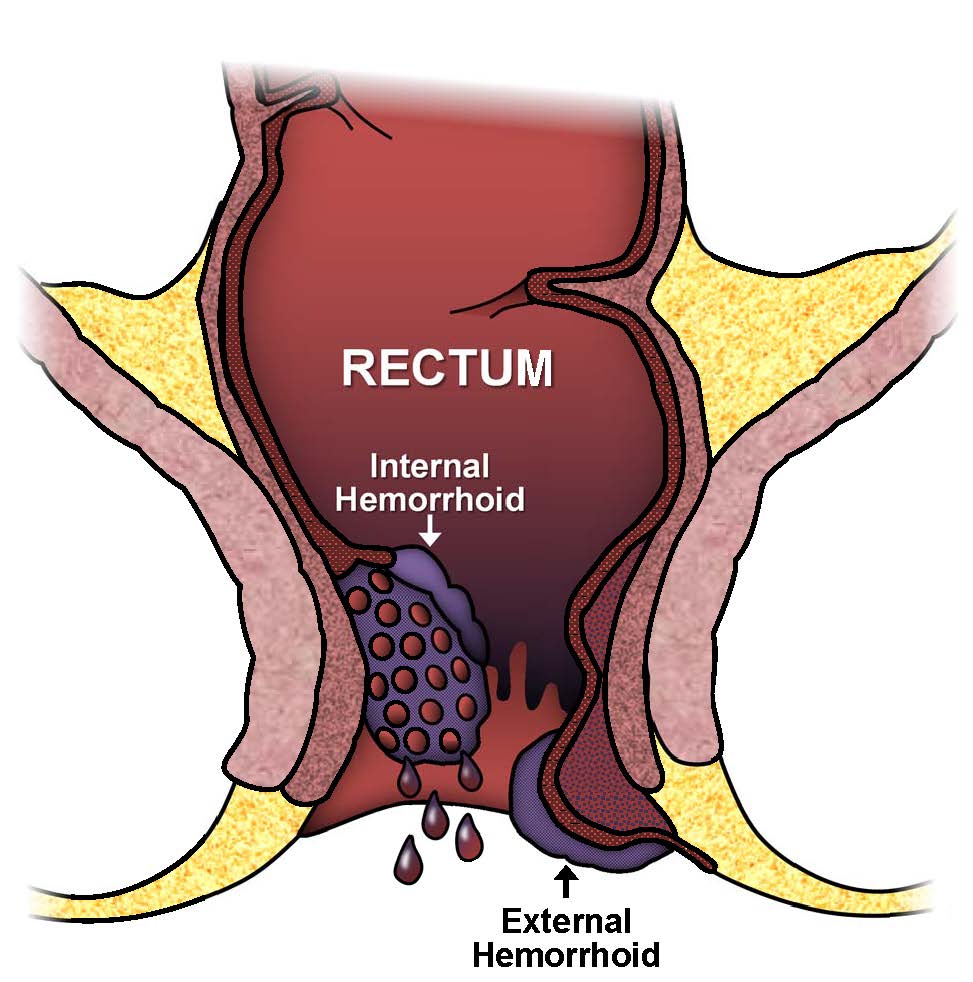
Hemorrhoids, also known as piles, are swollen veins in the lower rectum and anus. They are common and can cause discomfort, itching, and bleeding. Hemorrhoids are classified into two types:
- Internal Hemorrhoids: Located inside the rectum, usually painless but may cause bleeding.
- External Hemorrhoids: Found under the skin around the anus, often causing pain and discomfort.
Causes of Hemorrhoids
Several factors contribute to the development of hemorrhoids:
- Chronic Constipation: Straining during bowel movements increases pressure on rectal veins.
- Prolonged Sitting: Sitting for long periods, especially on hard surfaces, can aggravate hemorrhoids.
- Pregnancy: Increased pressure on pelvic veins can lead to hemorrhoid formation.
- Obesity: Excess weight raises abdominal pressure, impacting rectal veins.
- Low-Fiber Diet: Insufficient fiber intake results in harder stools and straining.
- Aging: As tissues weaken with age, veins become more prone to swelling.
Symptoms of Hemorrhoids
The most common symptoms include:
- Rectal bleeding, often noticed during bowel movements
- Itching and irritation around the anus
- Swelling or a lump near the anus
- Discomfort or pain, particularly with external hemorrhoids
- Mucus discharge from the anus
Diagnosis of Hemorrhoids
Healthcare professionals may use the following methods to diagnose hemorrhoids:
- Physical Examination: External hemorrhoids are visible, while internal ones require further inspection.
- Digital Rectal Exam (DRE): A lubricated, gloved finger is inserted into the rectum to detect abnormalities.
- Anoscopy or Proctoscopy: A small tube with a light is used to view internal hemorrhoids.
Treatment for Hemorrhoids
Effective treatment depends on the severity of the condition:
Home Remedies
- High-Fiber Diet: Consume fiber-rich foods like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains to soften stools.
- Sitz Baths: Soaking the anal area in warm water for 15-20 minutes relieves discomfort.
- Topical Treatments: Creams containing hydrocortisone or witch hazel reduce inflammation and itching.
- Oral Pain Relievers: Over-the-counter medications like ibuprofen can alleviate pain.
Medical Procedures
- Rubber Band Ligation: A small band is placed around the hemorrhoid base to cut off blood flow, causing it to shrink.
- Sclerotherapy: An injection of a chemical solution shrinks hemorrhoids.
- Infrared Coagulation: Heat is applied to shrink internal hemorrhoids.
- Hemorrhoidectomy: Surgical removal is performed in severe cases.
Preventing Hemorrhoids
Preventive measures can significantly reduce the risk of developing hemorrhoids:
- Increase Fiber Intake: Aim for 25-30 grams of fiber daily.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water to soften stools.
- Exercise Regularly: Physical activity promotes healthy digestion.
- Avoid Straining: Take your time during bowel movements and avoid forcing it.
- Don’t Delay Bowel Movements: Respond to the urge to prevent constipation.
When to See a Doctor
Seek medical attention if you experience:
- Persistent bleeding
- Severe pain or discomfort
- Swelling that does not improve with home treatment
FAQs
Can Hemorrhoids Go Away on Their Own?
Yes, mild hemorrhoids can resolve without treatment, especially with lifestyle changes.
What Is the Fastest Way to Relieve Hemorrhoid Pain?
Over-the-counter creams, sitz baths, and cold compresses provide quick relief.
Are Hemorrhoids a Sign of Cancer?
No, hemorrhoids are not cancerous, but rectal bleeding should be evaluated by a doctor.
How Long Do Hemorrhoids Last?
Mild cases may resolve in a few days, while severe cases may require medical intervention.
Is Surgery Necessary for Hemorrhoids?
Surgery is typically recommended for severe or recurring hemorrhoids that do not respond to other treatments.