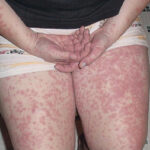
Hymenolepiasis infection is a parasitic disease caused by Hymenolepis nana (dwarf tapeworm) or Hymenolepis diminuta. It primarily affects the gastrointestinal tract and is prevalent worldwide, particularly in regions with poor sanitation and hygiene practices.
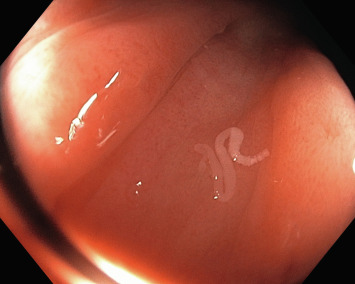
Causes and Transmission of Hymenolepiasis
Hymenolepiasis is caused by ingesting eggs of the Hymenolepis species. The primary causes include:
- Contaminated Food and Water: Ingesting contaminated food or water is the most common transmission route.
- Poor Hygiene Practices: Unwashed hands after toilet use or before eating can spread the infection.
- Infected Insects: In the case of Hymenolepis diminuta, insects like beetles can serve as intermediate hosts, carrying infective larvae.
Risk Factors for Hymenolepiasis Infection
Individuals with higher risk include:
- Children, especially in daycare or school environments
- People living in areas with poor sanitation
- Individuals with compromised immune systems
Symptoms of Hymenolepiasis Infection
Symptoms may vary depending on the parasite load. Common symptoms include:
- Abdominal pain and discomfort
- Diarrhea or constipation
- Nausea and vomiting
- Loss of appetite
- Weight loss and weakness
- Irritability and disturbed sleep (especially in children)
Severe cases may lead to malnutrition and developmental issues in children.
Diagnosis of Hymenolepiasis
The diagnosis of hymenolepiasis involves several methods:
- Stool Examination: The presence of Hymenolepis eggs or proglottids in stool samples is the most definitive diagnostic method.
- Serological Tests: Blood tests may help identify parasitic infections in some cases.
- Endoscopy: In rare cases, endoscopy may be required for intestinal inspection.
Treatment of Hymenolepiasis Infection
Effective treatment typically includes antiparasitic medications:
- Praziquantel: The most common drug used for treating hymenolepiasis; it paralyzes and dislodges the worm.
- Niclosamide: An alternative medication that effectively eliminates adult tapeworms.
Treatment Steps
- Initial Medication Dose: Doctors often prescribe a single dose of praziquantel.
- Follow-up Stool Examination: Repeat tests are conducted after 2-4 weeks to confirm the infection’s eradication.
- Supportive Care: Hydration, nutritional support, and probiotics may be advised to restore gut health.
Prevention of Hymenolepiasis Infection
Preventive strategies can significantly reduce the risk of infection:
- Maintain proper hand hygiene
- Thoroughly wash fruits, vegetables, and food items
- Avoid consumption of untreated water
- Implement effective pest control to minimize insect infestations
Complications of Hymenolepiasis
Untreated hymenolepiasis may result in:
- Intestinal inflammation and obstruction
- Chronic malnutrition, particularly in children
- Delayed growth and cognitive development
Epidemiology of Hymenolepiasis
Hymenolepiasis is prevalent worldwide, with higher incidence rates in:
- Tropical and subtropical regions
- Communities with limited access to clean water and sanitation
- Areas with insect infestations
FAQs:
1. Is hymenolepiasis contagious?
Yes, it can spread through direct contact with contaminated objects, food, or water.
2. Can hymenolepiasis recur?
Yes, reinfection is possible, particularly in unsanitary conditions.
3. What are the common medications for hymenolepiasis?
Praziquantel and niclosamide are the most effective treatments.
4. How long does it take to recover from hymenolepiasis?
With proper treatment, recovery typically occurs within one to two weeks.
5. Is hymenolepiasis common in developed countries?
While less frequent, cases can still occur due to travel or imported food contamination.
Hymenolepiasis infection, while treatable, can lead to severe complications if left unattended. Prompt diagnosis, effective treatment, and improved hygiene practices are essential for prevention. Understanding the parasite’s life cycle, risk factors, and preventive measures can help reduce the prevalence of this infection globally.