Bursitis is a common yet often misunderstood condition characterized by the inflammation of bursae—the small, fluid-filled sacs that cushion bones, tendons, and muscles near joints. While bursitis can be painful and restrict movement, understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options can significantly improve quality of life.
What is Bursitis?
Its occurs when the bursae become irritated and inflamed, resulting in pain and swelling. These sacs reduce friction and cushion pressure points between bones and surrounding soft tissues. When they function abnormally, everyday movements can become uncomfortable or even debilitating.
Commonly Affected Areas
- Shoulders: Subacromial bursitis is common due to repetitive overhead motions.
- Elbows: Olecranon bursitis often occurs in people who lean on their elbows frequently.
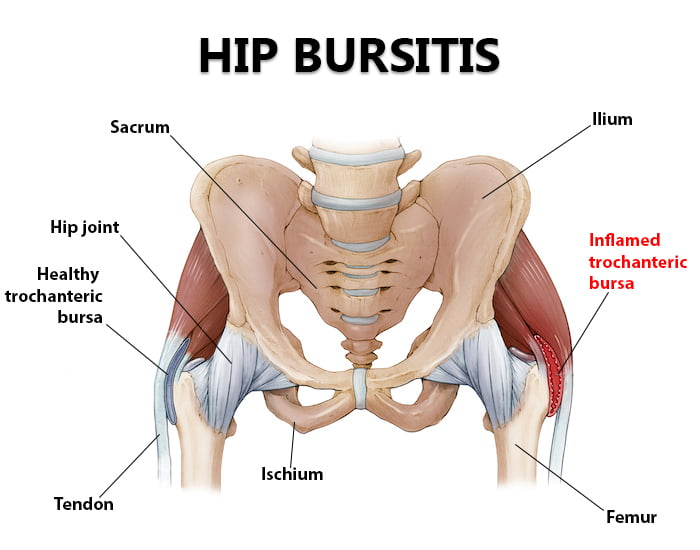
- Hips: Trochanteric bursitis is prevalent among runners and active individuals.
- Knees: Prepatellar bursitis, or “housemaid’s knee,” results from kneeling for prolonged periods.
- Heels: Retrocalcaneal bursitis affects those who wear tight shoes or engage in repetitive activities like running.
Causes
Repetitive Motion
Frequent and repetitive movements or pressure on a joint can irritate the bursae. Athletes, manual laborers, and musicians are particularly at risk.
Injury
A sudden impact or trauma to a joint may lead to acute inflammation of the bursae.
Age and Wear
With aging, bursae lose their elasticity, making them more susceptible to inflammation.
Underlying Conditions
Chronic illnesses like rheumatoid arthritis, gout, or diabetes can increase the risk of bursitis.
Infections
Bacterial infections of bursae, known as septic bursitis, require immediate medical attention.
Symptoms
- Pain: Typically localized near the affected joint and worsens with movement.
- Swelling: Visible swelling may occur, especially in superficial bursae.
- Stiffness: Restricted range of motion in the affected joint.
- Redness and Warmth: Indicate infection in cases of septic bursitis.
Diagnosis of Bursitis
Physical Examination
A healthcare provider will assess the affected joint for swelling, tenderness, and range of motion.
Imaging Studies
- X-rays: Rule out other joint conditions like fractures or arthritis.
- Ultrasound or MRI: Visualize inflammation in deeper bursae.
Lab Tests
For suspected septic bursitis, fluid from the affected bursa may be tested for bacteria or crystals.
Treatment Options
Rest and Activity Modification
Avoiding activities that exacerbate symptoms is crucial for recovery.
Medications
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Relieve pain and reduce inflammation.
- Corticosteroid Injections: Provide localized, potent anti-inflammatory effects.
- Antibiotics: Treat bacterial infections in septic bursitis.
Physical Therapy
Strengthening and stretching exercises can improve joint stability and reduce pressure on the bursae.
Aspiration
Draining excess fluid from the bursa can relieve swelling and discomfort.
Surgery
In rare, severe cases, surgical removal of the affected bursa may be necessary.
Prevention
Ergonomic Practices
- Use cushioned mats or knee pads when kneeling.
- Maintain proper posture during activities.
Gradual Activity Increases
Avoid sudden increases in physical activity intensity.
Regular Exercise
Strengthening muscles around joints reduces strain on bursae.
Proper Footwear
Wear well-fitting shoes to minimize pressure on foot bursae.
Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight reduces stress on joints.
Home Remedies
Ice and Heat Therapy
- Apply ice packs to reduce swelling in the first 48 hours.
- Use heat therapy to relax muscles and improve circulation afterward.
Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers
Medications like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can manage mild symptoms.
Elevation and Compression
Elevating the affected area and using a compression wrap can help alleviate swelling.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If symptoms persist despite home treatments, worsen rapidly, or include signs of infection such as fever, redness, or warmth, consult a healthcare provider promptly.
Bursitis in Common Areas
its causes, and its treatments, individuals can take proactive steps to manage symptoms and prevent recurrence. Early intervention and lifestyle modifications are key to maintaining joint health and mobility.