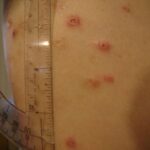
Skin irritation is a widespread dermatological concern that affects individuals across all age groups. It presents in various forms—rashes, itching, redness, stinging, or dryness—and may arise from both internal and external factors. Managing irritated skin begins with understanding its underlying causes and implementing targeted treatments and prevention strategies.
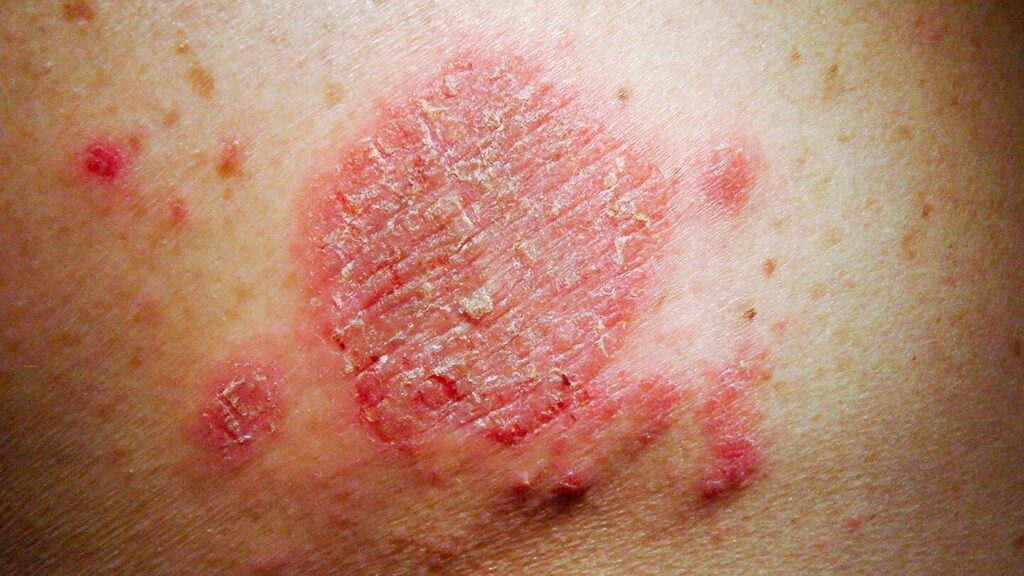
What Is Skin Irritation?
Skin irritation refers to the inflammatory response triggered by physical, chemical, or environmental stimuli that compromise the skin’s protective barrier. This response manifests as discomfort, visible skin changes, and, in some cases, secondary complications like infection. The irritation can be acute—resolving within hours or days—or chronic, persisting due to repeated exposure or underlying conditions.
Common Causes of Skin Irritation
Understanding the causative agents is crucial for effective treatment and prevention. These causes typically fall into the following categories:
1. Chemical Irritants
- Soaps, detergents, and household cleaners
- Skincare products with alcohol, fragrances, or preservatives
- Hair dyes and bleach
2. Physical Irritants
- Rough clothing materials like wool
- Excessive scrubbing or exfoliation
- Friction from tight clothing or masks
3. Environmental Factors
- Extreme heat or cold
- Dry air or low humidity
- Pollution and allergens in the air
4. Biological Agents
- Insect bites
- Fungal or bacterial infections
- Contact with plants like poison ivy
5. Medical Conditions
- Eczema (atopic dermatitis)
- Psoriasis
- Seborrheic dermatitis
- Allergic contact dermatitis
Symptoms of Skin Irritation
Skin irritation may present with varying intensity and appearance depending on the irritant and individual susceptibility. Typical symptoms include:
- Redness (erythema): Inflammatory response that increases blood flow to the area
- Itching (pruritus): Often severe, leading to scratching and further irritation
- Dryness and flaking: Compromised moisture barrier results in scaly skin
- Swelling (edema): Mild to moderate puffiness from localized inflammation
- Burning or stinging: Especially when applying products to broken or sensitive skin
- Blisters or sores: In cases of strong irritants or allergic reactions
Types of Skin Irritation
Different dermatological conditions can cause or exacerbate irritation. Each requires specific treatment strategies.
1. Contact Dermatitis
Occurs due to direct skin exposure to an irritant or allergen.
- Irritant Contact Dermatitis (ICD): Results from non-allergic reactions to harsh substances.
- Allergic Contact Dermatitis (ACD): Involves immune-mediated responses to allergens like nickel or latex.
2. Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema)
Chronic condition marked by dry, itchy, inflamed skin, often triggered by allergens or environmental factors.
3. Seborrheic Dermatitis
Affects oil-rich areas such as the scalp and face. Manifests as red, scaly patches with greasy appearance.
4. Heat Rash (Miliaria)
Caused by blocked sweat ducts during hot weather. Presents as small red bumps and itching.
5. Urticaria (Hives)
Sudden outbreak of swollen, pale red welts from allergic reactions or stress.
Treatment Options for Skin Irritation
1. Topical Therapies
- Moisturizers: Emollient-rich creams and ointments restore the skin barrier.
- Corticosteroids: Reduce inflammation and itching for severe irritation.
- Calcineurin inhibitors: Non-steroidal creams used for eczema and sensitive areas.
2. Systemic Medications
- Antihistamines: Control allergic reactions and itching.
- Oral corticosteroids: For widespread or persistent inflammation.
- Antibiotics or antifungals: In cases of secondary infections.
3. Home Remedies
- Cold compresses: Relieve itching and inflammation.
- Oatmeal baths: Soothe irritated skin and reduce itching.
- Aloe vera gel: Provides cooling and anti-inflammatory effects.
Prevention Strategies for Skin Irritation
1. Avoid Known Irritants
Identify and steer clear of products or materials that trigger flare-ups.
2. Use Gentle Skincare
Opt for fragrance-free, hypoallergenic products with minimal ingredients.
3. Maintain Skin Hydration
Apply moisturizers regularly, especially after bathing, to lock in moisture.
4. Protect the Skin
Wear gloves when handling cleaning agents and choose breathable, soft fabrics.
5. Environmental Control
Use a humidifier in dry seasons and apply sunscreen to prevent sun-induced irritation.
Skin Irritation in Different Populations
1. Children
Children’s skin is more sensitive and prone to irritants like diapers, wipes, and harsh soaps.
2. Elderly
Aging skin loses natural oils and becomes thinner, increasing susceptibility to dryness and irritation.
3. Individuals with Allergies
More prone to allergic contact dermatitis and atopic eczema, often requiring patch testing for identification.
When to See a Dermatologist
Professional evaluation is essential when:
- Irritation persists beyond a few days
- Symptoms worsen despite home care
- Blisters, pus, or bleeding develop
- Suspected allergic reaction is involved
- Skin becomes increasingly painful or affects daily activities
Skin irritation is a multifactorial condition that can significantly impact comfort and quality of life. By recognizing early symptoms, identifying causative agents, and implementing both short-term treatments and long-term preventive measures, we can effectively manage and reduce the incidence of irritated skin. For persistent or severe cases, dermatological consultation ensures accurate diagnosis and tailored therapy.