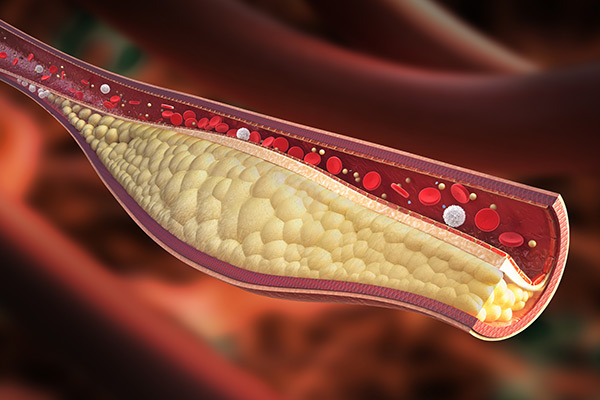
Hypercholesterolemia refers to abnormally high levels of cholesterol in the blood. Cholesterol is a waxy substance essential for cell formation, but excessive amounts can increase the risk of cardiovascular diseases. Hypercholesterolemia is classified based on total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, and high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol levels.
Causes of Hypercholesterolemia
1. Genetic Factors
- Familial Hypercholesterolemia (FH): An inherited condition that significantly raises cholesterol levels from birth.
- Mutations in genes like LDLR, APOB, and PCSK9 contribute to this disorder.
2. Lifestyle Factors
- Diet: Consuming foods rich in saturated fats, trans fats, and cholesterol.
- Lack of Exercise: Sedentary habits can reduce HDL (good) cholesterol.
- Obesity: Excess weight contributes to higher LDL levels.
3. Medical Conditions
- Diabetes Mellitus
- Hypothyroidism
- Kidney Disease
- Liver Disorders
Symptoms of Hypercholesterolemia
Hypercholesterolemia often has no noticeable symptoms until complications arise. However, signs may include:
- Xanthomas: Fatty deposits under the skin or around tendons.
- Xanthelasma: Cholesterol-rich deposits around the eyes.
- Arcus Senilis: A grayish-white ring around the cornea in adults.
Health Risks Associated with Hypercholesterolemia
| Cholesterol Type | Ideal Level | Risk Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Total Cholesterol | < 200 mg/dL | Heart disease, stroke |
| LDL Cholesterol | < 100 mg/dL | Artery blockage, atherosclerosis |
| HDL Cholesterol | > 60 mg/dL | Protective against heart disease |
Diagnosis of Hypercholesterolemia
1. Lipid Profile Test
This blood test measures:
- Total Cholesterol
- LDL Cholesterol
- HDL Cholesterol
- Triglycerides
2. Genetic Testing
For individuals with a family history of hypercholesterolemia, genetic testing can identify inherited risks.
Treatment and Management of Hypercholesterolemia
1. Lifestyle Modifications
- Healthy Diet: Incorporate more fiber, fruits, and vegetables. Reduce saturated fats and trans fats.
- Exercise: Engage in aerobic activities like brisk walking, cycling, or swimming for at least 150 minutes per week.
- Weight Management: Maintain a healthy BMI through balanced nutrition and physical activity.
2. Medications
- Statins: Commonly prescribed to lower LDL cholesterol.
- Ezetimibe: Reduces cholesterol absorption in the intestine.
- PCSK9 Inhibitors: Effective for severe hypercholesterolemia cases.
3. Dietary Supplements
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids
- Plant Sterols and Stanols
- Niacin (Vitamin B3)
4. Alternative Therapies
- Regular consumption of green tea, garlic, and psyllium husk may assist in lowering cholesterol levels.
Prevention Strategies
1. Balanced Diet
- Emphasize whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Minimize processed foods and sugary beverages.
2. Regular Exercise
Physical activity raises HDL levels and enhances cardiovascular health.
3. Routine Screenings
Adults above 40 should undergo regular cholesterol checks to detect issues early.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is considered dangerously high cholesterol?
Cholesterol levels above 240 mg/dL (total) or 160 mg/dL (LDL) are considered dangerously high.
2. Can hypercholesterolemia be reversed?
While genetic forms may require lifelong management, lifestyle changes and medications can effectively lower cholesterol levels.
3. Are statins safe for long-term use?
Yes, statins are generally safe but may cause side effects like muscle pain or liver issues in some individuals.
4. How often should cholesterol levels be checked?
Adults aged 20 and above should have their cholesterol checked every 4 to 6 years. Those with risk factors may need more frequent tests.
5. What foods should be avoided for hypercholesterolemia?
Limit consumption of fried foods, processed meats, full-fat dairy products, and sugary snacks.
Hypercholesterolemia is a manageable condition with proper lifestyle adjustments, medications, and preventive care. Early detection through regular screenings and proactive health choices significantly reduces the risk of heart-related complications.