Acute Staphylococcus aureus otitis externa is a bacterial infection of the outer ear canal caused by the pathogen Staphylococcus aureus. This condition, commonly referred to as “swimmer’s ear,” can cause significant discomfort and requires prompt medical attention. In this article, we delve into the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention strategies for this condition, providing a detailed resource for patients and healthcare providers alike.
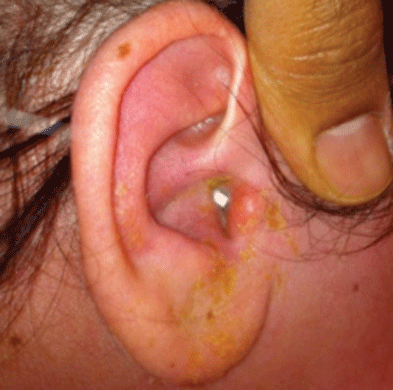
What is Acute Staphylococcus Aureus Otitis Externa?
Acute otitis externa is an inflammation or infection of the external ear canal, often triggered by bacterial or fungal pathogens. When Staphylococcus aureus is the causative agent, the condition is specifically termed Staphylococcus aureus otitis externa. This bacterium is a common culprit in skin and soft tissue infections, and its presence in the ear canal can lead to painful symptoms and complications if left untreated.
Causes and Risk Factors
Staphylococcus aureus otitis externa typically occurs when the natural defenses of the ear canal are compromised. Common causes and risk factors include:
- Excessive moisture: Prolonged exposure to water, such as swimming or humid environments, can create a breeding ground for bacteria.
- Trauma to the ear canal: Scratching or inserting objects like cotton swabs can damage the skin, allowing bacteria to invade.
- Skin conditions: Eczema or psoriasis can weaken the skin barrier, increasing susceptibility to infection.
- Narrow ear canals: Anatomical variations can trap moisture and debris, promoting bacterial growth.
- Weakened immune system: Individuals with compromised immunity are at higher risk of infections.
Symptoms of Acute Staphylococcus Aureus Otitis Externa
The symptoms of this condition can range from mild to severe and often develop rapidly. Key symptoms include:
- Ear pain: Often intense and exacerbated by touching or pulling the ear.
- Itching: A persistent itch in the ear canal.
- Discharge: Yellow or white pus may drain from the ear.
- Swelling: The ear canal may become swollen and red.
- Hearing loss: Temporary hearing impairment due to blockage of the ear canal.
- Fever: In severe cases, systemic symptoms like fever may occur.
Diagnosis and Differential Diagnosis
Accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment. Healthcare providers typically perform the following:
- Clinical examination: Visual inspection of the ear canal using an otoscope.
- Microbial testing: Swabs may be taken to identify the causative organism, particularly Staphylococcus aureus.
- Differential diagnosis: Conditions like fungal otitis externa, middle ear infections, or dermatitis must be ruled out.
Treatment Options for Acute Staphylococcus Aureus Otitis Externa
Treatment focuses on eradicating the infection, relieving symptoms, and preventing complications. Common approaches include:
1. Topical Antibiotics
- Ear drops: Antibiotic ear drops containing neomycin, polymyxin, or fluoroquinolones are often prescribed.
- Corticosteroids: These may be added to reduce inflammation and swelling.
2. Oral Antibiotics
- For severe infections or cases where topical treatment is insufficient, oral antibiotics like cephalexin or amoxicillin-clavulanate may be recommended.
3. Pain Management
- Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help manage discomfort.
4. Ear Cleaning
- Gentle cleaning of the ear canal by a healthcare provider to remove debris and discharge.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing acute Staphylococcus aureus otitis externa involves minimizing risk factors and maintaining ear hygiene:
- Dry ears thoroughly: After swimming or showering, use a towel or hairdryer on a low setting to dry the ears.
- Avoid inserting objects: Refrain from using cotton swabs or other objects in the ear canal.
- Use earplugs: When swimming, use waterproof earplugs to prevent water entry.
- Treat skin conditions: Manage eczema or psoriasis to reduce the risk of infection.
Complications of Untreated Otitis Externa
If left untreated, acute Staphylococcus aureus otitis externa can lead to serious complications, including:
- Chronic otitis externa: Persistent or recurrent infections.
- Cellulitis: Spread of infection to surrounding skin and tissues.
- Malignant otitis externa: A rare but severe infection that can spread to the bones of the skull.
Acute Staphylococcus aureus otitis externa is a painful but treatable condition. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are essential to prevent complications and ensure a swift recovery. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and preventive measures, individuals can reduce their risk of developing this infection. For persistent or severe symptoms, consulting a healthcare provider is crucial to receive tailored treatment and care.