Myoclonic epilepsy is a neurological disorder characterized by sudden, involuntary muscle jerks or spasms. While primary treatment often involves antiepileptic drugs (AEDs), adjunct therapies play a crucial role in enhancing seizure control, reducing side effects, and improving patient quality of life.
Understanding Myoclonic Epilepsy
Causes and Risk Factors
- Genetic mutations (e.g., Juvenile Myoclonic Epilepsy, Progressive Myoclonic Epilepsy)
- Brain injuries or infections
- Metabolic disorders
Symptoms
- Sudden muscle jerks (myoclonus)
- Loss of consciousness (in some cases)
- Photosensitivity-induced seizures
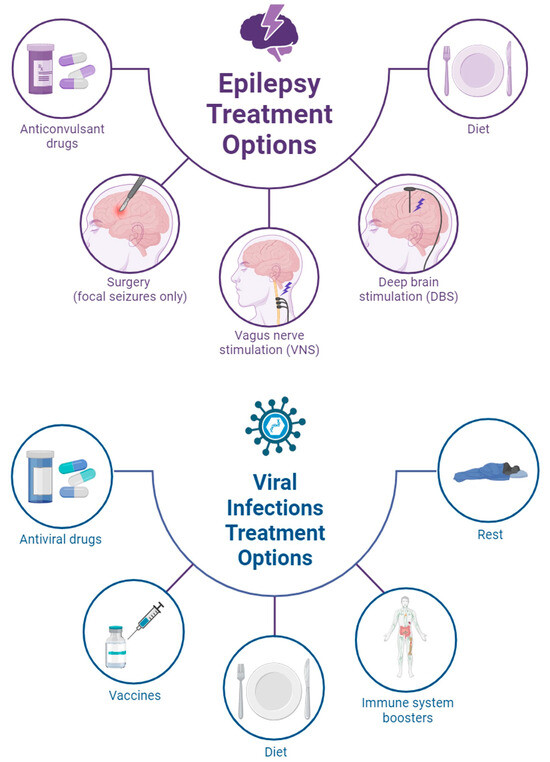
Standard Treatment Approaches
First-Line Medications
- Valproic Acid (Depakote) – Most effective but may cause weight gain and liver issues.
- Levetiracetam (Keppra) – Fewer side effects, but some patients experience mood disturbances.
- Clonazepam (Klonopin) – Used for acute myoclonic seizures but has a risk of dependence.
Adjunctive Therapies for Myoclonic Epilepsy
1. Additional Antiepileptic Medications
For patients not fully controlled with first-line drugs, adjunct AEDs include:
- Topiramate (Topamax) – Enhances seizure control with minimal side effects.
- Zonisamide (Zonegran) – Effective in refractory cases.
- Brivaracetam (Briviact) – A newer alternative with fewer cognitive side effects.
2. Ketogenic Diet
A high-fat, low-carb ketogenic diet has been clinically proven to reduce seizure frequency, especially in drug-resistant cases. Mechanisms include:
- Increasing ketone bodies, which stabilize neurons
- Reducing excitatory neurotransmitter activity
3. Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS)
VNS therapy involves implanting a device that sends mild electrical pulses to the vagus nerve, helping to regulate seizure activity. It is particularly beneficial for drug-resistant epilepsy patients.
4. Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS)
For severe cases, DBS involves implanting electrodes in the brain to disrupt abnormal electrical activity. This treatment is still in experimental stages for myoclonic epilepsy.
5. Lifestyle Modifications
- Avoiding seizure triggers (e.g., flashing lights, sleep deprivation)
- Regular exercise and stress management
- Maintaining a seizure diary to track patterns and triggers
Emerging Therapies
Gene Therapy
Ongoing research explores the possibility of correcting genetic mutations responsible for myoclonic epilepsy.
Cannabidiol (CBD) Treatment
CBD-based therapies have shown promise in reducing seizure frequency in drug-resistant epilepsy cases.
Adjunct treatments for myoclonic epilepsy provide valuable options for patients struggling with seizure control. Combining medication, dietary interventions, neuromodulation, and lifestyle adjustments enhances overall management and improves patient outcomes.