Hematopoietic Syndrome (HS) is a critical manifestation of Acute Radiation Syndrome (ARS) that primarily affects the bone marrow and blood-forming tissues. Exposure to high doses of ionizing radiation can severely damage the hematopoietic system, leading to life-threatening complications. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and available treatments is vital for effective management.
Causes of Hematopoietic Syndrome in ARS
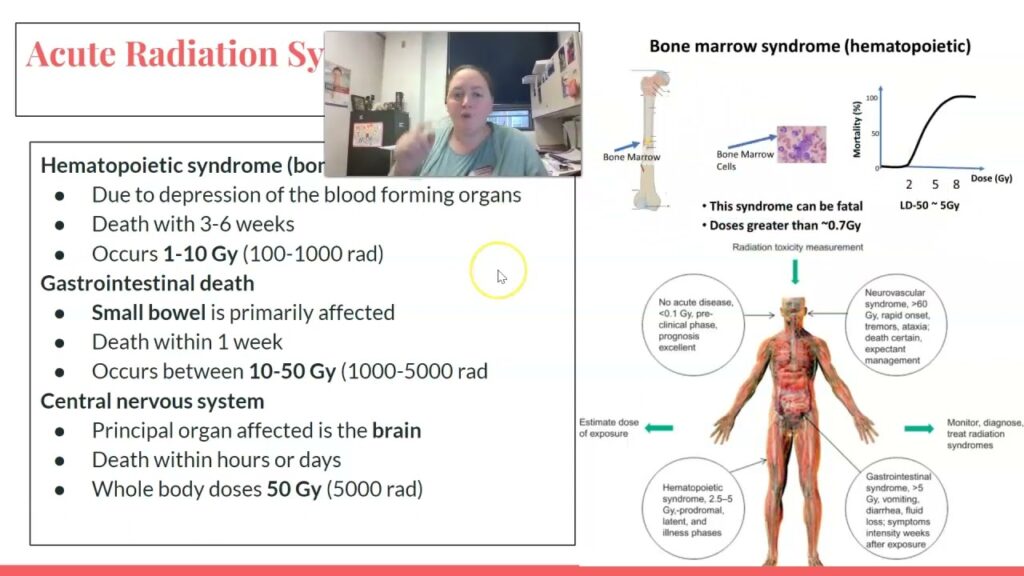
Hematopoietic Syndrome occurs due to exposure to ionizing radiation levels typically ranging from 1 to 10 Gy (Gray units). Such exposure can result from:
- Nuclear explosions
- Radiation accidents
- Medical radiation therapy mishaps
Radiation exposure above 1 Gy severely affects bone marrow cells, impairing the production of essential blood components such as white blood cells, red blood cells, and platelets.
Pathophysiology of Hematopoietic Syndrome
Upon exposure to radiation, hematopoietic stem cells in the bone marrow undergo apoptosis or necrosis. The reduction in cell production leads to:
- Leukopenia (low white blood cell count)
- Thrombocytopenia (low platelet count)
- Anemia (low red blood cell count)
These conditions collectively weaken the immune system, increase bleeding risks, and reduce oxygen delivery to tissues.
Symptoms of Hematopoietic Syndrome
Symptoms may appear within days to weeks following radiation exposure and include:
- Fatigue and weakness
- Fever and chills
- Easy bruising and bleeding
- Infections due to weakened immunity
- Pallor and shortness of breath
Diagnosis of Hematopoietic Syndrome
Early diagnosis is crucial and relies on:
- Complete blood count (CBC) to monitor white blood cell, red blood cell, and platelet levels
- Bone marrow biopsy to assess damage severity
- Cytogenetic analysis for detecting radiation-induced chromosomal damage
Treatment Strategies for Hematopoietic Syndrome
Supportive Care
- Fluid replacement to manage dehydration
- Antibiotics and antifungals to prevent and treat infections
- Transfusions to restore blood cell levels
Growth Factors and Cytokines
Medications such as filgrastim (G-CSF) and sargramostim (GM-CSF) can stimulate white blood cell production, improving immune recovery.
Stem Cell Transplantation
For severe cases, allogeneic stem cell transplantation may be required to regenerate the hematopoietic system.
Radiation Countermeasures
FDA-approved drugs like Neupogen, Nplate, and Leukine are effective in mitigating radiation-induced bone marrow damage.
Prognosis and Recovery
Prognosis depends on the radiation dose and the speed of medical intervention. Early administration of growth factors, antibiotics, and transfusions significantly improves survival rates. Patients with mild-to-moderate exposure generally recover within weeks to months, while severe cases may require long-term care.
Preventive Measures for Hematopoietic Syndrome
- Radiation shielding for at-risk personnel
- Emergency response protocols in nuclear facilities
- Potassium iodide administration in radiation emergencies
Hematopoietic Syndrome of Acute Radiation Syndrome is a severe condition that demands prompt diagnosis and treatment. By understanding its causes, symptoms, and management strategies, healthcare professionals can improve survival outcomes and mitigate complications for affected individuals.