Gynecomastia is a medical condition characterized by the enlargement of breast tissue in males. It is commonly caused by hormonal imbalances, where estrogen levels are elevated in comparison to testosterone. This condition can affect males of all ages, from infants to older men.
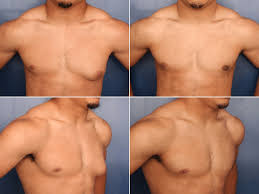
Causes of Gynecomastia
Understanding the causes of gynecomastia is crucial in determining appropriate treatment options. Key factors include:
Hormonal Imbalance
- Increased estrogen or decreased testosterone levels.
- Hormonal fluctuations during puberty or aging.
Medications
Certain drugs can lead to gynecomastia, including:
- Anti-androgens (e.g., finasteride, spironolactone)
- Anabolic steroids
- Anti-anxiety medications (e.g., diazepam)
- Antibiotics and antifungal drugs
Health Conditions
Underlying medical issues contributing to gynecomastia include:
- Liver disease
- Kidney failure
- Hyperthyroidism
- Tumors affecting hormone levels
Lifestyle Factors
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- Drug use (e.g., marijuana, heroin)
- Obesity, which increases estrogen production
Symptoms of Gynecomastia
Gynecomastia symptoms may vary in intensity and include:
- Swollen breast gland tissue
- Tenderness or pain in the affected area
- Nipple sensitivity
- Asymmetrical breast growth in some cases
Diagnosis of Gynecomastia
Proper diagnosis is essential to rule out other conditions such as breast cancer or fat deposits. A healthcare provider may conduct:
- Physical examination
- Blood tests to assess hormone levels
- Imaging tests (mammograms, ultrasounds)
- Tissue biopsy in rare cases
Treatment Options for Gynecomastia
Treatment depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition.
Non-Surgical Treatments
- Medications: Tamoxifen and raloxifene are effective in reducing breast tissue in severe cases.
- Hormone Therapy: Balancing testosterone and estrogen levels may help reduce symptoms.
Surgical Treatments
In advanced cases or when medications fail, surgery may be required:
- Liposuction: Effective for removing excess fatty tissue.
- Mastectomy: A procedure to remove glandular breast tissue.
Prevention of Gynecomastia
Preventive measures can minimize the risk of gynecomastia:
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Avoiding anabolic steroids and recreational drugs
- Managing medical conditions that affect hormone levels
- Limiting alcohol consumption
- Consulting a healthcare provider before starting medications with gynecomastia risks
Complications of Gynecomastia
If untreated, gynecomastia may result in:
- Emotional distress or anxiety
- Persistent pain or tenderness
- Reduced self-confidence
FAQs:
1. Is gynecomastia reversible without surgery?
Yes, if diagnosed early, hormonal therapies and medications can often reverse gynecomastia without surgical intervention.
2. Can exercise alone reduce gynecomastia?
Exercise can help reduce overall body fat, but it may not eliminate glandular tissue causing gynecomastia.
3. How long does gynecomastia last?
In puberty, gynecomastia often resolves within 6 months to 2 years without treatment. In adults, persistent cases may require medical intervention.
4. Is gynecomastia linked to cancer?
While rare, persistent breast lumps should always be evaluated to rule out cancer.
5. Can gynecomastia recur after surgery?
If hormonal imbalances persist, gynecomastia can return even after surgical removal.
Gynecomastia is a manageable condition that responds well to appropriate treatment. Early diagnosis and medical intervention can help prevent complications and restore confidence. Consulting a healthcare professional is crucial for personalized treatment plans.