Secretin stimulation testing is a specialized diagnostic procedure used to evaluate pancreatic exocrine function and confirm the presence of gastrin-secreting tumors, such as those seen in Zollinger-Ellison syndrome (ZES). Secretin, a gastrointestinal hormone, plays a critical role in stimulating pancreatic bicarbonate secretion and modulating gastric acid production through its action on G cells and pancreatic ducts.
Key Indications for Secretin Stimulation Testing
Diagnosis of Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome (ZES)
ZES is characterized by hypersecretion of gastrin due to gastrinomas, often found in the pancreas or duodenum. The secretin stimulation test is the most reliable provocative test to confirm ZES when fasting gastrin levels are elevated but not diagnostic.
Evaluation of Pancreatic Exocrine Function
Secretin also stimulates bicarbonate-rich pancreatic juice secretion. This test is instrumental in assessing pancreatic output in cases of suspected:
- Chronic pancreatitis
- Cystic fibrosis
- Post-surgical pancreatic insufficiency
Physiology of Secretin and Gastrin Interaction
Secretin normally inhibits gastrin release; however, in patients with gastrinomas, secretin paradoxically stimulates gastrin secretion, making this test highly specific for ZES.
Pre-Test Preparation and Patient Instructions
- Fasting: At least 8 hours before the test
- Medication Discontinuation: Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) should be withheld for 7 days; H2 blockers for 24–48 hours
- Baseline Testing: Initial fasting serum gastrin and gastric pH assessment required
Contraindications include:
- Severe comorbid conditions where endoscopy poses risk
- Recent use of medications affecting gastrin levels
- Uncorrected coagulopathy if endoscopic version is used
Secretin Stimulation Test Procedure
Gastrinoma Detection Protocol
- Baseline Serum Gastrin Measurement
- Secretin Administration: 2 units/kg IV over 1 minute
- Serial Blood Sampling: At 2, 5, 10, 15, and 30 minutes post-injection
- Interpretation: A rise in serum gastrin ≥120 pg/mL above baseline is considered diagnostic for ZES
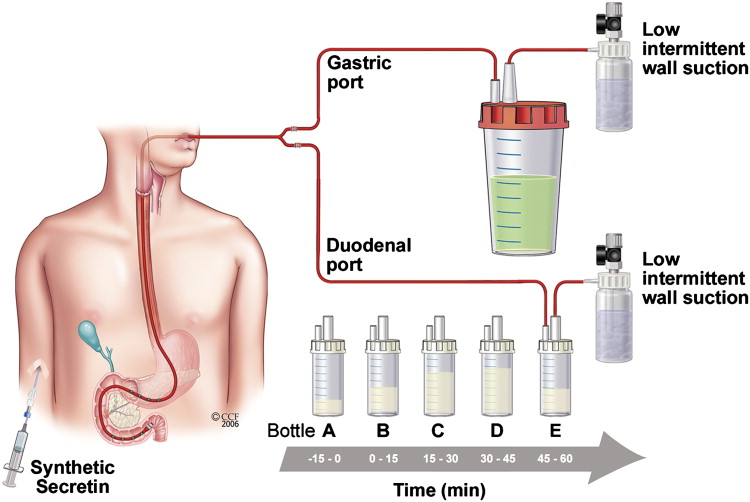
Pancreatic Function Assessment Protocol (Endoscopic)
- Duodenal Intubation via Endoscopy
- IV Secretin Injection (0.2 mcg/kg)
- Duodenal Fluid Collection: Every 15 minutes for up to 60 minutes
- Analysis: Bicarbonate concentration >80 mEq/L indicates normal exocrine function
Interpretation of Results
For ZES Diagnosis
| Result Type | Gastrin Change Post-Secretin | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Positive | ≥120 pg/mL increase | Suggestive of gastrinoma |
| Equivocal | 110–119 pg/mL increase | Repeat or further testing required |
| Negative | <110 pg/mL increase | ZES unlikely |
For Pancreatic Function
| Bicarbonate Output | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| >80 mEq/L | Normal |
| 50–80 mEq/L | Indeterminate |
| <50 mEq/L | Suggestive of pancreatic insufficiency |
Limitations and Considerations
- False positives can occur in chronic atrophic gastritis or retained antrum syndrome
- False negatives may arise if the patient is still on acid-suppressive medications
- Test specificity increases when combined with imaging and clinical findings
- Requires specialized laboratory support for accurate gastrin assays
Adjunct Tests and Imaging
Secretin stimulation testing is best interpreted in conjunction with:
- Fasting serum gastrin levels
- Gastric pH assessment
- Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS)
- Somatostatin receptor scintigraphy (Octreoscan)
- CT or MRI of abdomen
These tools help localize gastrinomas and evaluate for metastatic spread.
Clinical Relevance and Prognostic Value
Early diagnosis of gastrinoma through secretin stimulation testing allows prompt initiation of PPI therapy or surgical resection, potentially preventing complications such as severe peptic ulcer disease or perforation. In pancreatic evaluation, the test helps identify exocrine insufficiency, guiding enzyme replacement therapy and nutritional support.
Secretin stimulation testing remains a cornerstone in the diagnosis of Zollinger-Ellison syndrome and in assessing pancreatic exocrine function. Its precise execution, in combination with clinical, biochemical, and radiological findings, ensures accurate diagnosis and optimal patient management.