Chronic Venous Insufficiency (CVI) is a prevalent vascular disorder where the veins in the lower extremities fail to efficiently return blood to the heart. This inefficiency often leads to the accumulation of fluid in the tissues, a condition known as edema. Understanding the intricate relationship between CVI and edema is crucial for effective management and treatment.
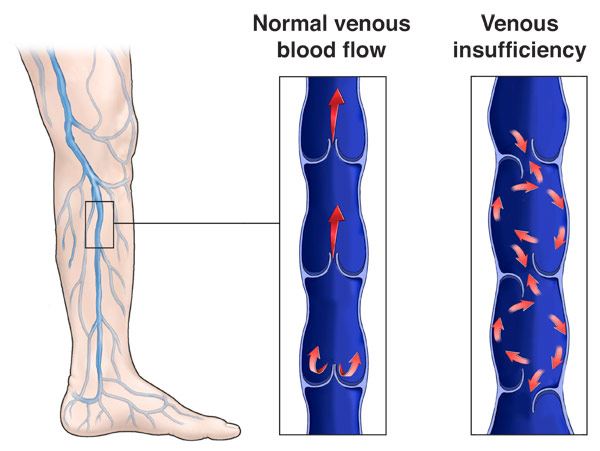
Pathophysiology of Edema in Chronic Venous Insufficiency
In a healthy venous system, unidirectional valves facilitate the upward flow of blood from the legs to the heart. In CVI, these valves are compromised, leading to venous reflux and increased venous pressure. This elevated pressure causes fluid to leak from the capillaries into the interstitial spaces, resulting in edema. The persistent fluid accumulation not only leads to swelling but also initiates inflammatory processes that can cause skin changes and ulcerations.
Clinical Manifestations
Edema associated with CVI typically presents with:
- Swelling: Predominantly in the lower legs and ankles, worsening with prolonged standing.
- Skin Changes: Discoloration, often a reddish-brown hue, indicative of hemosiderin deposition.
- Discomfort: Sensations of heaviness, aching, or cramping in the legs.
- Dermatitis: Itching and flaking of the skin, sometimes progressing to stasis dermatitis.
- Ulceration: In advanced cases, non-healing sores, especially near the ankles.
Diagnostic Approach
Accurate diagnosis involves:
- Clinical Examination: Assessing visible signs such as varicose veins, skin discoloration, and edema.
- Duplex Ultrasound: Evaluating blood flow, venous reflux, and ruling out deep vein thrombosis.
- Venography: In select cases, to visualize vein anatomy and function.
Management Strategies
Effective management of edema in CVI encompasses:
- Compression Therapy: Utilizing graduated compression stockings to enhance venous return and reduce swelling.
- Pharmacological Interventions: Venoactive medications may be prescribed to improve venous tone and decrease edema.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Encouraging regular exercise, leg elevation, and weight management to alleviate symptoms.
- Surgical Options: In severe cases, procedures such as vein ablation or stripping may be considered to rectify venous insufficiency.
Preventive Measures
Preventing the progression of CVI and associated edema includes:
- Regular Physical Activity: Promotes efficient blood flow and strengthens calf muscles.
- Avoiding Prolonged Immobility: Regular movement prevents blood pooling in the lower extremities.
- Weight Management: Reduces pressure on the veins.
- Skin Care: Maintaining skin integrity to prevent infections and ulcerations.