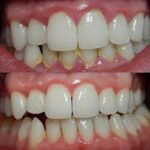
Gingivostomatitis is a common oral condition that causes inflammation of the gums and mouth. It is often seen in children but can affect adults as well. This condition results from viral or bacterial infections, and it may also develop due to poor oral hygiene, stress, or nutritional deficiencies.
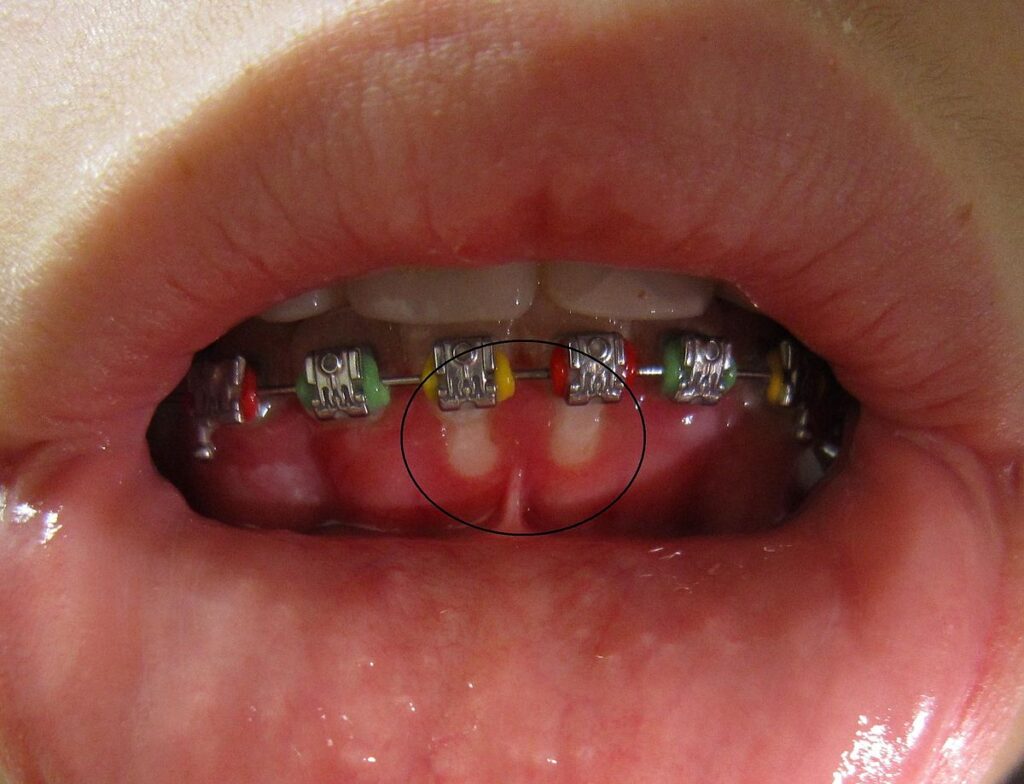
Causes of Gingivostomatitis
The primary causes of gingivostomatitis include:
- Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV-1): The most common viral cause, often resulting in cold sores.
- Coxsackievirus: A frequent cause in children, linked to hand, foot, and mouth disease.
- Bacterial Infections: Commonly caused by Streptococcus or other bacteria.
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Accumulation of plaque and bacteria can exacerbate the condition.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Lack of vitamins like B12, folate, or iron may contribute.
- Weakened Immune System: Conditions like HIV, cancer treatments, or other immune-compromising factors may increase susceptibility.
Symptoms of Gingivostomatitis
Key symptoms include:
- Red, swollen, and bleeding gums
- Painful ulcers or sores inside the mouth
- Bad breath (halitosis)
- Fever, fatigue, or swollen lymph nodes (in severe cases)
- Difficulty eating and drinking
- Excessive drooling (especially in children)
Diagnosis of Gingivostomatitis
Healthcare providers diagnose gingivostomatitis through:
- Visual Examination: Identifying lesions, swelling, and redness.
- Medical History: Evaluating past viral infections or immune conditions.
- Laboratory Tests: In severe cases, swabs or blood tests may confirm viral presence.
Treatment Options for Gingivostomatitis
Treatment aims to reduce discomfort, speed healing, and prevent complications. Key approaches include:
1. Home Care Remedies
- Maintain proper oral hygiene by brushing gently with a soft-bristle toothbrush.
- Rinse the mouth with warm saltwater to reduce inflammation.
- Drink plenty of fluids to stay hydrated.
- Consume soft, non-irritating foods to prevent discomfort.
2. Medications
- Antiviral Drugs: Acyclovir or Valacyclovir may be prescribed for HSV-1 cases.
- Pain Relievers: Ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help manage pain and fever.
- Antiseptic Mouthwashes: Chlorhexidine or similar rinses reduce bacterial growth.
- Topical Anesthetics: Gels containing benzocaine offer pain relief.
3. Professional Dental Care
- Dental cleanings may be required for severe plaque buildup.
- Antibiotics may be prescribed if bacterial infections are present.
Complications of Gingivostomatitis
If untreated, gingivostomatitis can lead to:
- Dehydration due to pain-induced reduced food and fluid intake
- Secondary bacterial infections
- Spreading of HSV-1 to other parts of the body
Preventing Gingivostomatitis
Preventive strategies include:
- Practicing good oral hygiene with regular brushing and flossing
- Avoiding sharing utensils, toothbrushes, or cups to prevent viral spread
- Ensuring a balanced diet rich in essential vitamins and minerals
- Regular dental check-ups to identify issues early
When to See a Doctor
Seek medical advice if:
- Symptoms persist beyond two weeks
- Sores worsen or become excessively painful
- You experience high fever or swollen lymph nodes
Gingivostomatitis can be effectively managed with proper treatment and preventive measures. Early diagnosis and attentive care are key to minimizing discomfort and ensuring a swift recovery.