Acute Lymphoid Leukemia (ALL) is an aggressive hematologic malignancy characterized by the rapid proliferation of immature lymphocytes in the bone marrow and blood. As a leading cause of cancer-related mortality in children, ALL demands urgent medical attention and tailored therapeutic interventions. This article provides a detailed exploration of ALL, including its pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, diagnostic protocols, and cutting-edge treatments.
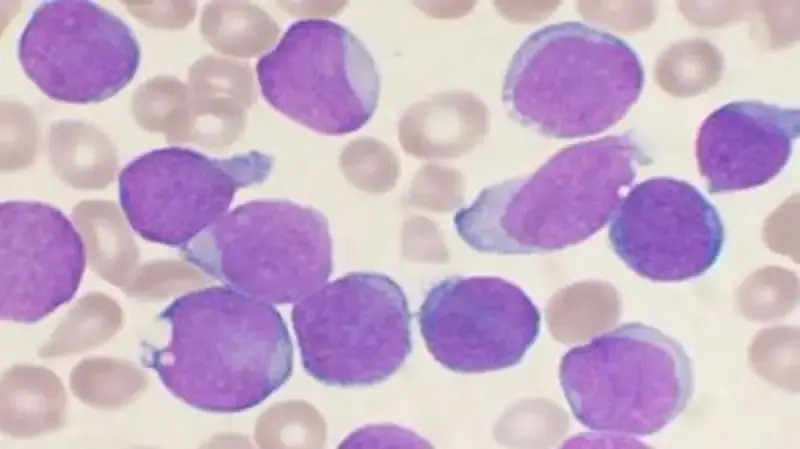
What Is Acute Lymphoid Leukemia?
Acute Lymphoid Leukemia arises from genetic mutations in lymphoid progenitor cells, leading to unchecked cellular division and impaired maturation. These malignant cells overcrowd the bone marrow, suppressing healthy hematopoiesis and resulting in cytopenias. While 80% of cases occur in children under 5 years, adults account for 20% of diagnoses, often with poorer prognoses due to complex cytogenetic abnormalities.
Key Symptoms and Early Warning Signs of ALL
Early detection of ALL significantly improves outcomes. Common symptoms include:
- Persistent fatigue due to anemia.
- Fever and infections from neutropenia.
- Easy bruising or bleeding caused by thrombocytopenia.
- Bone pain from marrow expansion.
- Lymphadenopathy and hepatosplenomegaly.
Uncommon presentations like central nervous system involvement (headaches, seizures) warrant immediate evaluation.
Diagnostic Criteria for Acute Lymphoid Leukemia
A definitive ALL diagnosis requires a multi-modal approach:
1. Blood Tests and Peripheral Smear Analysis
Complete blood counts (CBC) often reveal anemia, thrombocytopenia, and elevated white blood cells with lymphoblasts. Flow cytometry identifies cell surface markers (e.g., CD19, CD10) to confirm lymphoid lineage.
2. Bone Marrow Aspiration and Biopsy
Marrow samples with ≥20% lymphoblasts confirm ALL. Cytogenetic testing (e.g., FISH, PCR) detects chromosomal abnormalities like the Philadelphia chromosome (BCR-ABL1 fusion), critical for risk stratification.
3. Imaging and Lumbar Puncture
CT/MRI scans assess organomegaly or extramedullary disease. Cerebrospinal fluid analysis checks for CNS infiltration.
Treatment Protocols for Acute Lymphoid Leukemia
Modern ALL therapy is risk-adapted and phase-based:
Induction Therapy
Aims to achieve remission using vincristine, corticosteroids, and anthracyclines. Pediatric remission rates exceed 95%, while adults reach 70-90%.
Consolidation/Intensification
High-dose methotrexate or cytarabine eliminates residual disease. Philadelphia chromosome-positive ALL requires tyrosine kinase inhibitors (e.g., imatinib).
Maintenance Therapy
Low-dose chemotherapy (6-mercaptopurine, methotrexate) continues for 2-3 years to prevent relapse.
Advanced Therapies
- Immunotherapy: Blinatumomab (BiTE) and CAR-T cell therapies (e.g., Kymriah) target CD19.
- Stem Cell Transplantation: Reserved for high-risk or relapsed cases.
Prognostic Factors and Survival Rates
Age, cytogenetics, and minimal residual disease (MRD) status dictate outcomes:
- Children: 5-year survival exceeds 90% for standard-risk ALL.
- Adults: 5-year survival ranges from 30-50%.
- MRD-Negativity post-Induction: Correlates with prolonged remission.
Innovations in ALL Research and Future Directions
Emerging therapies aim to reduce toxicity and overcome resistance:
- CRISPR-Based Gene Editing: Corrects mutations in malignant clones.
- Dual-Antigen CAR-T Cells: Target CD19/CD22 to mitigate antigen escape.
- Vaccine Therapy: Stimulates immune responses against leukemia-specific antigens.
Acute Lymphoid Leukemia remains a complex but increasingly treatable malignancy. Advances in precision medicine, immunotherapy, and supportive care continue to transform prognoses. Early diagnosis, risk-adapted therapy, and clinical trial participation are pivotal to improving survival across all age groups.