Hemophilia is a rare genetic disorder in which blood does not clot properly due to insufficient clotting factors. Hemorrhaging in hemophilia can result in severe internal and external bleeding, posing serious health risks. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment methods is crucial for managing this condition effectively.
What is Hemophilia?
Hemophilia is a bleeding disorder characterized by defective blood clotting. The two primary types are:
- Hemophilia A: Caused by a deficiency of clotting factor VIII.
- Hemophilia B: Caused by a deficiency of clotting factor IX.
Both types increase the risk of prolonged bleeding, including spontaneous internal hemorrhages.
Causes of Hemorrhaging in Hemophilia
Hemorrhaging in individuals with hemophilia is primarily due to reduced levels of essential clotting proteins. Factors that can trigger bleeding episodes include:
- Injuries or Trauma: Even minor cuts or bruises can lead to severe bleeding.
- Spontaneous Bleeding: Occurs without any apparent cause, commonly affecting joints or muscles.
- Surgical Procedures: Patients with hemophilia face a heightened risk of excessive bleeding post-surgery.
- Dental Work: Routine dental procedures may induce uncontrolled bleeding.
Common Symptoms of Hemorrhaging in Hemophilia
Recognizing hemorrhage symptoms is vital to prevent complications. Common signs include:
- Joint Swelling and Pain: Common in knees, elbows, and ankles.
- Prolonged Bleeding: Excessive bleeding from cuts, injuries, or medical procedures.
- Blood in Urine or Stool: Indicating internal bleeding.
- Bruising and Hematomas: Large, deep bruises appearing without obvious trauma.
- Severe Headaches and Neurological Issues: Potential signs of intracranial hemorrhage.
Types of Hemorrhaging in Hemophilia
Hemorrhages in hemophilia patients can be categorized into:
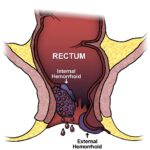
- External Hemorrhages: Visible bleeding from cuts, abrasions, or wounds.
- Internal Hemorrhages: Occurs in muscles, joints, or internal organs.
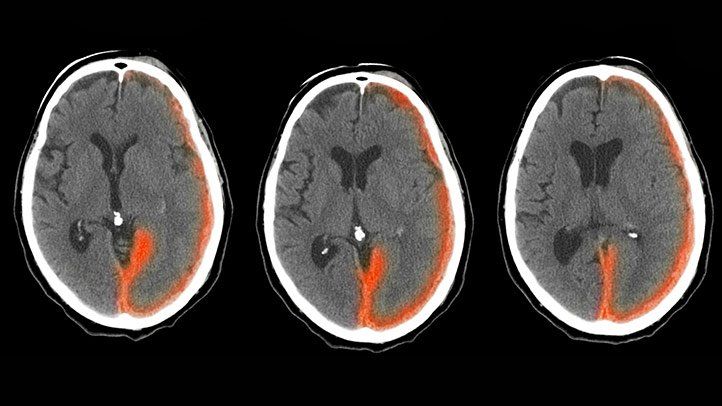
- Intracranial Hemorrhage: A life-threatening condition involving bleeding in the brain.
Diagnosis of Hemorrhaging in Hemophilia
Healthcare providers employ various methods to diagnose bleeding complications in hemophilia patients:
- Blood Tests: To assess clotting factor levels.
- Imaging Scans: MRI or CT scans to identify internal bleeding.
- Physical Examination: Identifying joint pain, swelling, or bruising.
Treatment and Management Strategies
Effective management of hemorrhaging in hemophilia involves a combination of therapies and preventive measures:
- Clotting Factor Replacement Therapy:
- Regular infusions of factor VIII or IX to maintain adequate clotting levels.
- Desmopressin (DDAVP):
- A synthetic hormone used to boost clotting factor levels in mild cases.
- Antifibrinolytic Medications:
- Drugs like tranexamic acid that help stabilize blood clots.
- Physical Therapy:
- Helps strengthen joints and muscles, reducing the risk of bleeding.
- Emergency Care:
- Immediate administration of clotting factors during severe bleeding episodes.
Preventive Measures
Patients with hemophilia can adopt various preventive strategies to reduce hemorrhaging risks:
- Avoid High-Risk Activities: Engaging in low-impact exercises like swimming or walking.
- Protective Gear: Wearing padding for joints during physical activities.
- Routine Medical Checkups: Regular monitoring helps manage clotting factor levels effectively.
- Proactive Dental Care: Maintaining oral hygiene to prevent gum bleeding.
Living with Hemophilia
While living with hemophilia requires constant vigilance, adopting the right lifestyle choices can significantly improve quality of life. Regular therapy, lifestyle adjustments, and awareness can help individuals manage their condition effectively.
FAQs
1. What are the warning signs of internal bleeding in hemophilia?
Signs include joint pain, muscle stiffness, unexplained swelling, and severe headaches. Seek medical attention if these occur.
2. How often should hemophilia patients receive clotting factor therapy?
The frequency depends on the severity of the condition. Severe cases may require routine infusions multiple times a week.
3. Can people with hemophilia lead normal lives?
Yes, with proper treatment, lifestyle adjustments, and medical supervision, individuals with hemophilia can maintain a healthy life.
4. What steps can be taken during a bleeding episode at home?
Apply pressure to the bleeding area, elevate the affected limb, and use an ice pack to reduce swelling. Contact healthcare providers for severe cases.
5. Is gene therapy available for hemophilia treatment?
Gene therapy advancements are being explored to offer potential long-term solutions for hemophilia patients.