Herpes zoster, commonly known as shingles, is a viral infection caused by the varicella-zoster virus (VZV). This virus is the same one responsible for chickenpox. Once a person recovers from chickenpox, the virus remains dormant in the nervous system and can reactivate years later as shingles.
Causes of Herpes Zoster
Herpes zoster occurs when the dormant varicella-zoster virus reactivates. While the exact trigger for reactivation is not always clear, several factors increase the risk:
- Weakened immune system due to aging, illness, or immunosuppressive medications
- Stress and fatigue
- Certain medical conditions such as cancer or HIV
- Aging as the immune response weakens with age
Symptoms of Herpes Zoster
The symptoms of herpes zoster typically appear in stages:
Initial Symptoms
- Tingling, itching, or burning sensation on the skin
- Sensitivity to touch or pain in a localized area
- Flu-like symptoms including fever and headache
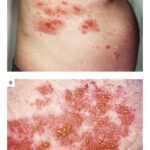
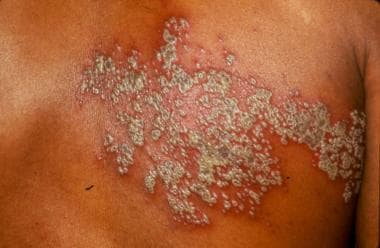
Rash Development
- Red patches that evolve into fluid-filled blisters
- The rash typically appears on one side of the body, often in a stripe or belt-like pattern
- Blisters may break open, crust over, and heal within 2 to 4 weeks
Complications
In some cases, herpes zoster can lead to severe complications such as:
- Postherpetic neuralgia (PHN) – Persistent nerve pain lasting for months or years after the rash clears
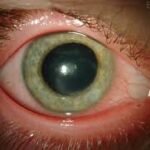
- Vision loss – If the rash develops around the eye
- Neurological issues – Such as facial paralysis or hearing problems
- Skin infections if blisters become infected with bacteria
Diagnosis of Herpes Zoster
Healthcare providers diagnose herpes zoster through:
- Visual examination of the rash and symptom patterns
- Laboratory tests such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR) or viral culture for confirmation
Treatment for Herpes Zoster
Prompt treatment can help reduce the severity and duration of symptoms.
Antiviral Medications
- Acyclovir
- Valacyclovir
- Famciclovir
These drugs are most effective when administered within 72 hours of the rash’s appearance.
Pain Management
- Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen
- Prescription medications such as anticonvulsants or antidepressants for nerve pain
- Topical creams containing capsaicin or lidocaine
Home Remedies
- Cool compresses to soothe itching
- Oatmeal baths for comfort
- Loose clothing to reduce irritation
Prevention of Herpes Zoster
Vaccination is the most effective prevention strategy:
- Shingrix is recommended for adults over 50 and provides over 90% protection
- Zostavax (an older vaccine) is less effective but still offers protection
Additional Preventive Measures
- Maintaining a healthy immune system through a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management
Risk Factors for Herpes Zoster
Certain groups are at higher risk of developing herpes zoster:
- Individuals over 50
- People with compromised immune systems
- Those who have had chickenpox earlier in life
Managing and Coping with Herpes Zoster
- Early diagnosis and timely treatment can significantly reduce discomfort.
- Proper skin care, pain management strategies, and lifestyle adjustments can aid recovery.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Is herpes zoster contagious?
Herpes zoster itself is not contagious, but the varicella-zoster virus can spread to individuals who have never had chickenpox, causing chickenpox rather than shingles.
Can herpes zoster recur?
While uncommon, herpes zoster can recur, especially in individuals with weakened immune systems.
How long does herpes zoster last?
Most cases resolve within 3 to 5 weeks, although complications like postherpetic neuralgia can persist for longer.
Can stress trigger herpes zoster?
Yes, high levels of stress can weaken the immune system, potentially triggering the reactivation of the virus.
What foods should I avoid during herpes zoster?
It’s advisable to reduce the intake of high-arginine foods such as nuts, chocolate, and seeds, as they can potentially promote viral replication.
Herpes zoster is a manageable condition with early diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Timely medical intervention, combined with preventive strategies like vaccination, can minimize the risk of severe complications. Individuals should seek medical advice if they experience symptoms suggestive of herpes zoster.