Myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow to the heart muscle is blocked, leading to tissue damage or death. The primary cause is coronary artery disease (CAD), which results from plaque buildup in the arteries.
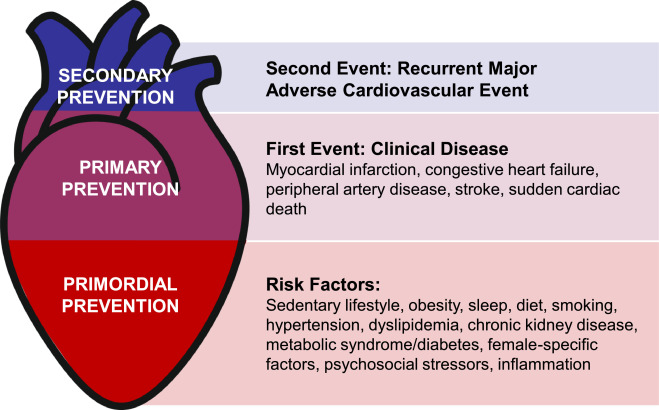
Risk Factors for Myocardial Infarction
Several risk factors contribute to the likelihood of a heart attack:
- Modifiable Factors: High cholesterol, hypertension, smoking, obesity, diabetes, and sedentary lifestyle.
- Non-Modifiable Factors: Age, family history, and genetic predisposition.
Lifestyle Modifications for Prevention
1. Adopting a Heart-Healthy Diet
A balanced diet plays a crucial role in reducing the risk of myocardial infarction:
- Increase: Fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and omega-3 fatty acids.
- Reduce: Saturated fats, trans fats, processed foods, and excessive salt intake.
- Monitor: Cholesterol and blood sugar levels regularly.
2. Regular Physical Activity
Engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week lowers heart disease risk. Recommended activities include:
- Brisk walking or jogging
- Cycling or swimming
- Strength training exercises
3. Weight Management
Obesity significantly increases MI risk. Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise reduces cardiovascular strain.
4. Smoking Cessation
Tobacco use damages blood vessels and increases clot formation. Quitting smoking immediately improves heart health and lowers MI risk.
5. Alcohol Moderation
Excessive alcohol consumption contributes to hypertension and heart disease. Limiting intake to moderate levels (one drink per day for women, two for men) is advisable.
Medical Interventions for Prevention
1. Managing Hypertension and Cholesterol
- Blood Pressure Control: Keep blood pressure below 120/80 mmHg with medication, diet, and exercise.
- Cholesterol Regulation: Maintain LDL (bad cholesterol) below 100 mg/dL and HDL (good cholesterol) above 60 mg/dL.
2. Diabetes Management
Diabetes elevates heart disease risk. Keeping blood sugar levels within target ranges through diet, exercise, and medication helps prevent complications.
3. Medications for Heart Protection
Certain medications lower the risk of myocardial infarction:
- Statins: Reduce cholesterol levels.
- Aspirin: Prevents clot formation (prescribed in high-risk individuals).
- Beta-blockers & ACE inhibitors: Control blood pressure and reduce heart strain.
Early Warning Signs and Emergency Response
Recognizing MI symptoms early can save lives:
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Shortness of breath
- Nausea or dizziness
- Cold sweats
Immediate medical attention is crucial. Call emergency services and administer aspirin if advised by a healthcare professional.
Preventing myocardial infarction requires a combination of lifestyle modifications, medical interventions, and awareness of risk factors. Prioritizing heart health through a balanced diet, regular exercise, and proper medical care can significantly reduce the risk of a heart attack.