Condylomata acuminata, commonly known as genital warts, represent a prevalent sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by specific strains of the human papillomavirus (HPV). These lesions manifest as skin-colored, fleshy growths in the anogenital region, affecting both males and females. Understanding the etiology, clinical presentation, diagnostic procedures, treatment modalities, and preventive measures is crucial for effective management and control of this condition.
Etiology and Pathogenesis
HPV, a double-stranded DNA virus, is the etiological agent responsible for condylomata acuminata. Among the over 100 identified HPV types, approximately 40 infect the anogenital area. Notably, HPV types 6 and 11 are implicated in approximately 90% of genital wart cases. Transmission occurs primarily through sexual contact, including vaginal, anal, and oral intercourse. Factors such as age, sexual behavior, and immune status influence susceptibility to infection.
Clinical Presentation
Patients with condylomata acuminata typically present with the following features:
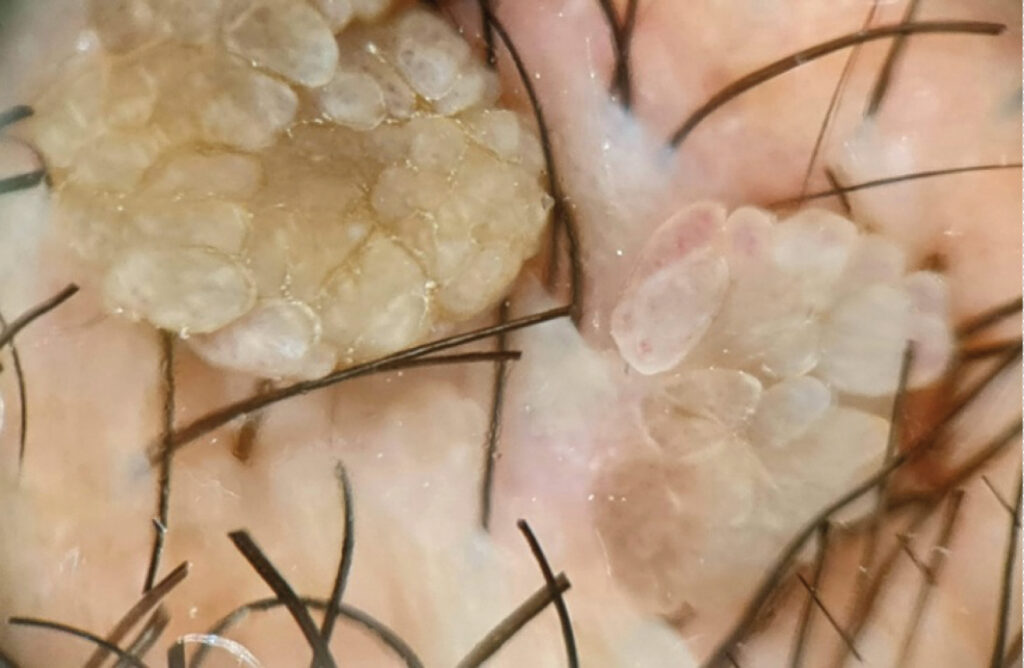
- Lesion Appearance: Soft, flesh-colored or grayish papules that may be flat, dome-shaped, or cauliflower-like in appearance.
- Distribution: Lesions commonly occur in the genital and perianal regions but can also appear on the cervix, urethra, and, less frequently, the oral cavity.
- Symptoms: While often asymptomatic, some individuals may experience itching, discomfort, or bleeding, especially if the lesions are traumatized.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of condylomata acuminata is primarily clinical, based on the characteristic appearance of the lesions. Additional diagnostic approaches include:
- Acetic Acid Application: Applying a 3-5% acetic acid solution to the suspected area may turn the lesions white, aiding visualization.
- Biopsy: Indicated when the diagnosis is uncertain, lesions are atypical, or there is a lack of response to standard treatments. Histopathological examination can confirm the diagnosis and rule out malignancy.
Treatment Options
Management of condylomata acuminata aims to remove visible lesions, alleviate symptoms, and reduce transmission risk. Treatment modalities are categorized into patient-applied and provider-administered therapies:
Patient-Applied Treatments
- Imiquimod Cream: An immune response modifier applied topically to enhance local immune activity against HPV.
- Podophyllotoxin Solution or Gel: An antimitotic agent that induces necrosis of warty tissue.
Provider-Administered Treatments
- Cryotherapy: Application of liquid nitrogen to freeze and destroy lesions.
- Trichloroacetic Acid (TCA): A chemical cauterant applied directly to warts.
- Surgical Options: Including excision, electrosurgery, or laser therapy, particularly for extensive or refractory lesions.
The choice of treatment depends on factors such as lesion size, number, anatomical location, patient preference, and provider expertise. It is important to note that while treatments can remove visible warts, they may not eradicate the underlying HPV infection, and recurrences are possible.
Prevention Strategies
Preventive measures are essential in reducing the incidence and transmission of condylomata acuminata:
- HPV Vaccination: Prophylactic vaccines targeting HPV types 6, 11, 16, and 18 have demonstrated efficacy in preventing genital warts and HPV-related cancers. Vaccination is recommended for both males and females, ideally before the onset of sexual activity.
- Safe Sexual Practices: Consistent and correct use of condoms can reduce, but not eliminate, the risk of HPV transmission. Limiting the number of sexual partners and engaging in mutually monogamous relationships further decreases risk.
- Regular Screening: Routine cervical cancer screening for women can detect precancerous changes associated with high-risk HPV types, facilitating early intervention.