Ecthyma is a bacterial skin infection characterized by ulcerative lesions that penetrate deep into the dermis. Often considered a deeper form of impetigo, ecthyma presents as crusted sores beneath which ulcers form, leading to potential scarring if not properly treated.
Etiology: Causes of Ecthyma
The primary causative agents of ecthyma are:
- Streptococcus pyogenes: A group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus known for causing various skin and systemic infections.
- Staphylococcus aureus: A common bacterium that can lead to skin infections, including ecthyma, especially when the skin’s integrity is compromised.
These bacteria can enter the skin through minor traumas such as insect bites, scratches, or pre-existing skin conditions, leading to infection.
Epidemiology: Who Is at Risk?
Ecthyma can affect individuals of all ages and backgrounds; however, certain factors increase susceptibility:
- Age: More frequent in children and the elderly.
- Immunocompromised States: Conditions like diabetes, neutropenia, HIV, or those undergoing immunosuppressive treatments.
- Environmental Factors: Hot and humid climates, poor hygiene, and crowded living conditions.
- Pre-existing Skin Conditions: Dermatitis, insect bites, or untreated impetigo can predispose individuals to ecthyma.
Clinical Manifestations: Signs and Symptoms
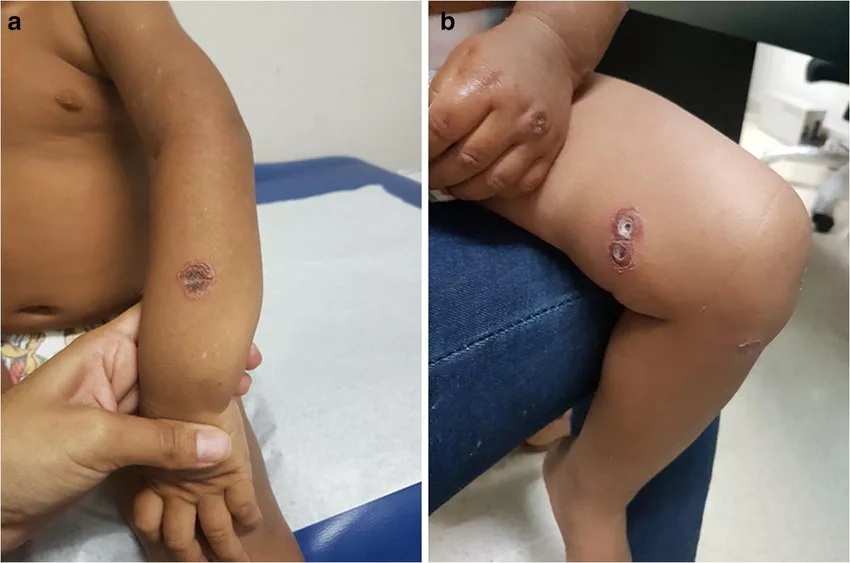
Ecthyma typically presents with the following features:
- Initial Lesion: Begins as a vesicle or pustule on inflamed skin.
- Ulcer Formation: The lesion progresses to a hardened crust covering a deep, indurated ulcer that may be red, swollen, and exudative.
- Size: Lesions can enlarge up to 0.5–3 cm in diameter.
- Location: Commonly affects the lower extremities, such as buttocks, thighs, legs, ankles, and feet.
- Healing: Lesions heal slowly and often leave scars.
- Lymphadenopathy: Regional lymph nodes may become swollen and tender.
Complications Associated with Ecthyma
If left untreated, ecthyma can lead to several complications:
- Secondary Infections: Including cellulitis, erysipelas, lymphangitis, gangrene, and bacteremia.
- Scarring: Permanent skin damage and scarring are common due to deep dermal involvement.
- Post-streptococcal Glomerulonephritis: A rare but serious kidney complication following streptococcal skin infections.
Diagnostic Approach
Diagnosis of ecthyma primarily involves:
- Clinical Examination: Identification of characteristic lesions by a healthcare professional.
- Laboratory Tests:
- Bacterial Cultures: Swabbing the lesion to identify the causative organism.
- Blood Tests: To assess for underlying conditions like diabetes or immunodeficiencies.
Treatment Strategies
Management of ecthyma includes both non-pharmacological and pharmacological approaches:
Non-Pharmacological Interventions
- Hygiene Measures: Regular washing of affected areas with antiseptic solutions and maintaining overall cleanliness.
- Debridement: Gentle removal of crusts to facilitate healing and allow topical treatments to penetrate effectively.
Pharmacological Treatments
- Topical Antibiotics: For localized infections, mupirocin or fusidic acid ointments applied several times daily are effective.
- Oral Antibiotics: Extensive or unresponsive cases may require systemic antibiotics such as dicloxacillin or cephalexin. In penicillin-allergic individuals, alternatives like clindamycin may be used.
- Duration: Treatment typically continues for 7–14 days, depending on the severity and response.
Prevention Measures
Preventing ecthyma involves addressing risk factors and maintaining skin integrity:
- Skin Care: Prompt cleaning and treatment of minor skin injuries.
- Hygiene: Regular bathing and changing of clothing and bed linens.
- Environmental Controls: Using insect repellents in areas prone to insect bites.
- Managing Underlying Conditions: Effective control of chronic diseases like diabetes to reduce susceptibility.