Hypoparathyroidism is a rare endocrine disorder characterized by insufficient production of parathyroid hormone (PTH) by the parathyroid glands. PTH is essential for regulating calcium and phosphorus levels in the blood. When PTH levels drop abnormally low, it leads to calcium deficiency (hypocalcemia) and excess phosphorus in the body.
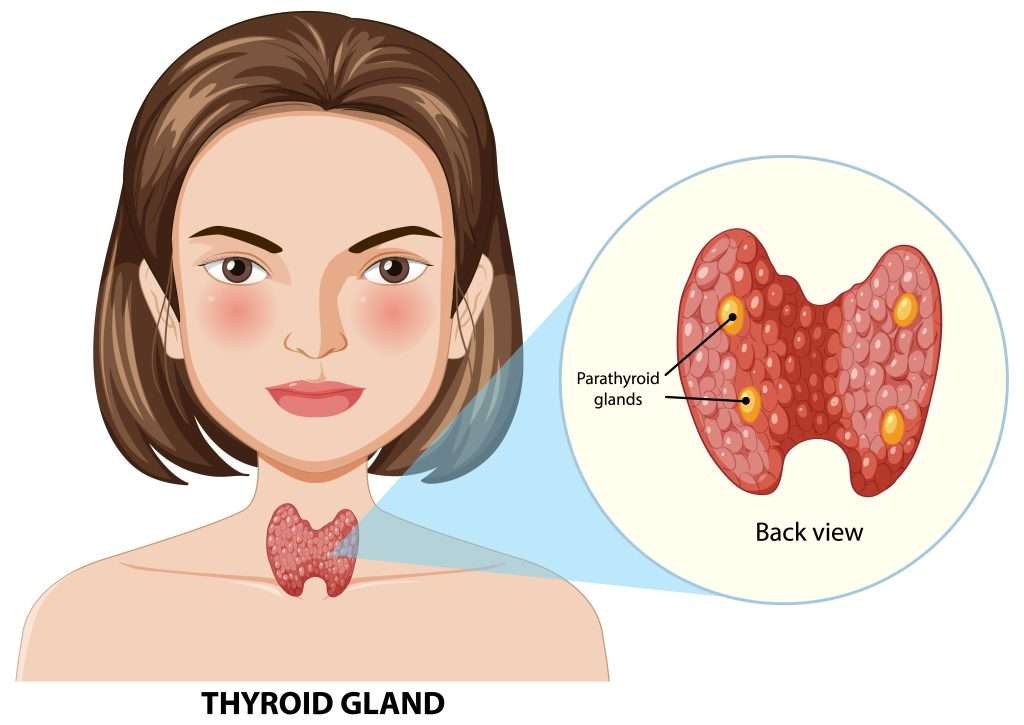
Causes of Hypoparathyroidism
Several factors can trigger hypoparathyroidism, including:
- Surgical Procedures: The most common cause, particularly after thyroid or neck surgeries, where the parathyroid glands may be damaged or removed accidentally.
- Autoimmune Disorders: The immune system may mistakenly attack the parathyroid glands.
- Genetic Disorders: Conditions like DiGeorge syndrome may involve congenital hypoparathyroidism.
- Magnesium Deficiency: Magnesium is vital for PTH secretion; low magnesium levels can hinder hormone production.
- Radiation Therapy: Treatment for head and neck cancers may impair parathyroid gland function.
Symptoms of Hypoparathyroidism
Common symptoms associated with hypoparathyroidism include:
- Muscle Cramps and Spasms: Particularly in the face, hands, and feet.
- Tingling Sensations: Often affecting the fingers, toes, and lips.
- Fatigue and Weakness: Reduced calcium levels contribute to general lethargy.
- Dry Skin and Brittle Nails: Skin may appear coarse, and nails may become brittle.
- Cognitive Impairment: Brain fog, memory issues, and poor concentration.
- Seizures: In severe cases, calcium imbalances can trigger convulsions.
Diagnosis of Hypoparathyroidism
Healthcare providers typically diagnose hypoparathyroidism through the following methods:
- Blood Tests: Measuring calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, and PTH levels.
- Urine Tests: Evaluating calcium excretion and kidney function.
- Genetic Testing: Recommended for individuals with a family history of endocrine disorders.
Treatment for Hypoparathyroidism
While hypoparathyroidism requires ongoing management, effective treatments can help control symptoms and maintain balanced calcium levels:
Calcium and Vitamin D Supplements
- Calcium Carbonate or Citrate: Supplements help replenish calcium levels.
- Active Vitamin D (Calcitriol): Enhances calcium absorption from the intestines.
Recombinant Parathyroid Hormone (PTH) Therapy
- Natpara (PTH 1-84): An FDA-approved treatment for managing chronic hypoparathyroidism in patients who cannot maintain stable calcium levels with conventional supplements.
Magnesium Supplementation
Magnesium plays a crucial role in PTH secretion and calcium regulation. Correcting magnesium deficiencies is vital.
Dietary Recommendations
Patients should consume calcium-rich foods such as:
- Dairy products (milk, cheese, yogurt)
- Leafy greens like kale and spinach
- Fortified foods (orange juice, cereals)
- Nuts and seeds
Complications of Hypoparathyroidism
If left untreated, hypoparathyroidism may lead to serious complications, including:
- Kidney Stones: Due to excess calcium excretion.
- Heart Problems: Calcium imbalances can affect heart rhythm.
- Cataracts: Persistent low calcium may cause eye lens calcification.
- Stunted Growth in Children: Impaired bone development may occur in untreated pediatric cases.
Living with Hypoparathyroidism
Managing hypoparathyroidism requires consistent monitoring and lifestyle adjustments. Tips for improved well-being include:
- Regularly monitoring blood calcium and vitamin D levels.
- Following a balanced diet rich in calcium and low in phosphorus.
- Staying informed about medication schedules and side effects.
- Maintaining follow-up visits with healthcare providers.
Hypoparathyroidism is a manageable yet complex condition that requires lifelong care. Early diagnosis and adherence to prescribed treatments can significantly improve quality of life. Patients should collaborate closely with healthcare providers to maintain optimal calcium balance and minimize complications.