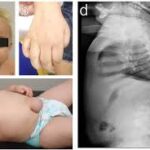
Mucocutaneous herpes simplex is a condition caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV), which affects the skin and mucous membranes, including areas such as the lips, genital regions, and eyes. While the infection is common and often manageable, understanding its causes, symptoms, treatment options, and preventative measures is crucial for effective management and care. This comprehensive guide explores these aspects in depth, providing you with valuable insights into this viral infection.
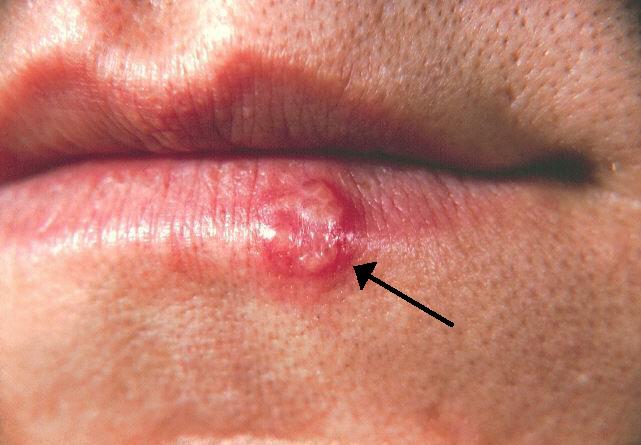
What is Mucocutaneous Herpes Simplex?
Mucocutaneous herpes simplex refers to infections caused by the herpes simplex virus, which primarily affects the mucous membranes and the skin. The virus exists in two main types: HSV-1 and HSV-2, both of which can cause sores or blisters in various areas of the body.
- HSV-1 is the more common cause of oral herpes, resulting in cold sores around the mouth.
- HSV-2 typically causes genital herpes, which involves outbreaks in the genital and anal regions.
While these types have traditional associations with specific locations, both can infect any area of the body, leading to mucocutaneous lesions. The infection is highly contagious, often transmitted through direct skin-to-skin contact, including kissing or sexual contact.
Symptoms of Mucocutaneous Herpes Simplex
The symptoms of mucocutaneous herpes simplex vary depending on the type of herpes virus and the area of infection.
Oral Herpes (HSV-1)
Oral herpes commonly causes cold sores or fever blisters on or around the lips. Symptoms include:
- Painful, fluid-filled blisters that may burst and crust over.
- Tingling or itching sensations before the outbreak.
- Swelling and redness around the affected area.
- In severe cases, swollen lymph nodes, fever, and sore throat.
Genital Herpes (HSV-2)
Genital herpes can affect both men and women, leading to symptoms such as:
- Painful blisters or ulcers around the genital area, buttocks, or thighs.
- Itching or burning sensations during urination.
- Painful or swollen lymph nodes.
- Flu-like symptoms such as fever, muscle aches, and headaches.
Both types of herpes simplex virus can remain dormant in the body for long periods. When reactivation occurs, it may be triggered by factors such as stress, illness, hormonal changes, or a weakened immune system.
How is Mucocutaneous Herpes Simplex Transmitted?
Mucocutaneous herpes simplex is primarily spread through direct contact with infected skin or mucous membranes. This can happen in several ways:
- Oral to Oral: Kissing someone with an active cold sore can transmit HSV-1.
- Oral to Genital: Oral sex can transfer HSV-1 to the genital area.
- Genital to Genital: Sexual intercourse with an infected partner is the most common mode of transmission for HSV-2.
- Contact with Broken Skin: Sharing personal items like towels, razors, or lip balm with someone who has an active infection can also spread the virus.
It is important to note that the virus can be transmitted even when there are no visible sores, which is known as asymptomatic shedding.
Diagnosis of Mucocutaneous Herpes Simplex
To diagnose mucocutaneous herpes simplex, healthcare professionals will typically rely on a combination of the following:
- Physical Examination: A healthcare provider will examine the blisters or sores to determine if they are characteristic of herpes.
- Viral Culture or PCR Test: A sample from an open sore can be cultured or tested using polymerase chain reaction (PCR) to confirm the presence of the herpes simplex virus.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests can detect antibodies to HSV-1 or HSV-2, indicating a past infection, even if there are no current symptoms.
Treatment Options for Mucocutaneous Herpes Simplex
While there is no cure for herpes simplex infections, various treatments can help manage outbreaks and reduce symptoms.
Antiviral Medications
The most effective way to treat mucocutaneous herpes simplex is through antiviral medications. These medications help shorten the duration of outbreaks, reduce their severity, and minimize the risk of transmission to others. Common antiviral drugs include:
- Acyclovir
- Valacyclovir
- Famciclovir
These medications can be taken orally, applied topically, or administered intravenously in severe cases.
Pain Relief
In addition to antiviral treatment, over-the-counter pain relief medications like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help alleviate discomfort caused by the sores. Topical creams containing lidocaine or hydrocortisone may also provide local relief.
Daily Suppressive Therapy
For individuals with frequent outbreaks, daily suppressive antiviral therapy may be recommended. This reduces the frequency of outbreaks and lowers the chances of transmitting the virus to others.
Prevention of Mucocutaneous Herpes Simplex
Preventing the spread of mucocutaneous herpes simplex involves both personal hygiene and lifestyle modifications:
- Avoiding Direct Contact During Outbreaks: Refrain from kissing or engaging in sexual activity when sores are present.
- Using Protection During Sexual Activity: Condoms can help reduce the risk of transmitting genital herpes but may not fully prevent the spread of HSV-1 from oral contact.
- Daily Antiviral Therapy: For individuals with frequent outbreaks, daily antiviral medications can prevent transmission.
- Good Hygiene Practices: Wash hands regularly and avoid sharing personal items, such as towels or razors, that might come into contact with the virus.
Diet and Stress Management
While there is no direct dietary cure for herpes simplex, certain foods and lifestyle changes can help strengthen the immune system. Consuming foods rich in vitamins C and E, as well as amino acids like L-lysine, may help reduce the frequency of outbreaks. Stress management techniques, such as meditation and exercise, can also play a significant role in reducing the likelihood of a flare-up.
Complications of Mucocutaneous Herpes Simplex
In most cases, mucocutaneous herpes simplex is manageable, but complications can arise, particularly in individuals with weakened immune systems. These may include:
- Herpetic Keratitis: An eye infection caused by HSV-1, which can lead to blindness if untreated.
- Herpes Encephalitis: A rare but serious infection of the brain caused by HSV.
- Neonatal Herpes: When a mother with genital herpes transmits the virus to her newborn during childbirth, leading to severe complications.
Mucocutaneous herpes simplex is a common yet often misunderstood viral infection. With proper knowledge, treatment, and prevention strategies, individuals affected by this condition can manage their symptoms and lead a healthy, fulfilling life. If you suspect you have herpes simplex, it is important to consult a healthcare provider for diagnosis and guidance on treatment options.