Dermatoses of the scalp encompass a variety of skin conditions affecting the scalp, leading to symptoms such as itching, inflammation, scaling, and hair loss. Recognizing and understanding these conditions is crucial for effective management and treatment.
Common Types of Scalp Dermatoses
Seborrheic Dermatitis
Seborrheic dermatitis is a chronic inflammatory skin disorder characterized by flaky, scaly, greasy, and occasionally itchy and inflamed skin. It commonly affects areas rich in oil-producing glands, including the scalp, face, and chest. In infants, it is known as cradle cap. The exact cause is unclear, but factors such as Malassezia yeast, genetic predisposition, and environmental influences are believed to play roles. Treatment typically involves antifungal agents and anti-inflammatory medications.
Erosive Pustular Dermatosis of the Scalp (EPDS)
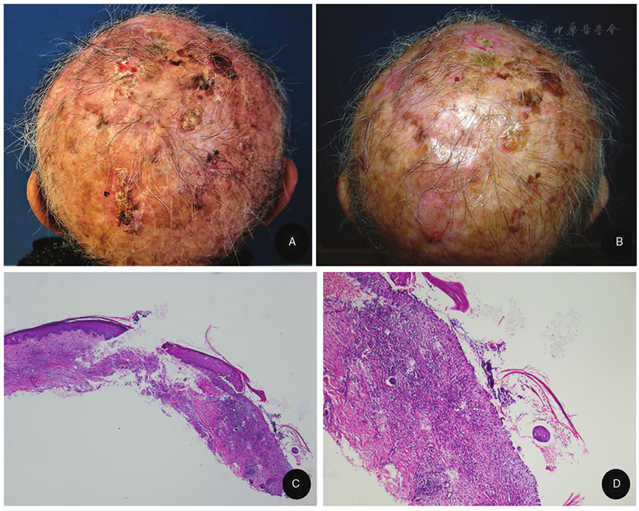
EPDS is a rare inflammatory condition predominantly affecting elderly individuals with sun-damaged, bald scalps. It presents with pustules, erosions, and crusts, which can lead to scarring alopecia if untreated. The exact cause is unknown, but factors such as skin trauma, infections, and surgical procedures have been implicated. Treatment often includes high-potency topical corticosteroids and calcineurin inhibitors.
Psoriasis
Psoriasis is an autoimmune condition that manifests as red, scaly patches on the skin, including the scalp. It is characterized by an accelerated skin cell turnover, leading to thickened, inflamed areas covered with silvery scales. Management includes topical treatments, phototherapy, and systemic medications for more severe cases.
Lichen Planus
Lichen planus is an inflammatory condition that can affect the skin, mucous membranes, nails, and hair. On the scalp, it may lead to lichen planopilaris, causing scarring hair loss. The exact cause is unknown, but it is believed to involve an immune-mediated mechanism. Treatment options include corticosteroids and immunosuppressive agents.
Folliculitis
Folliculitis refers to the inflammation of hair follicles, often due to bacterial or fungal infections. On the scalp, it presents as small, itchy pustules. Management includes antibacterial or antifungal shampoos and, in more severe cases, oral antibiotics or antifungals.
Causes and Risk Factors
The etiology of scalp dermatoses varies with each condition but may include:
- Genetic Predisposition: Family history can increase susceptibility.
- Immune System Dysregulation: Autoimmune responses play a role in conditions like psoriasis and lichen planus.
- Microbial Factors: Overgrowth of fungi such as Malassezia is implicated in seborrheic dermatitis.
- Environmental Factors: Sun exposure and skin trauma are linked to conditions like EPDS.
- Stress and Hormonal Changes: These can exacerbate or trigger certain scalp conditions.
Symptoms
While symptoms vary depending on the specific dermatosis, common manifestations include:
- Itching: A frequent symptom across many scalp conditions.
- Scaling and Flaking: Notable in conditions like seborrheic dermatitis and psoriasis.
- Redness and Inflammation: Indicative of underlying inflammation.
- Pustules or Crusts: Seen in conditions like EPDS and folliculitis.
- Hair Loss: Both temporary and permanent hair loss can occur, especially in scarring conditions.
Diagnosis of dermatosis of the scalp
Accurate diagnosis involves:
- Clinical Examination: Visual assessment of the scalp and lesions.
- Dermatoscopy: A tool to examine skin lesions in detail.
- Biopsy: Histopathological examination to confirm the diagnosis.
- Microbial Cultures: To identify infectious agents when infection is suspected.
Treatment Options
Treatment strategies are tailored to the specific condition and may include:
- Topical Therapies: Corticosteroids, antifungals, or calcineurin inhibitors to reduce inflammation and control microbial growth.
- Systemic Medications: For severe cases, oral medications such as immunosuppressants or retinoids may be prescribed.
- Phototherapy: Exposure to specific wavelengths of light can be beneficial, particularly in psoriasis.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Stress management, dietary changes, and proper scalp hygiene can aid in managing symptoms.
Prevention and Management
Preventive measures and management strategies include:
- Regular Scalp Care: Gentle cleansing to prevent buildup of oils and scales.
- Sun Protection: Wearing hats or using sunscreen to protect the scalp from UV damage.
- Avoiding Trauma: Being cautious with hair care practices to prevent scalp injury.
- Stress Management: Techniques such as meditation or exercise to reduce stress-related flare-ups.