Bacterial infections are a common medical concern caused by harmful bacteria invading the body and multiplying. These infections can range from mild to severe, affecting various organs and systems. Understanding the causes, symptoms, treatments, and prevention methods is crucial for effective management.
What Are Bacterial Infections?
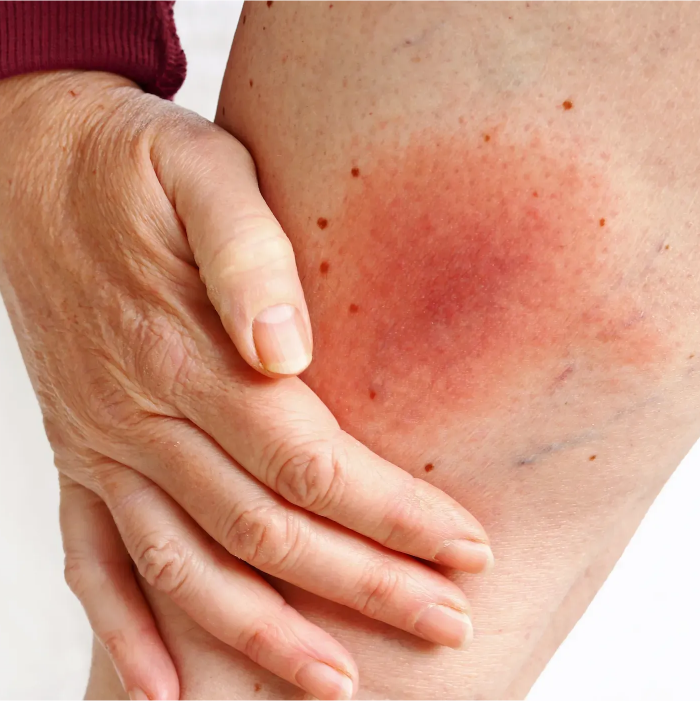
Bacterial infections occur when pathogenic bacteria enter the body, bypassing its natural defenses. While many bacteria are harmless or beneficial, certain types, known as pathogens, can cause diseases. These infections vary widely depending on the bacterial strain and the part of the body affected.
Common Causes of Bacterial Infections
Bacterial infections arise from exposure to harmful bacteria in various environments. Common causes include:
- Contact with Contaminated Surfaces: Bacteria on objects can transfer to the skin or mucous membranes.
- Ingestion of Contaminated Food or Water: Consuming improperly prepared or stored food can lead to bacterial infections.
- Open Wounds or Cuts: Bacteria can enter the body through breaks in the skin.
- Close Contact with Infected Individuals: Respiratory droplets or direct physical contact can spread bacterial infections.
Examples of Common Bacterial Pathogens:
- Escherichia coli (E. coli): Causes food poisoning.
- Streptococcus pneumoniae: Leads to pneumonia.
- Staphylococcus aureus: Associated with skin infections and more severe conditions like sepsis.
Symptoms of Bacterial Infections
The symptoms of bacterial infections depend on the type and location of the infection. General symptoms include:
- Fever: A common immune response to bacterial presence.
- Localized Pain or Swelling: Often occurs at the site of infection.
- Redness and Warmth: Indicators of inflammation.
- Fatigue and Weakness: Systemic infections can cause overall malaise.
- Discharge or Pus: In skin infections, this is a sign of bacterial activity.
Specific Examples:
- Respiratory Infections: Cough, shortness of breath, and chest pain.
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): Burning sensation during urination and frequent urges to urinate.
- Gastrointestinal Infections: Diarrhea, vomiting, and abdominal cramps.
Diagnosis of Bacterial Infections
Accurate diagnosis is essential for effective treatment. Healthcare providers use:
- Medical History and Symptoms Analysis: Identifying patterns in symptoms.
- Physical Examination: Detecting signs like redness, swelling, or discharge.
- Laboratory Tests:
- Blood Tests: Check for elevated white blood cell counts.
- Culture Tests: Identify the specific bacterial strain.
- Imaging: X-rays or CT scans to detect internal infections.
Treatment of Bacterial Infections
Antibiotics: The Primary Treatment
Antibiotics are the cornerstone of bacterial infection treatment. They target bacterial cells while sparing human cells. Common types include:
- Penicillins: Effective against a wide range of infections.
- Macrolides: Used for respiratory and skin infections.
- Cephalosporins: Treat severe or resistant infections.
Supportive Care
- Hydration: Essential for combating fever and preventing dehydration.
- Pain Management: Over-the-counter medications may be recommended.
- Hospitalization: Necessary for severe infections like sepsis.
Antibiotic Resistance
The overuse and misuse of antibiotics can lead to resistant bacterial strains. It is critical to:
- Use antibiotics only as prescribed.
- Complete the full course of treatment.
Prevention of Bacterial Infections
Preventing bacterial infections involves maintaining hygiene and adopting safe practices:
- Handwashing: Use soap and water, especially before meals and after contact with potentially contaminated surfaces.
- Proper Food Handling: Ensure thorough cooking and avoid cross-contamination.
- Vaccination: Protects against specific bacterial infections, such as meningitis and pneumonia.
- Wound Care: Keep cuts clean and covered to prevent infection.
- Avoiding Close Contact: Stay away from individuals with contagious infections.
Common Misconceptions About Bacterial Infections
- All Bacteria Are Harmful: Many bacteria are beneficial and essential for health.
- Antibiotics Cure All Infections: Antibiotics are ineffective against viral infections.
- Stopping Antibiotics Early is Safe: Always complete the prescribed course to prevent resistance
Bacterial infections, while common, are manageable with prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Preventive measures such as hygiene and vaccination play a significant role in reducing the risk. Stay informed and consult healthcare providers for personalized advice.
MYHEALTHMAG