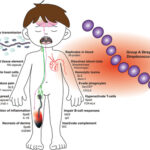
Skin disinfection plays a crucial role in preventing infections, maintaining hygiene, and promoting overall health. Whether it’s preparing for surgery, cleaning a wound, or preventing everyday germs from spreading, understanding effective skin disinfection techniques is essential. In this guide, we explore various methods of skin disinfection, the importance of antiseptics, and best practices to ensure optimal skin hygiene.
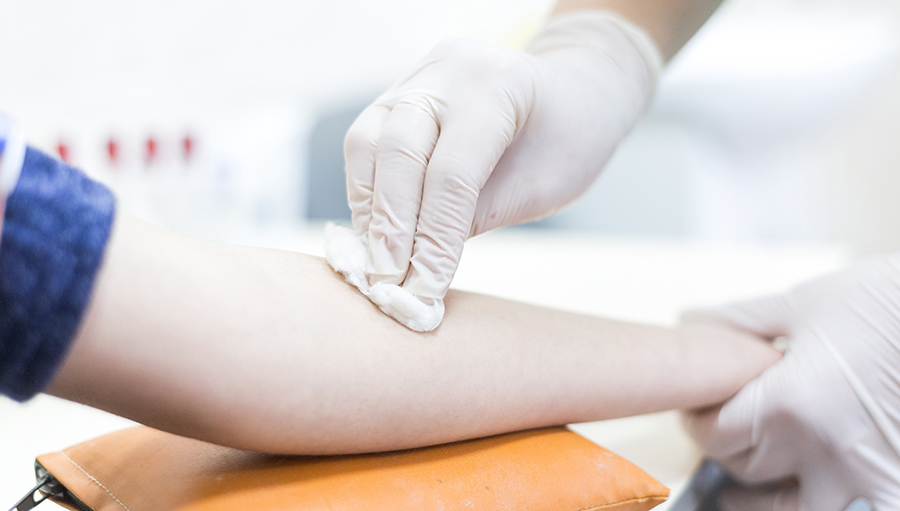
The Importance of Skin Disinfection in Infection Control
Effective skin disinfection is a fundamental aspect of infection control. Our skin, being the largest organ in the body, is constantly exposed to external elements, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi. Proper disinfection helps in eliminating harmful pathogens, reducing the risk of skin infections and other health issues.
Key Reasons for Skin Disinfection:
- Prevents Infections: Eliminates bacteria and pathogens that may lead to skin infections, such as cellulitis or impetigo.
- Promotes Healing: Proper cleaning of wounds accelerates the healing process by removing debris and contaminants.
- Reduces Cross-Contamination: Skin disinfection minimizes the risk of spreading infections from one person to another, particularly in healthcare settings.
- Prepares Skin for Procedures: Disinfection is crucial before surgical procedures or injections to reduce the risk of post-operative infections.
Common Methods of Skin Disinfection
Skin disinfection can be performed using a variety of methods, ranging from traditional antiseptic solutions to modern alcohol-based disinfectants. Below, we explore some of the most commonly used skin disinfection methods:
1. Alcohol-Based Disinfectants
Alcohol-based disinfectants are widely used for skin disinfection due to their rapid action and broad-spectrum efficacy against pathogens. Ethanol (ethyl alcohol) and isopropyl alcohol are the most common alcohols used for disinfecting the skin.
- Pros: Quick-drying, effective against a wide range of bacteria and viruses, easy to use.
- Cons: Can cause dryness or irritation with frequent use.
2. Chlorhexidine Gluconate
Chlorhexidine is a powerful antiseptic widely used in hospitals and healthcare facilities. It is effective against both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, as well as fungi and some viruses. Chlorhexidine is commonly used for surgical scrubs and pre-operative disinfection.
- Pros: Long-lasting residual effect, effective in preventing infections.
- Cons: May cause skin irritation or allergic reactions in some individuals.
3. Iodine-Based Disinfectants
Iodine-based solutions, such as povidone-iodine (Betadine), are commonly used for disinfecting the skin before surgeries or invasive procedures. Iodine is effective against a broad range of pathogens, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi.
- Pros: Broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity, well-suited for use on open wounds.
- Cons: Can cause skin staining and irritation in some people.
4. Hydrogen Peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide is a mild antiseptic commonly used for cleaning wounds. It works by releasing oxygen, which helps to clean and disinfect the affected area.
- Pros: Effective at cleaning wounds, breaks down into water and oxygen, minimizing irritation.
- Cons: Prolonged use can delay wound healing due to its cytotoxic effects on healthy cells.
5. Antiseptic Creams and Ointments
Topical antiseptic creams and ointments, such as Neosporin, combine multiple antimicrobial agents, including neomycin, polymyxin B, and bacitracin, to prevent infection and promote healing.
- Pros: Easy to apply, helps keep wounds moist for better healing.
- Cons: May cause allergic reactions or skin sensitivities in some individuals.
Best Practices for Skin Disinfection
Proper skin disinfection involves more than just applying an antiseptic. Here are some essential best practices to ensure effective disinfection:
1. Clean the Skin First
Before applying any disinfectant, it’s important to clean the skin of any dirt, oils, or other contaminants. Use mild soap and water to wash the area thoroughly, as this will help the disinfectant work more effectively.
2. Apply Disinfectant Generously
Use enough disinfectant to cover the area completely. Gently apply the antiseptic in a circular motion to ensure thorough coverage, especially if you’re disinfecting a wound.
3. Allow for Proper Drying
After applying the disinfectant, allow it to dry naturally. Avoid wiping the area, as this could remove the disinfectant before it has time to work. Letting the skin air dry will ensure the antiseptic has maximum effectiveness.
4. Disinfect After Touching Contaminated Surfaces
If you touch any potentially contaminated surfaces, such as door handles or public equipment, disinfect your hands immediately to prevent the spread of harmful pathogens.
5. Use the Correct Product for the Situation
Not all disinfectants are suitable for all types of skin disinfection. For example, alcohol-based disinfectants are ideal for general use but may not be suitable for wound care, where iodine or chlorhexidine might be more appropriate.
Choosing the Right Skin Disinfectant for Different Situations
Different scenarios require different disinfecting agents. Below is a guide to choosing the right product based on your specific needs.
1. For General Skin Hygiene
- Alcohol-based hand sanitizers or wipes are an excellent option for general skin disinfection in everyday settings.
2. For Wound Care
- Hydrogen peroxide or povidone-iodine are effective for cleaning wounds and preventing infection.
3. For Surgical Preparation
- Chlorhexidine gluconate or povidone-iodine are the go-to choices in medical settings for surgical site preparation.
4. For Skin Infections
- Antiseptic ointments containing a combination of antimicrobial agents are ideal for preventing or treating localized skin infections.
Risks and Considerations of Skin Disinfection
While skin disinfection is vital for infection control, improper use can cause skin irritation or other side effects. It is important to understand the risks associated with frequent or incorrect use of disinfectants.
Common Risks:
- Skin Irritation: Some disinfectants, such as alcohol, can cause dryness and irritation, particularly with frequent use.
- Allergic Reactions: Certain individuals may be allergic to ingredients in antiseptics like iodine, which can cause redness, itching, or swelling.
- Disruption of Skin Microflora: Overuse of strong disinfectants may disrupt the skin’s natural microflora, potentially leading to overgrowth of harmful bacteria.
Tips to Minimize Risks:
- Always follow the instructions for each product, including application methods and frequency.
- Use mild antiseptics when possible to reduce skin irritation.
- If irritation occurs, discontinue use of the product and consult with a healthcare professional for alternatives.
Skin Disinfection and Wound Healing: The Relationship
Proper skin disinfection is not just essential for preventing infections but also plays a significant role in promoting optimal wound healing. While antiseptics clean the wound, they also help to maintain a moist environment, which is critical for the healing process. The right disinfectant can help speed up recovery by preventing secondary infections and promoting tissue regeneration.
Skin disinfection is a crucial practice for preventing infections and promoting overall skin health. Whether you are cleaning a wound, preparing for surgery, or simply maintaining personal hygiene, using the right products and following best practices is essential. By understanding the methods and risks involved, you can ensure that your skin stays clean, healthy, and protected from harmful pathogens.