Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism (HH) is a medical condition characterized by inadequate production of sex hormones due to impaired gonadotropin release. This disorder results from dysfunction in the hypothalamus or pituitary gland, leading to low levels of luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH).
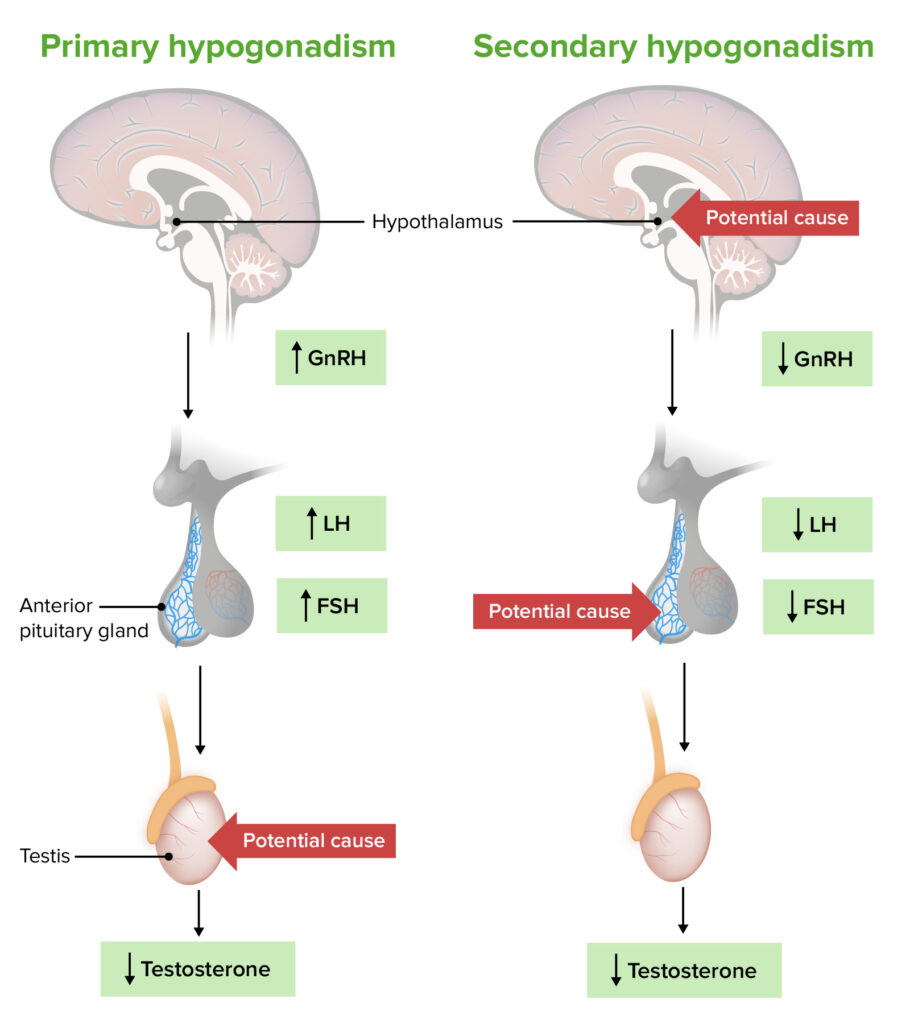
Causes of Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism
Congenital Causes
- Kallmann Syndrome: A genetic disorder associated with anosmia (loss of smell) and delayed puberty.
- CHARGE Syndrome: A complex condition linked to multiple anomalies, including genital abnormalities.
- Prader-Willi Syndrome: A genetic disorder often resulting in obesity, reduced muscle tone, and hypogonadism.
Acquired Causes
- Pituitary Tumors: Growths in the pituitary gland can impair hormone secretion.
- Head Trauma: Injuries affecting the hypothalamic-pituitary axis.
- Radiation Therapy: Treatments targeting the brain may damage the pituitary gland.
- Chronic Illnesses: Conditions like diabetes, obesity, and severe malnutrition can contribute to HH.
Symptoms of Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism
In Males
- Delayed puberty
- Reduced facial and body hair
- Decreased libido and erectile dysfunction
- Infertility
- Muscle mass reduction
In Females
- Delayed puberty
- Amenorrhea (absence of menstruation)
- Infertility
- Decreased breast development
- Osteoporosis risk
Diagnosis of Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism
Hormone Testing
- Serum LH and FSH Levels: Typically low in HH.
- Testosterone (in males) and Estrogen (in females): Markedly reduced.
Imaging Studies
- MRI or CT Scans: Essential for identifying structural abnormalities in the hypothalamus or pituitary gland.
Genetic Testing
- Identification of Genetic Mutations: Especially relevant in congenital HH cases like Kallmann syndrome.
Treatment Options for Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism
Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT)
- Testosterone Therapy: Administered via injections, gels, or patches for males.
- Estrogen and Progesterone Therapy: Recommended for females to restore hormonal balance.
Gonadotropin Therapy
- hCG (Human Chorionic Gonadotropin): Stimulates testosterone production in males.
- FSH Injections: Indicated to promote fertility in both sexes.
Lifestyle Modifications
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight can improve hormonal balance.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity may enhance testosterone levels naturally.
Surgical Intervention
- Tumor Removal: Required if a pituitary tumor is identified as the underlying cause.
Potential Complications
- Osteoporosis: Due to prolonged low testosterone or estrogen levels.
- Infertility: Even with treatment, fertility may remain impaired in some cases.
- Psychological Effects: Depression, anxiety, and reduced quality of life are common in untreated individuals.
Prognosis and Long-Term Management
With proper diagnosis and treatment, patients with hypogonadotropic hypogonadism can achieve improved quality of life. Early intervention is crucial to prevent complications and ensure optimal outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions:
What is the most common cause of hypogonadotropic hypogonadism?
Kallmann syndrome is a leading congenital cause, while pituitary tumors and head trauma are common acquired causes.
Can hypogonadotropic hypogonadism be cured?
While congenital forms may require lifelong treatment, acquired cases can often improve with appropriate medical interventions.
Is fertility treatment effective for HH patients?
Yes, gonadotropin therapy and assisted reproductive technologies can significantly improve fertility outcomes.
How can hypogonadotropic hypogonadism affect mental health?
Hormonal imbalance may contribute to mood disorders, requiring psychological support and medical therapy.
Are there lifestyle changes that can help manage hypogonadotropic hypogonadism?
Weight management, a balanced diet, and regular exercise can help optimize hormone levels.
Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism is a complex condition requiring comprehensive evaluation and tailored treatment. Early diagnosis and appropriate intervention can mitigate complications and enhance overall well-being.