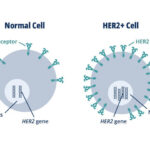
HER2 positive carcinoma of the breast is an aggressive subtype of breast cancer characterized by the overexpression of the human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) protein. This condition requires specific treatment strategies due to its unique molecular profile and increased proliferation rates.
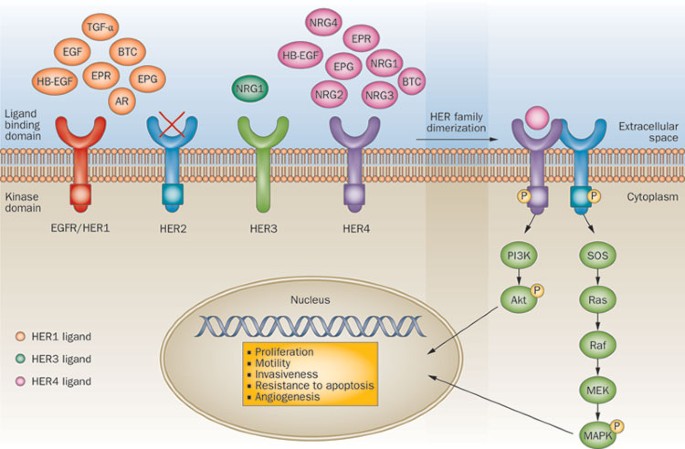
Understanding HER2 Positive Breast Cancer
HER2 positive breast cancer accounts for approximately 20% of all breast cancer cases. The HER2 gene produces HER2 proteins, which regulate cell growth. Overexpression of this protein leads to uncontrolled cell division, promoting cancer progression.
Key Characteristics of HER2 Positive Breast Cancer
- Increased tumor aggressiveness
- Higher likelihood of recurrence
- Distinct molecular signature identified through immunohistochemistry (IHC) or fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH)
Causes and Risk Factors
Although the precise cause of HER2 positive carcinoma is not fully understood, several risk factors are associated with its development:
- Genetic Mutations: Mutations in the HER2 gene increase the likelihood of abnormal protein overproduction.
- Hormonal Factors: Higher estrogen exposure may contribute to HER2 positive cancer formation.
- Family History: A strong family history of breast cancer elevates the risk.
Diagnosis of HER2 Positive Carcinoma
Accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment planning. Common diagnostic tests include:
1. Immunohistochemistry (IHC):
- Measures HER2 protein levels in tumor cells.
- Results are scored from 0 to 3+, with scores of 3+ confirming HER2 positivity.
2. Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization (FISH):
- Detects HER2 gene amplification.
- Recommended when IHC results are inconclusive (score of 2+).
3. Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS):
- Identifies molecular abnormalities and potential treatment targets.
Treatment Strategies for HER2 Positive Carcinoma
Treatment for HER2 positive carcinoma typically combines targeted therapies with conventional approaches.
1. Targeted Therapy:
- Trastuzumab (Herceptin): Monoclonal antibody blocking HER2 receptors.
- Pertuzumab (Perjeta): Often combined with Trastuzumab for enhanced efficacy.
- Ado-trastuzumab emtansine (Kadcyla): Delivers cytotoxic agents directly to HER2 positive cells.
2. Chemotherapy:
- Frequently combined with targeted therapies to improve response rates.
3. Hormone Therapy:
- Used in cases where cancer is also hormone receptor-positive.
4. Surgical Options:
- Lumpectomy: Preferred for smaller tumors.
- Mastectomy: Recommended for larger tumors or multicentric disease.
5. Radiation Therapy:
- Reduces recurrence risk by targeting residual cancer cells post-surgery.
Prognosis and Survival Rates
The prognosis for HER2 positive breast cancer has improved significantly with targeted therapies. Key factors influencing survival include:
- Early detection and timely intervention
- Patient response to targeted therapies
- Presence or absence of metastatic spread
Lifestyle and Preventive Measures
While HER2 positive breast cancer may not be entirely preventable, certain lifestyle strategies can reduce risk:
- Maintain a balanced diet rich in antioxidants
- Engage in regular physical activity
- Limit alcohol consumption
- Undergo routine breast screenings, especially for high-risk individuals
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What is the difference between HER2 positive and HER2 negative breast cancer?
HER2 positive breast cancer overexpresses the HER2 protein, while HER2 negative types do not. This distinction determines the treatment approach.
2. Can HER2 positive breast cancer be cured?
With modern treatments like targeted therapies, many patients achieve remission, especially if diagnosed early.
3. Are there side effects with HER2 targeted therapies?
Common side effects include fatigue, nausea, and potential heart-related issues. Regular monitoring minimizes risks.
4. Is HER2 positive breast cancer hereditary?
While HER2 positive breast cancer itself is not typically inherited, genetic mutations contributing to it may run in families.
5. What is the survival rate for HER2 positive breast cancer?
With targeted therapy advancements, survival rates for early-stage cases are high, exceeding 90% in some cases.
HER2 positive carcinoma of the breast requires specialized treatment strategies to improve outcomes. Advances in targeted therapies have revolutionized care, offering patients a promising outlook. Regular screenings and early diagnosis remain critical in managing this aggressive form of breast cancer.