Skin inflammation is a common condition that can affect individuals of all ages and backgrounds. It refers to the body’s immune response to harmful stimuli, leading to symptoms like redness, swelling, pain, and sometimes heat. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for skin inflammation is crucial for managing and preventing these often uncomfortable conditions. This article will explore the various types of skin inflammation, their causes, symptoms, and the most effective ways to manage and treat them.
What is Skin Inflammation?
Skin inflammation is the body’s natural response to injury, infection, or irritants. It typically involves the activation of the immune system, which releases various chemicals that increase blood flow and lead to swelling, redness, and pain. While inflammation is a protective mechanism that helps the body heal, it can become problematic if it becomes chronic or severe.
There are several types of skin inflammation, ranging from mild conditions like contact dermatitis to more severe conditions such as eczema or psoriasis.
Causes of Skin Inflammation
Skin inflammation can be triggered by a wide range of factors. These triggers are often categorized into two main types: internal and external. Understanding the root causes of skin inflammation is essential for determining the appropriate treatment.
1. External Factors
External factors typically involve environmental irritants or allergens that cause the skin to react.
- Allergens: Substances like pollen, certain foods, or pet dander can provoke an allergic reaction in some individuals, leading to skin inflammation.
- Infections: Bacterial, viral, or fungal infections can cause inflammation. For instance, impetigo (a bacterial skin infection) or herpes simplex virus (HSV) can result in inflamed patches of skin.
- Contact Irritants: Harsh chemicals, cosmetics, or detergents can irritate the skin and lead to inflammation. This is commonly seen in conditions like contact dermatitis.
- Physical Injury: Cuts, scrapes, or burns can lead to acute skin inflammation as the body works to repair damaged tissue.
2. Internal Factors
Internal factors are often linked to underlying health conditions or immune system dysfunctions.
- Autoimmune Diseases: Conditions like psoriasis or lupus cause the immune system to attack healthy skin cells, resulting in chronic inflammation.
- Genetic Predisposition: Some individuals are genetically predisposed to inflammatory skin conditions, such as eczema or rosacea.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations, such as those that occur during pregnancy or puberty, can increase the likelihood of developing skin inflammation.
Symptoms of Skin Inflammation
The symptoms of skin inflammation can vary depending on the severity and underlying cause. However, common signs of skin inflammation include:
- Redness: The skin appears red or flushed due to increased blood flow to the affected area.
- Swelling: Inflammation often causes the skin to puff up, making the affected area feel swollen or puffy.
- Pain and Tenderness: The inflamed skin may be sore to the touch or tender, as the nerves become more sensitive due to increased blood flow.
- Heat: In some cases, the inflamed skin may feel warm or hot to the touch, as blood vessels dilate to increase circulation.
- Itching: Many inflammatory skin conditions are accompanied by itching, which can worsen the discomfort and lead to scratching that may exacerbate the inflammation.
- Peeling or Crusting: In chronic cases, the skin may begin to peel, crack, or form scabs, especially in conditions like eczema or psoriasis.
Common Types of Skin Inflammation
Several types of skin inflammation are commonly encountered. These can range from mild cases of irritation to more severe, chronic conditions.
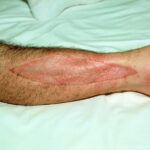
1. Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis)
Eczema is a chronic inflammatory skin condition characterized by dry, itchy, and inflamed skin. It often appears in patches and can be exacerbated by allergens, irritants, or stress. Eczema typically affects the face, hands, and flexural areas of the body (e.g., behind the knees or elbows).
- Symptoms: Dry, scaly, and red patches of skin, along with intense itching.
- Treatment: Moisturizers, corticosteroid creams, antihistamines, and avoiding known triggers.
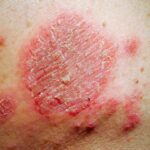
2. Psoriasis
Psoriasis is an autoimmune condition that accelerates skin cell turnover, leading to the buildup of thick, scaly patches. These patches can be itchy, painful, and inflamed. Psoriasis commonly affects areas like the elbows, knees, scalp, and lower back.
- Symptoms: Red, raised patches with silvery scales, itching, and soreness.
- Treatment: Topical treatments (steroids, vitamin D analogs), phototherapy, and systemic medications for severe cases.
3. Contact Dermatitis
Contact dermatitis occurs when the skin comes into contact with an allergen or irritant, causing an inflammatory reaction. It may be caused by substances like poison ivy, cosmetics, or harsh chemicals.
- Symptoms: Redness, swelling, blistering, and itching.
- Treatment: Avoidance of the irritant, use of corticosteroid creams, and antihistamines to reduce itching.
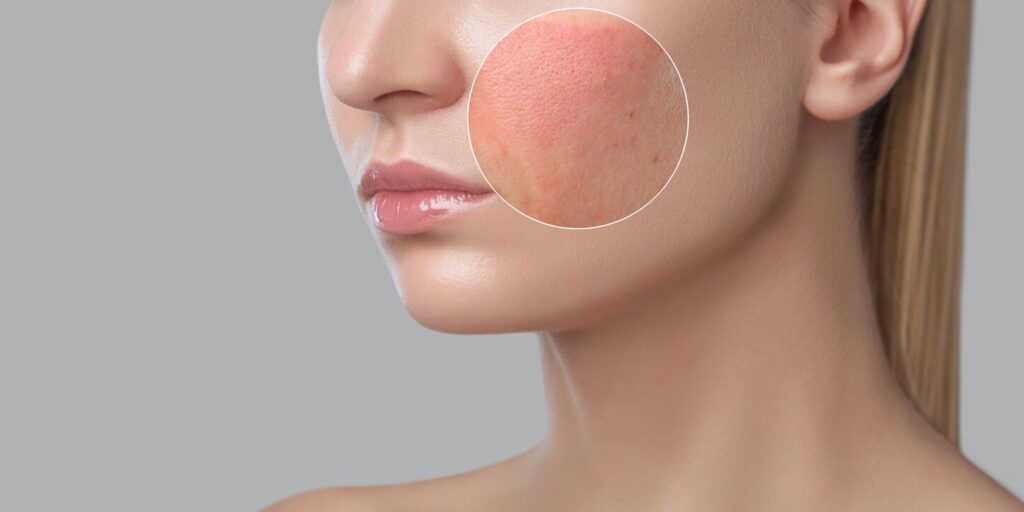
4. Rosacea
Rosacea is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that causes redness, visible blood vessels, and pustules on the face, often affecting the nose, cheeks, and forehead. It can be triggered by sun exposure, stress, hot beverages, and spicy foods.
- Symptoms: Persistent redness, acne-like bumps, and visible blood vessels.
- Treatment: Topical antibiotics, oral medications, and avoiding triggers.
5. Acne Vulgaris
Acne is a common inflammatory skin condition that occurs when hair follicles become clogged with oil and dead skin cells, leading to the formation of pimples, blackheads, or cysts. While acne is often associated with adolescence, it can affect individuals of all ages.
- Symptoms: Pimples, blackheads, whiteheads, cysts, and inflammation of the skin.
- Treatment: Topical treatments (retinoids, benzoyl peroxide), oral antibiotics, and in severe cases, isotretinoin.
Treatment Options for Skin Inflammation
Effective treatment for skin inflammation depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. In most cases, the goal is to reduce inflammation, alleviate symptoms, and promote healing. Below are some common treatments:
1. Topical Medications
- Corticosteroids: Anti-inflammatory creams and ointments that help reduce redness and swelling.
- Calcineurin Inhibitors: Used for conditions like eczema to reduce inflammation without the side effects of steroids.
- Antihistamines: Help control itching, especially in allergic reactions.
- Moisturizers: Essential for maintaining skin hydration and preventing flare-ups, especially in conditions like eczema and psoriasis.
2. Systemic Medications
- Oral Steroids: For severe inflammation, oral corticosteroids may be prescribed to reduce systemic inflammation.
- Immunosuppressants: In cases of autoimmune conditions like psoriasis or lupus, medications that suppress the immune system can be used to control inflammation.
- Biologics: Target specific components of the immune system to treat chronic inflammatory conditions like psoriasis.
3. Lifestyle Changes and Home Remedies
- Avoiding Triggers: Identifying and avoiding irritants or allergens that trigger flare-ups is key.
- Proper Skincare: Gentle cleansing and moisturizing can help manage skin inflammation. Use mild, fragrance-free products to avoid irritation.
- Dietary Adjustments: Some individuals find that certain foods can trigger skin inflammation, particularly in conditions like acne and rosacea.
Preventing Skin Inflammation
Preventing skin inflammation involves a combination of lifestyle changes, skincare routines, and identifying potential triggers. Here are some practical tips:
- Hydration: Keep the skin hydrated to maintain its barrier function.
- Sun Protection: Use sunscreen to protect the skin from UV rays, which can exacerbate conditions like rosacea and eczema.
- Avoid Known Triggers: If you have sensitive skin, avoid contact with irritants or allergens known to cause flare-ups.
Skin inflammation is a common yet diverse condition with various causes and manifestations. Understanding the different types of skin inflammation, their symptoms, and the most effective treatment options is essential for managing and preventing flare-ups. By recognizing triggers, practicing proper skincare, and utilizing the appropriate treatments, individuals can effectively reduce the impact of skin inflammation on their lives.