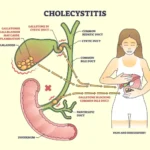
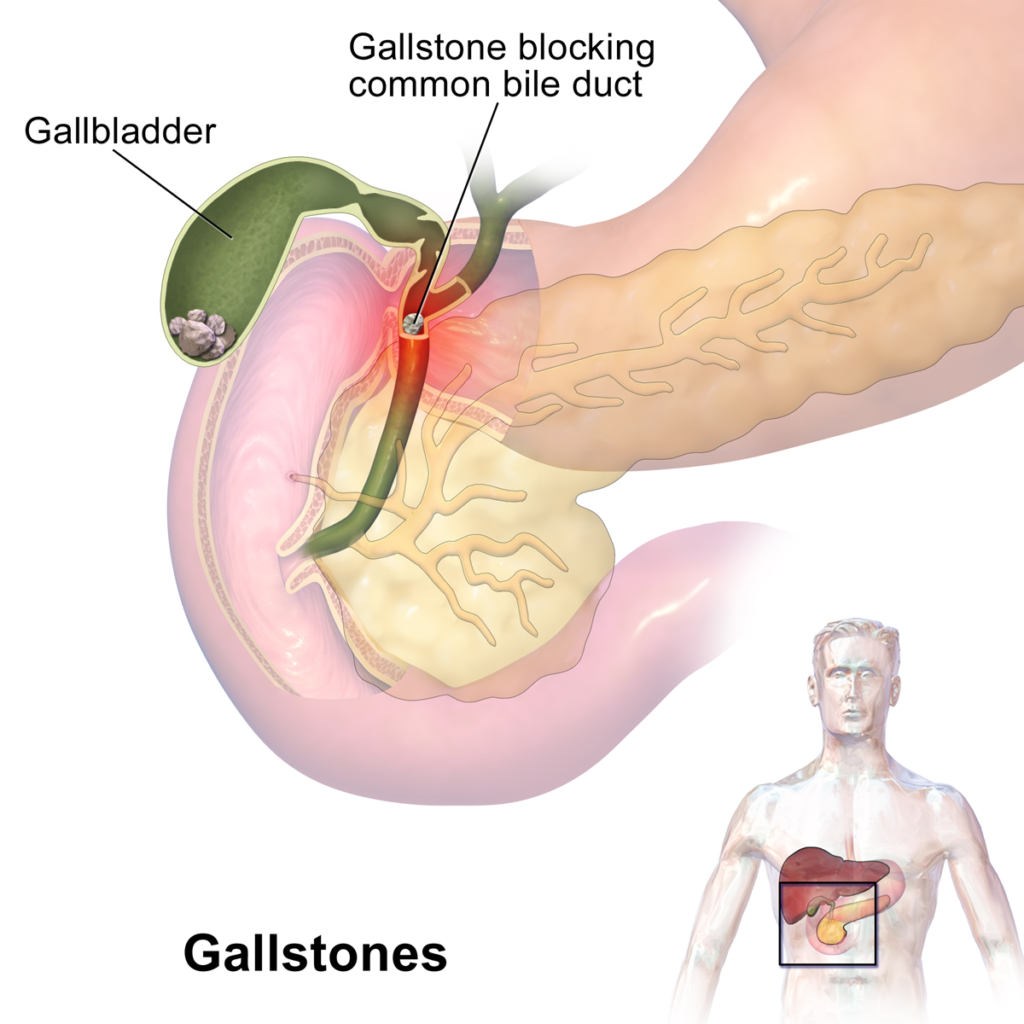
Cholelithiasis, commonly known as gallstones, refers to the formation of solid particles in the gallbladder. These stones can lead to various complications, including inflammation, infection, and blockages in the bile ducts. While treatment options are available, prevention remains the most effective strategy to avoid the discomfort and potential risks associated with gallstones.
Risk Factors for Cholelithiasis
Preventing cholelithiasis begins with understanding its risk factors, which include:
- Obesity: Excess weight can lead to increased cholesterol levels in bile, a significant contributor to gallstone formation.
- Age and Gender: Women and individuals over 40 years old are at higher risk.
- Dietary Habits: High-fat, low-fiber diets promote gallstone development.
- Rapid Weight Loss: Crash diets or bariatric surgery can disrupt bile composition.
- Family History: Genetics play a role in susceptibility.
Dietary Recommendations for Prevention
A balanced diet is crucial for maintaining gallbladder health. Follow these guidelines:
1. Increase Fiber Intake
Consume plenty of whole grains, fruits, and vegetables. Fiber improves digestion and helps regulate bile production, reducing the risk of gallstone formation.
2. Limit Saturated Fats
Avoid foods high in saturated fats, such as fried items, processed snacks, and fatty meats. Opt for healthy fats like those found in avocados, nuts, seeds, and fish.
3. Maintain Moderate Caloric Intake
Prevent obesity by eating nutrient-dense foods and avoiding overeating. Balanced meals can help maintain a healthy weight.
4. Hydrate Adequately
Drink sufficient water daily to ensure optimal bile flow and digestion.
Lifestyle Changes for Gallstone Prevention
In addition to dietary adjustments, adopt these habits:
1. Regular Physical Activity
Engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic exercise weekly. Physical activity reduces obesity and improves overall digestion.
2. Gradual Weight Loss
If weight loss is necessary, aim for a gradual reduction of 1-2 pounds per week to avoid disrupting bile composition.
3. Avoid Smoking and Alcohol Excess
Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can negatively affect overall digestive health, including the gallbladder.
Medical Insights and Supplements
Certain medical strategies and supplements may aid in preventing gallstones:
- Statins: These cholesterol-lowering drugs may help reduce bile cholesterol levels.
- Ursodeoxycholic Acid: This medication may be prescribed for individuals at high risk of gallstones.
- Vitamin C: Adequate levels of Vitamin C can improve bile composition.
- Magnesium-Rich Foods: Magnesium supports healthy bile production.
Screening and Early Detection
Regular medical check-ups, especially for individuals at higher risk, can help detect gallstone formation early. Ultrasound imaging is a non-invasive diagnostic tool that can identify gallstones before symptoms arise.