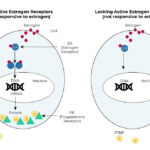
Hormone receptor-positive (HR+) early breast cancer is a subtype of breast cancer characterized by the presence of estrogen receptors (ER) and/or progesterone receptors (PR) on cancer cells. These receptors fuel cancer growth through hormone stimulation.
Risk Factors for Hormone Receptor-Positive Early Breast Cancer
Identifying risk factors helps in early detection and preventive strategies. Common risk factors include:
- Age and Gender: Women over 50 have a higher risk.
- Family History: Genetic mutations like BRCA1/BRCA2 increase susceptibility.
- Hormonal Exposure: Prolonged estrogen exposure due to early menstruation or late menopause.
- Obesity: Excess fat tissue can increase estrogen levels.
- Lifestyle Factors: Alcohol consumption, smoking, and physical inactivity.
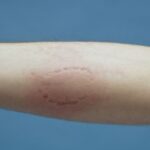
Symptoms of HR+ Early Breast Cancer
Key symptoms include:
- Lump in the breast or underarm
- Breast pain or tenderness
- Changes in breast shape or size
- Nipple discharge or inversion
- Skin dimpling or redness
Diagnostic Techniques for HR+ Early Breast Cancer
Early detection greatly improves prognosis. Key diagnostic methods include:
1. Mammogram
A low-dose X-ray that detects tumors and abnormalities.
2. Ultrasound
Used to determine whether a lump is solid or fluid-filled.
3. Biopsy
A sample of breast tissue is examined for hormone receptor status.
4. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) Testing
Determines ER and PR positivity through staining techniques.
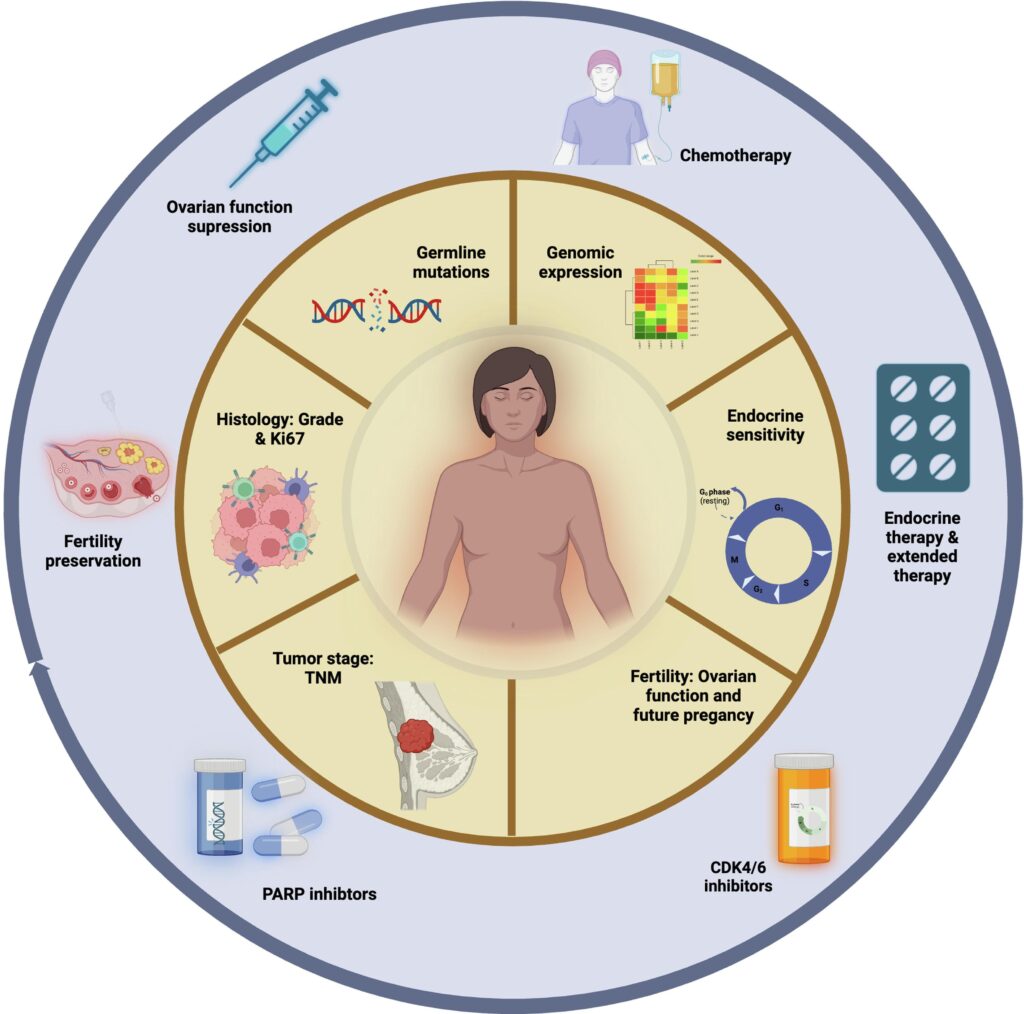
Treatment Options for HR+ Early Breast Cancer
Treatment strategies often combine therapies to improve outcomes. Key options include:
1. Surgery
- Lumpectomy: Removing only the tumor and surrounding tissue.
- Mastectomy: Full removal of one or both breasts.
2. Radiation Therapy
Targets residual cancer cells post-surgery to reduce recurrence risk.
3. Hormone Therapy
Designed to block hormone production or its interaction with cancer cells.
- Tamoxifen: Blocks estrogen receptors in breast tissue.
- Aromatase Inhibitors: Reduce estrogen production in postmenopausal women.
4. Chemotherapy
Used in high-risk cases to target rapidly dividing cells.
5. Targeted Therapy
Medications like CDK4/6 inhibitors improve outcomes in combination with hormone therapy.
6. Immunotherapy
Still under clinical investigation, it may enhance immune response against cancer cells.
Prognosis and Survival Rates
Prognosis for HR+ early breast cancer is generally favorable when diagnosed early. The five-year survival rate exceeds 90% with appropriate treatment.
Lifestyle Changes and Preventive Measures
Implementing healthy lifestyle practices can reduce the risk of HR+ breast cancer recurrence:
- Regular Exercise: Maintains hormonal balance and a healthy weight.
- Balanced Diet: Rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Limiting Alcohol: Reduces estrogen-related risks.
- Breastfeeding: Reduces long-term breast cancer risk.
Follow-Up Care for HR+ Early Breast Cancer Patients
Regular follow-ups are crucial for monitoring recurrence and managing side effects. Follow-up care typically includes:
- Routine mammograms
- Blood tests to track hormone levels
- Bone density scans if undergoing aromatase inhibitor therapy
FAQs:
1. What is the most effective treatment for hormone receptor-positive early breast cancer?
The combination of surgery, hormone therapy, and radiation therapy provides optimal outcomes for HR+ breast cancer.
2. How often should I have a mammogram if I am at risk for HR+ breast cancer?
Women over 40 are advised to have mammograms annually or as recommended by their healthcare provider.
3. Can HR+ breast cancer return after treatment?
Yes, recurrence is possible, but regular follow-ups and hormone therapy significantly reduce this risk.
4. Are there side effects to hormone therapy for HR+ breast cancer?
Common side effects include hot flashes, fatigue, and bone density loss. Consult your doctor for personalized management strategies.
5. Is hormone receptor-positive breast cancer hereditary?
While HR+ breast cancer itself isn’t directly inherited, genetic mutations like BRCA1/BRCA2 can increase risk.