What is Chlamydia Cervicitis?
Chlamydia cervicitis is a bacterial infection of the cervix caused by Chlamydia trachomatis, a common sexually transmitted infection (STI). This condition affects individuals with a cervix and can lead to severe reproductive health complications if left untreated.
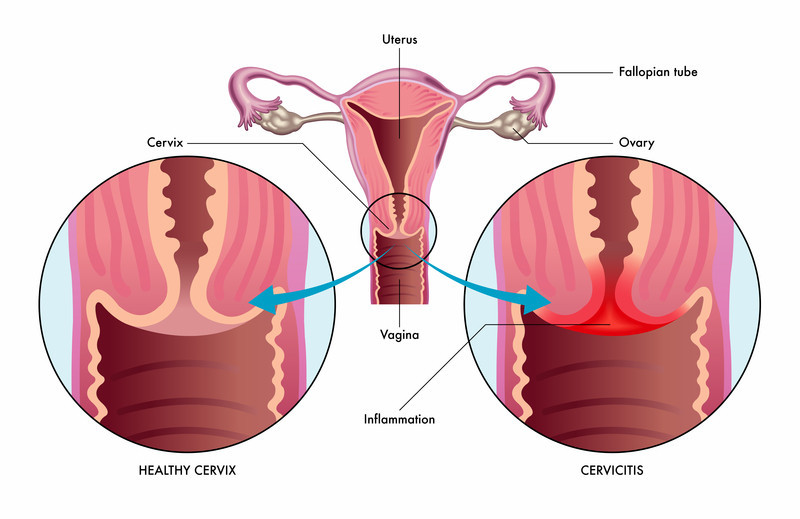
Causes of Chlamydia Cervicitis
The primary cause is sexual transmission of the bacterium Chlamydia trachomatis. Risk factors include:
- Unprotected sexual activity
- Multiple sexual partners
- History of other sexually transmitted infections (STIs)
- Engaging in sexual activity with an infected partner
Symptoms
While many individuals remain asymptomatic, symptoms may develop and include:
- Vaginal discharge (yellow or green in color)
- Painful urination
- Post-coital bleeding (bleeding after intercourse)
- Lower abdominal pain or pelvic discomfort
- Pain during intercourse
If symptoms occur, they often appear 1 to 3 weeks after exposure to the bacteria.
Complications of Untreated Chlamydia Cervicitis
Untreated its can lead to serious health complications, including:
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID):
- Inflammation of the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries.
- Increased risk of infertility and ectopic pregnancy.
- Chronic Pelvic Pain:
- Persistent pain resulting from untreated infections.
- Increased Risk of HIV Infection:
- The inflamed cervix is more susceptible to HIV transmission.
- Neonatal Complications:
- Infected mothers can transmit the bacteria to newborns during childbirth, leading to conjunctivitis or pneumonia in infants.
Diagnosis
Accurate diagnosis of chlamydia cervicitis is crucial to initiate timely treatment. Diagnostic methods include:
- Nucleic Acid Amplification Test (NAAT):
- The most sensitive test, performed on vaginal swabs or urine samples.
- Physical Examination:
- Visual inspection of the cervix for signs of inflammation.
- Culture Test:
- Culturing cervical cells to detect Chlamydia trachomatis.
Treatment Options
Chlamydia cervicitis is curable with appropriate antibiotic therapy. Common treatments include:
- Antibiotics:
- Azithromycin: Single-dose oral therapy.
- Doxycycline: Taken twice daily for 7 days.
- Partner Notification and Treatment:
- All sexual partners must be treated to prevent reinfection.
- Follow-Up Testing:
- A repeat NAAT is recommended 3 months post-treatment to confirm eradication.
Prevention of Chlamydia Cervicitis
Preventative measures play a crucial role in reducing the incidence . Key strategies include:
- Consistent Use of Condoms:
- Effective in reducing transmission of STIs.
- Regular STI Screenings:
- Especially important for sexually active individuals under 25 years old.
- Limit Number of Sexual Partners:
- Reducing the number of partners decreases exposure risk.
- Open Communication with Partners:
- Discussing sexual health and STI status with partners.
- Education and Awareness:
- Promoting awareness about the symptoms and risks of STIs.