Vitreoretinal surgery, particularly pars plana vitrectomy (PPV), demands meticulous precision and clear intraoperative visualization. The transparent nature of vitreous gel, epiretinal membranes (ERMs), and internal limiting membrane (ILM) presents significant challenges during surgery. Enhancing visualization is critical for safe tissue dissection, complete removal of pathological membranes, and minimizing iatrogenic trauma. We examine key adjuncts and visualization-enhancing agents used in modern vitrectomy.
The Role of Vitrectomy Adjuncts in Surgical Success
Adjuncts in vitrectomy refer to dyes, visualization agents, and illumination tools that improve the contrast, clarity, and visibility of transparent ocular structures. These tools enhance the surgeon’s ability to:
- Identify and differentiate fine intraocular tissues
- Confirm complete removal of membranes
- Reduce surgical time
- Minimize retinal trauma and complications
Adjuncts have become indispensable in procedures involving macular holes, ERM peeling, ILM peeling, and proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR).
Vital Dyes and Staining Agents: Enhancing Tissue Contrast
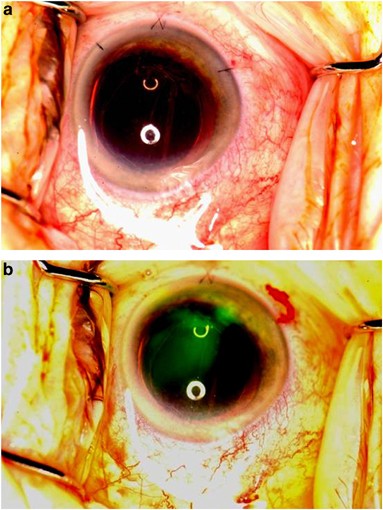
Chromovitrectomy—dye-assisted vitreoretinal surgery—utilizes specific dyes to stain intraocular tissues for easier visualization. The choice of dye depends on the target tissue and the surgical objective.
1. Trypan Blue
- Target: Epiretinal membranes (ERM)
- Usage: Commonly used in ERM peeling to enhance membrane delineation
- Properties: Selective affinity for degenerative membranes, relatively safe when used at proper concentrations
2. Brilliant Blue G (BBG)
- Target: Internal limiting membrane (ILM)
- Usage: Preferred dye for ILM peeling due to its excellent contrast and low retinal toxicity
- Advantages: Better tissue specificity and safer than indocyanine green (ICG)
3. Indocyanine Green (ICG)
- Target: ILM
- Considerations: Provides strong staining but has been associated with retinal toxicity and phototoxic effects
- Usage: Requires precise dilution and light exposure minimization
4. Dual or Combined Dyes
- Examples: MembraneBlue-Dual (trypan blue + BBG), Doubledyne
- Advantage: Allows staining of both ERM and ILM simultaneously, enhancing efficiency and reducing surgical time
Triamcinolone Acetonide: A Versatile Visualization Tool
Triamcinolone acetonide (TA) is a corticosteroid used to enhance visualization of transparent structures during vitrectomy.
Applications in Vitrectomy:
- Posterior Vitreous Detachment (PVD) Induction: TA particles adhere to vitreous collagen, revealing posterior hyaloid
- Visualization of Residual Vitreous Cortex: Assists in complete removal of vitreous strands in diabetic retinopathy and uveitis
- Safety: Generally well tolerated; preservative-free formulations are preferred to reduce toxicity risks
Perfluorocarbon Liquids (PFCLs): Stabilizing the Surgical Field
PFCLs are heavy liquids used intraoperatively to flatten the retina and stabilize tissues.
Advantages:
- Provide a clear interface during membrane peeling
- Displace subretinal fluid or blood
- Facilitate safe removal of posterior membranes
PFCLs are particularly useful in complex retinal detachments and PDR cases with tractional membranes.
Advanced Illumination Techniques and Systems
Modern vitrectomy relies on optimized light sources to improve visualization without increasing phototoxic risk.
Types of Illumination:
- Chandelier Illumination: Hands-free lighting for bimanual surgery
- High-Intensity LED and Xenon Light: Improved tissue contrast with reduced retinal damage
- Filters: Yellow or amber filters minimize blue light damage during chromovitrectomy
Intraoperative Optical Coherence Tomography (iOCT)
iOCT provides real-time cross-sectional imaging of retinal layers during surgery.
Benefits:
- Confirms completeness of membrane peeling
- Reduces reliance on tactile feedback
- Enhances decision-making in macular hole and traction cases
Although not a dye, iOCT is considered a visualization adjunct that provides unparalleled precision during retinal surgery.
Considerations for Safe and Effective Use of Adjuncts
To maximize benefits and minimize risks, careful attention must be paid to:
- Concentration and Volume of dyes
- Exposure Time to avoid retinal toxicity
- Injection Technique to prevent intraocular pressure spikes
- Dye Removal through controlled aspiration post-staining
- Preservative-Free Formulations to minimize inflammatory reactions
Clinical Impact of Visualization Adjuncts
Numerous studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of visualization adjuncts in improving surgical outcomes:
- Higher Success Rates in macular hole closure
- Faster Membrane Peeling with reduced iatrogenic injury
- Improved Retinal Function Recovery as observed on OCT and visual acuity tests
- Lower Reoperation Rates in complex cases
Future Directions in Visualization Enhancement
Ongoing research aims to develop:
- Next-generation dyes with higher specificity and safety
- Fluorescent agents for targeted visualization
- Nanoparticle-based adjuncts with enhanced tissue binding
- Augmented reality integration with iOCT for real-time 3D surgical mapping
These innovations will further refine the precision and safety of vitreoretinal surgery.
The use of adjuncts in vitrectomy has become a cornerstone of modern vitreoretinal surgery, significantly enhancing intraoperative visualization. From vital dyes to corticosteroids, PFCLs, and intraoperative imaging, these tools enable surgeons to navigate the delicate retinal architecture with greater confidence and precision. With continued advancements, visualization adjuncts will remain pivotal in elevating surgical outcomes and patient safety.

