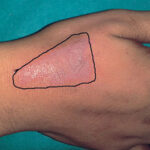
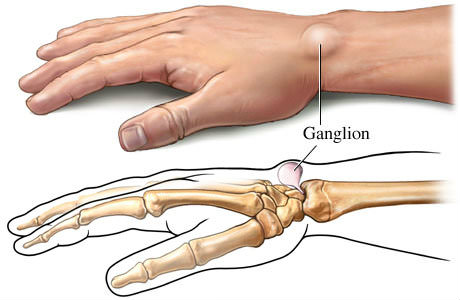
A ganglion cyst is a noncancerous lump that often develops along the tendons or joints of the wrists, hands, feet, or ankles. These fluid-filled sacs can vary in size and may cause discomfort or restrict movement if they press on a nerve. While generally harmless, ganglion cysts can sometimes require medical intervention.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of ganglion cysts remains unclear, but several factors may contribute:
- Joint or Tendon Irritation: Repetitive stress on joints may lead to fluid accumulation.
- Injury or Trauma: Past injuries may cause fluid buildup, leading to cyst formation.
- Age and Gender: Most common in individuals between 20 and 40 years old, especially women.
- Osteoarthritis: Those with arthritis in the finger joints may be at higher risk.
Common Symptoms
Ganglion cysts typically exhibit the following signs:
- Visible Lump: A round or oval-shaped lump near a joint.
- Pain or Discomfort: Can range from mild to severe, especially when pressed.
- Numbness or Tingling: If the cyst presses on a nerve.
- Limited Mobility: Larger cysts may hinder joint movement.
Diagnosis
A healthcare provider may use the following methods to diagnose a ganglion cyst:
- Physical Examination: Pressing the cyst to check for tenderness or mobility.
- Transillumination Test: Shining a light through the lump to determine fluid content.
- Imaging Tests:
- X-rays: To rule out bone-related issues.
- Ultrasound: Helps differentiate between cysts and solid tumors.
- MRI Scan: Provides detailed images, especially if the cyst is small or deep-seated.
Treatment Options
Treatment varies based on symptoms and cyst size:
1. Non-Surgical Treatments
- Observation: If painless and non-restrictive, no treatment is necessary.
- Immobilization: Using a brace or splint to reduce movement and cyst growth.
- Aspiration: A doctor may drain the fluid with a needle, though recurrence is common.
2. Surgical Removal
For persistent or painful cysts, surgery may be required:
- Open Surgery: The surgeon removes the cyst and part of the joint capsule or tendon sheath.
- Arthroscopic Surgery: A minimally invasive procedure with smaller incisions and faster recovery.
Home Remedies for Relief
While home treatments cannot eliminate a cyst, they may help manage symptoms:
- Warm Compress: Reduces discomfort but does not shrink the cyst.
- Avoiding Repetitive Strain: Reducing stress on the affected joint.
- Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers: NSAIDs like ibuprofen can ease pain.
Prevention Tips
Although ganglion cysts cannot always be prevented, the following steps may reduce risk:
- Avoid repetitive joint strain.
- Use protective gear if engaging in activities that stress the wrists or hands.
- Maintain joint health through stretching and strengthening exercises.
When to See a Doctor
Consult a healthcare provider if you experience:
- Persistent pain or discomfort.
- Difficulty moving the affected joint.
- Rapid cyst growth or signs of infection (redness, warmth, or drainage).
Ganglion cysts are typically harmless but can cause discomfort or limit movement. While some resolve independently, others may require medical treatment. Consulting a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and management is essential for effective relief.