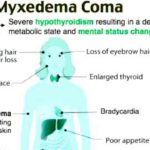
Myxedema is a life-threatening complication of severe hypothyroidism. It is characterized by a significant decrease in thyroid hormone levels, leading to impaired metabolism and multiple organ dysfunction. This condition requires immediate medical intervention due to its high mortality risk.
Causes and Risk Factors
Myxedema results from untreated or inadequately treated hypothyroidism. Some primary causes include:
- Autoimmune disorders such as Hashimoto’s thyroiditis
- Iodine deficiency or excess
- Thyroid surgery or radioactive iodine therapy
- Certain medications (e.g., lithium, amiodarone)
- Pituitary or hypothalamic disorders affecting thyroid function
Recognizing Myxedema Symptoms
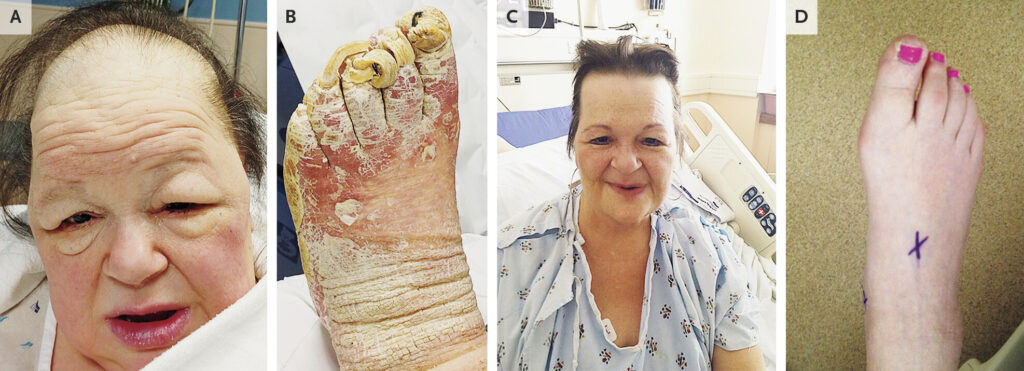
Myxedema presents with severe and life-threatening symptoms, including:
- Profound fatigue and lethargy
- Cold intolerance and hypothermia
- Swelling of the face, hands, and feet
- Slow heart rate (bradycardia) and low blood pressure
- Respiratory depression and hypoxia
- Confusion, delirium, or coma (myxedema coma)
Diagnosis and Medical Evaluation
Diagnosing myxedema involves clinical assessment and laboratory tests, including:
- Thyroid Function Tests: Extremely low T3/T4 levels and elevated TSH
- Electrolyte Panel: Hyponatremia and hypoglycemia
- Blood Gas Analysis: Identifying respiratory failure and hypoxia
- Imaging: Brain MRI or CT scan if pituitary dysfunction is suspected
Treatment Strategies for Myxedema
Emergency Management
Patients with myxedema coma require intensive care:
- Intravenous (IV) thyroid hormone replacement (levothyroxine, liothyronine)
- Supportive care, including mechanical ventilation if needed
- Corticosteroids to address possible adrenal insufficiency
- Warm IV fluids to correct hypothermia
Long-Term Management
Once stabilized, patients require lifelong thyroid hormone replacement therapy. Regular monitoring of TSH and free T4 levels ensures optimal dosing.
Complications and Prognosis
If left untreated, myxedema can lead to severe complications such as:
- Respiratory failure
- Heart failure and arrhythmias
- Multi-organ dysfunction
Early diagnosis and proper treatment significantly improve survival rates and long-term outcomes.
Preventing Myxedema
Preventative measures include:
- Early diagnosis and treatment of hypothyroidism
- Regular thyroid function monitoring in at-risk individuals
- Patient education on medication adherence
Myxedema is a medical emergency requiring rapid intervention. Awareness, early diagnosis, and proper treatment are crucial in preventing fatal complications. Patients must adhere to lifelong thyroid hormone therapy and regular check-ups to maintain health and prevent recurrence.