining a healthy BMI reduces the risk of hypertension and diabetes.
4. Smoking Cessation
- Quitting smoking improves overall cardiovascular health.
5. Medication Management
- Statins, antihypertensive drugs, and antiplatelet agents are commonly prescribed to manage cholesterol, blood pressure, and clot risks.
Treatment Options for ASCVD
Treatment strategies depend on the severity of the condition:
1. Lifestyle Modifications
- Comprehensive dietary changes, exercise routines, and stress management.
2. Medications
- Statins, ACE inhibitors, and beta-blockers help manage risk factors.
3. Surgical Interventions
- Angioplasty and Stenting: A procedure to open blocked arteries.
- Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG): Used in severe cases to restore blood flow.
Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease is a serious yet preventable condition. By understanding its risk factors, adopting a healthy lifestyle, and seeking appropriate medical care, individuals can reduce their chances of developing ASCVD and improve their overall heart health.
FAQs
Q1: What lifestyle changes are most effective in reducing ASCVD risk?
A1: Prioritizing a balanced diet, regular exercise, and quitting smoking are among the most impactful changes.
Q2: Can ASCVD develop without noticeable symptoms?
A2: Yes, many individuals experience no warning signs until significant artery blockages occur.
Q3: Are genetic factors significant in ASCVD risk?
A3: Yes, a family history of heart disease can elevate your risk, even with a healthy lifestyle.
Q4: What foods should be avoided to reduce ASCVD risk?
A4: Limit processed foods, trans fats, and excessive sodium to promote heart health.
Q5: Is ASCVD reversible?
A5: While plaque buildup cannot be entirely reversed, lifestyle changes and medications can stabilize and reduce it.