Maintaining healthy bowel evacuation is essential for overall well-being. Efficient bowel movements indicate a healthy digestive system, while irregularities can signal underlying issues. This guide delves into the processes, importance, and tips for achieving optimal bowel health.
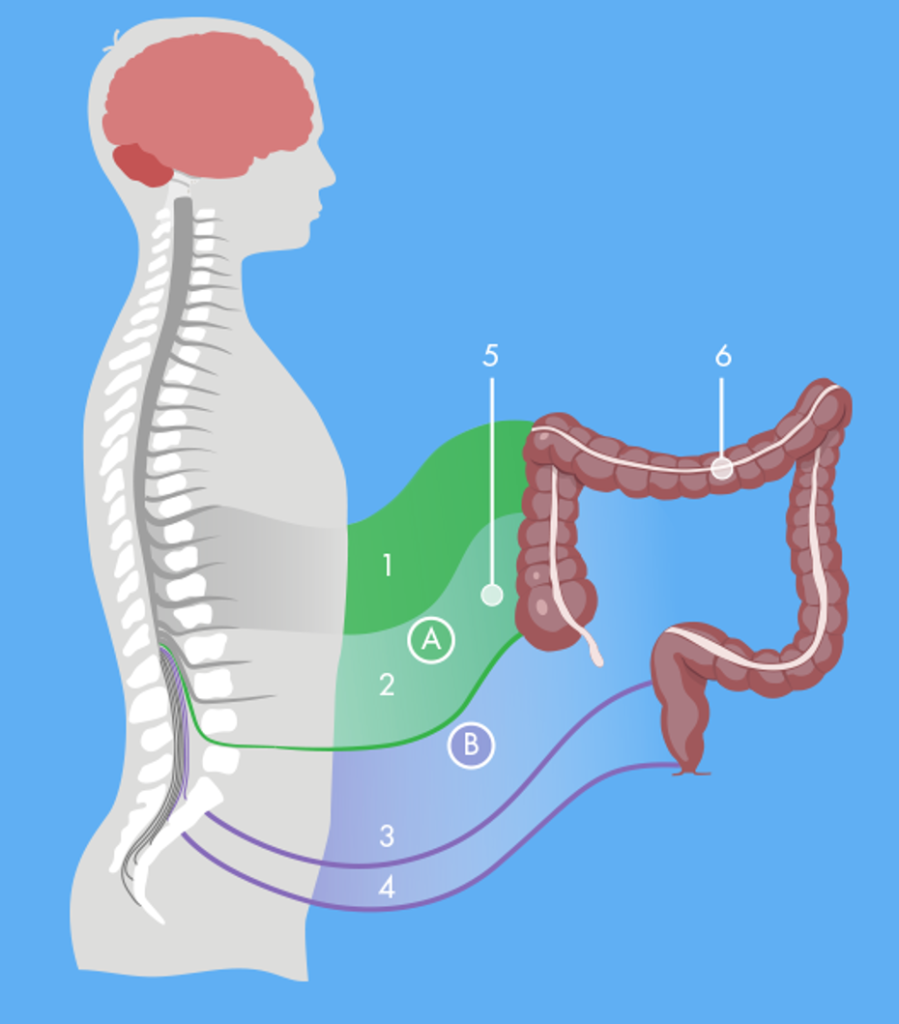
What Is Bowel Evacuation?
Bowel evacuation, commonly referred to as a bowel movement, is the process of expelling waste products from the body through the rectum and anus. It represents the final step in digestion, where undigested food, bacteria, and other waste materials are eliminated.
The Digestive Process Leading to Bowel Evacuation
The digestive system operates through a series of steps:
- Ingestion: Food enters the mouth, where digestion begins.
- Digestion: Stomach acids and enzymes break down food into nutrients.
- Absorption: The small intestine absorbs nutrients into the bloodstream.
- Waste Formation: The large intestine consolidates waste into stool.
- Excretion: Stool exits the body during bowel evacuation.
Importance of Regular Bowel Movements
Regular bowel movements are critical for maintaining a healthy digestive system. They:
- Prevent the accumulation of toxins in the body.
- Indicate proper functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Reduce the risk of conditions such as constipation, hemorrhoids, and colorectal cancer.
Ideal Frequency and Stool Consistency
While frequency can vary, most individuals should aim for 1-3 bowel movements per day. Consistency should resemble a soft, well-formed stool, classified as Type 3 or Type 4 on the Bristol Stool Chart.
Common Issues with Bowel Evacuation
1. Constipation
Constipation occurs when bowel movements are infrequent or difficult to pass. It is commonly caused by:
- Insufficient dietary fiber.
- Dehydration.
- Sedentary lifestyle.
Remedies:
- Increase water intake.
- Add high-fiber foods like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Engage in regular physical activity.
2. Diarrhea
Diarrhea involves loose or watery stools and may result from:
- Infections.
- Food intolerances.
- Certain medications.
Remedies:
- Stay hydrated with electrolyte-rich fluids.
- Avoid trigger foods.
- Use over-the-counter remedies as needed.
3. Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
IBS can cause alternating constipation and diarrhea, abdominal pain, and bloating. Managing IBS often involves:
- Identifying and avoiding trigger foods.
- Stress management techniques.
- Medical consultation for tailored treatments.
Tips for Improving Bowel Evacuation
- Hydration: Drink at least 8 glasses of water daily.
- Dietary Fiber: Include soluble and insoluble fiber sources to improve stool consistency.
- Probiotics: Consume yogurt, kefir, or probiotic supplements to enhance gut microbiota.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in moderate physical activities like walking or yoga.
- Routine: Establish a regular schedule for meals and bathroom visits.
- Limit Processed Foods: Reduce intake of high-fat, low-fiber foods that hinder digestion.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Consult a healthcare professional if you experience:
- Persistent constipation or diarrhea lasting more than a week.
- Blood in stool.
- Severe abdominal pain.
- Sudden unexplained weight loss.
Understanding and maintaining regular bowel evacuation is vital for digestive health. By adopting a balanced diet, staying hydrated, and engaging in regular exercise, individuals can promote effective waste elimination and overall well-being. Persistent issues should not be ignored and warrant professional evaluation to rule out serious conditions.