Americium, a synthetic element discovered in the mid-20th century, has found applications in various industries, notably in smoke detectors due to its radioactive properties. However, exposure to americium radiation poses significant health risks, necessitating a comprehensive understanding of its effects and the implementation of stringent safety protocols.
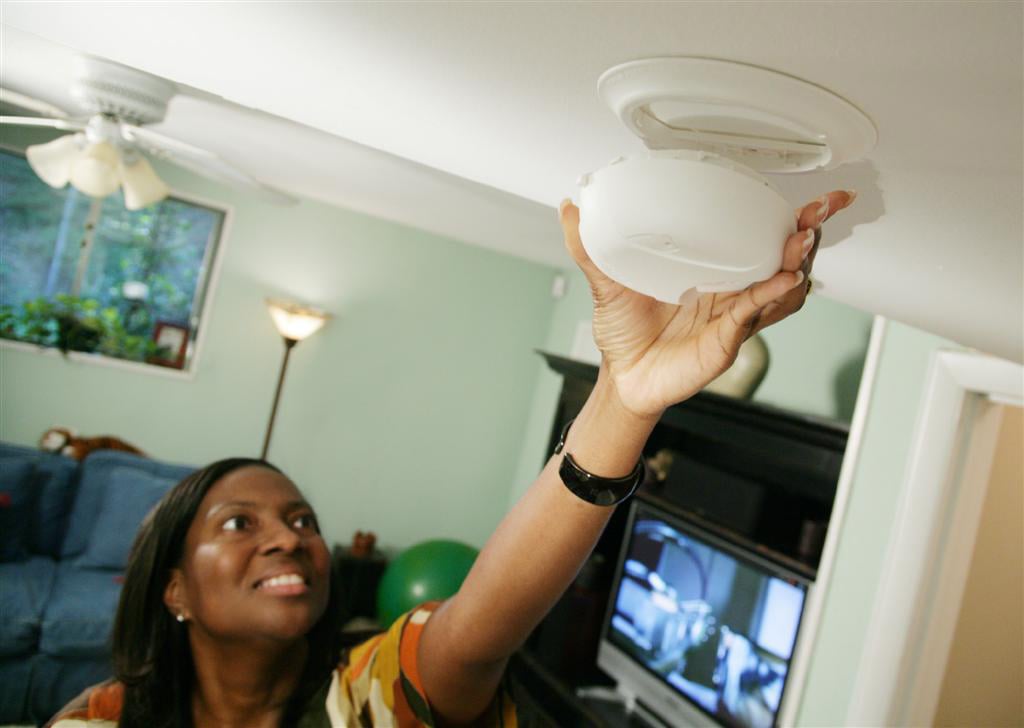

Understanding Americium and Its Isotopes
Americium is a member of the actinide series and exhibits high radioactivity. The most prevalent isotope, americium-241 (^241Am), is widely used in commercial devices. Despite its utility, ^241Am emits alpha particles, which, while easily shielded by materials like paper, can cause severe biological damage if ingested or inhaled.
Health Risks Associated with Americium Exposure
Internal Contamination
Upon entering the human body, americium tends to accumulate in specific organs:
- Liver and Bones: Approximately 45% of absorbed americium deposits in the liver and another 45% in the bones. The biological half-life of ^241Am is about 50 years in bones and 20 years in the liver, leading to prolonged radiation exposure and an elevated risk of cancer in these organs. en.wikipedia.org
- Gonads: Americium can also localize in reproductive organs, where it remains indefinitely, potentially causing genetic mutations and reproductive health issues. en.wikipedia.org
Acute Radiation Syndrome (ARS)
Exposure to high levels of americium radiation can result in Acute Radiation Syndrome, characterized by symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, fatigue, and, in severe cases, neurological impairments. The severity of ARS depends on the radiation dose received.
Environmental Impact of Americium
Improper disposal of americium-containing devices, like smoke detectors, can lead to environmental contamination. Once released, americium persists in soil and water, entering the food chain through plants and animals, thus posing indirect exposure risks to humans.
Safety Measures and Handling Guidelines
To mitigate the risks associated with americium radiation exposure, the following safety measures are recommended:
- Controlled Environments: Handle americium and its compounds exclusively in specialized laboratories equipped with appropriate safety protocols to prevent accidental exposure. en.wikipedia.org
- Protective Equipment: Utilize personal protective equipment (PPE), including gloves, lab coats, and respiratory protection, to minimize direct contact and inhalation risks.
- Proper Disposal: Adhere to regulatory guidelines for the disposal of americium-containing devices to prevent environmental contamination. For instance, in the UK, it is permissible to dispose of a smoke detector containing americium by placing it in the dustbin with normal household rubbish, but each dustbin worth of rubbish is limited to only containing one smoke detector. en.wikipedia.org
- Emergency Protocols: Establish and practice emergency response procedures to address potential americium spills or accidental exposures effectively.
While americium, particularly ^241Am, plays a valuable role in various applications, it is imperative to recognize and respect the health risks associated with its radiation. Implementing stringent safety measures and handling protocols is essential to protect individuals and the environment from the adverse effects of americium exposure.