Herpes simplex keratoconjunctivitis is an ocular condition caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV), typically HSV-1. This viral infection primarily affects the cornea and conjunctiva, leading to inflammation, irritation, and potential visual impairment. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment is essential for effective management and prevention of complications.
Causes of Herpes Simplex Keratoconjunctivitis
The primary cause of herpes simplex keratoconjunctivitis is the herpes simplex virus. HSV-1, responsible for oral cold sores, is the most common culprit, while HSV-2 can also contribute in rare cases. The virus can enter the eye through:
- Direct contact with infected saliva or secretions
- Autoinoculation from active herpes lesions
- Reactivation of dormant HSV in the trigeminal ganglion
Risk factors include:
- Compromised immune systems
- Ocular trauma
- Stress or fever
- Excessive sun exposure
Symptoms of Herpes Simplex Keratoconjunctivitis
The symptoms vary in severity and may include:
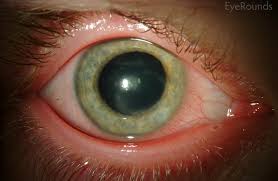
- Eye redness and irritation
- Pain or discomfort in the eye
- Watery discharge
- Photophobia (sensitivity to light)
- Blurred vision
- Formation of dendritic ulcers on the cornea
Diagnosis of Herpes Simplex Keratoconjunctivitis
Diagnosing herpes simplex keratoconjunctivitis involves clinical examination and laboratory tests. Key diagnostic methods include:
- Slit-lamp examination: Identifies dendritic lesions on the cornea.
- Fluorescein staining: Highlights branching ulcers characteristic of HSV infection.
- Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR): Confirms viral presence with high sensitivity.
Treatment Options for Herpes Simplex Keratoconjunctivitis
Effective management involves antiviral medications, supportive care, and preventive strategies.
Antiviral Medications
- Topical Antivirals: Drugs like trifluridine, ganciclovir, and acyclovir are commonly prescribed to reduce viral replication.
- Oral Antivirals: Systemic medications such as acyclovir, valacyclovir, or famciclovir are used for severe or recurrent infections.
Supportive Care
- Artificial tears to soothe irritation
- Cold compresses to reduce inflammation
- Pain relievers for symptom control
Surgical Interventions
In cases of corneal scarring or persistent ulcers, procedures like corneal debridement or keratoplasty may be required.
Prevention Strategies for Herpes Simplex Keratoconjunctivitis
To minimize the risk of infection and recurrence:
- Avoid touching the eyes with unwashed hands
- Use protective eyewear in UV-intense environments
- Manage stress to reduce viral reactivation
- Maintain good hygiene practices, especially during cold sore outbreaks
Potential Complications
Without proper treatment, herpes simplex keratoconjunctivitis may lead to:
- Corneal scarring
- Permanent vision impairment
- Glaucoma
- Secondary bacterial infections
Prognosis and Long-Term Management
With timely treatment, most cases resolve without lasting damage. However, recurrence is common. Long-term use of prophylactic antivirals may be recommended for patients with frequent flare-ups.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: Can herpes simplex keratoconjunctivitis be cured?
While there’s no permanent cure for HSV, antiviral medications effectively manage symptoms and reduce recurrence risk.
Q2: Is herpes simplex keratoconjunctivitis contagious?
Yes, it can spread through direct contact with infected saliva, tears, or contaminated surfaces.
Q3: How long does a herpes simplex keratoconjunctivitis episode last?
Episodes typically resolve within 2 to 3 weeks with proper treatment.
Q4: Can herpes simplex keratoconjunctivitis cause blindness?
Severe or untreated cases can result in corneal scarring and vision loss.
Q5: How can recurrence be prevented?
Managing triggers such as stress, UV exposure, and maintaining good hygiene can reduce recurrence.
Herpes simplex keratoconjunctivitis requires prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment to prevent complications. By understanding its symptoms, causes, and prevention strategies, individuals can effectively manage the condition and maintain optimal eye health.