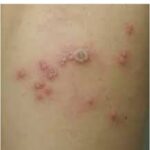
Genital herpes simplex is a common sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV). There are two types:
- HSV-1: Primarily causes oral herpes but can spread to the genitals through oral sex.
- HSV-2: Primarily responsible for genital herpes.
Genital herpes is highly contagious and remains in the body for life, with periodic outbreaks. Understanding its symptoms, treatments, and prevention is crucial for managing the condition.
Causes & Transmission of Genital Herpes
Genital herpes is transmitted through direct skin-to-skin contact with an infected person. Common transmission modes include:
- Sexual contact (vaginal, anal, or oral sex with an infected partner)
- Skin contact during an outbreak or viral shedding
- Mother-to-child transmission during childbirth (neonatal herpes)
HSV can be spread even if no symptoms are present, making prevention and awareness critical.
Symptoms of Genital Herpes
Symptoms can vary from mild to severe, and some individuals remain asymptomatic. Common signs include:
Primary Infection Symptoms
- Painful blisters or ulcers in the genital or anal area
- Burning or itching sensation
- Flu-like symptoms (fever, swollen lymph nodes, muscle aches)
- Painful urination
Recurrent Outbreak Symptoms
- Milder symptoms than the first outbreak
- Tingling or burning sensation before blisters appear
- Lesions that heal within 1-2 weeks
Asymptomatic Shedding
Even without visible sores, HSV can still be transmitted, making it essential to use protection and get tested regularly.
Diagnosis of Genital Herpes
A proper diagnosis includes:
- Physical Examination: Identification of sores or lesions
- PCR Testing: Detects viral DNA with high accuracy
- Viral Culture: Confirms active infection from a sore sample
- Blood Tests: Detects HSV antibodies but may not differentiate between recent and past infections
Treatment Options for Genital Herpes
While there is no cure, antiviral medications can help manage symptoms and reduce transmission.
Antiviral Medications
- Acyclovir (Zovirax)
- Valacyclovir (Valtrex)
- Famciclovir (Famvir)
These medications help:
- Shorten the duration of outbreaks
- Reduce severity of symptoms
- Lower transmission risk
Suppressive Therapy
For individuals with frequent outbreaks, daily antiviral therapy can reduce flare-ups and transmission.
Pain Management & Home Remedies
- Topical lidocaine for pain relief
- Warm baths to soothe irritation
- Loose clothing to reduce friction and discomfort
Complications of Genital Herpes
1. Increased Risk of Other STIs
Open sores make individuals more susceptible to HIV and other infections.
2. Neonatal Herpes
Pregnant individuals with active HSV infections may transmit the virus to their baby, leading to severe complications.
3. Psychological Impact
Genital herpes can cause anxiety, depression, and stigma-related stress, making emotional support crucial.
Prevention Strategies
1. Safe Sex Practices
- Use condoms and dental dams consistently
- Avoid sexual contact during outbreaks
2. Antiviral Therapy
Suppressive therapy reduces viral shedding and transmission risk.
3. Partner Communication
- Discuss STI status with partners
- Encourage mutual STI testing
4. Regular Testing
Frequent testing helps identify and manage the virus effectively.
The virus remains dormant in nerve cells and reactivates due to stress, illness, or hormonal changes.
Genital herpes simplex is a common but manageable STI. While no cure exists, antiviral treatments, safe sex practices, and regular screenings help reduce symptoms and transmission risk. By staying informed and proactive, individuals can lead a healthy and fulfilling life despite an HSV diagnosis.