The emergence of mpox (formerly known as monkeypox) as a global health concern has led to heightened awareness about the importance of vaccination. In recent years, mpox outbreaks have raised significant public health concerns, prompting health authorities to recommend preventive measures, including vaccination. Understanding the mpox vaccine—its effectiveness, availability, and how it protects against the virus—is essential for individuals seeking to safeguard themselves.

This article will explore the significance of mpox vaccination, the different types of vaccines available, their effectiveness, potential side effects, and the role vaccination plays in curbing the spread of mpox. With clear, concise information, we aim to provide all the necessary details to help individuals make informed decisions about their health.
What is Mpox (Monkeypox)?
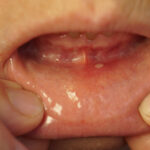
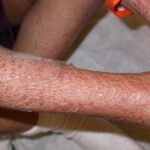
Mpox is a viral disease that is caused by the mpox virus, which belongs to the same family as the smallpox virus. Although mpox is relatively rare, it can spread between animals and humans, and between humans, through close contact, respiratory droplets, and even contaminated surfaces. The disease is often marked by symptoms that resemble smallpox, including fever, chills, muscle aches, and a distinctive rash, which can develop into fluid-filled blisters.
Despite its name, mpox is not as contagious or as deadly as smallpox. However, recent outbreaks, especially in non-endemic areas, have prompted global health authorities to take preventive measures seriously. The World Health Organization (WHO) and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) have emphasized the importance of vaccination to prevent the spread of the virus.
The Importance of Mpox Vaccination
Vaccination remains one of the most effective tools to prevent viral infections, and mpox is no exception. While not everyone will be exposed to the virus, vaccination plays a vital role in minimizing the spread of the disease, protecting vulnerable populations, and reducing the risk of severe disease progression.
The goal of mpox vaccination is twofold:
- To prevent infection: By providing immunity to individuals who may be at higher risk of exposure to the virus.
- To reduce the severity of the disease: Vaccinated individuals who do contract mpox are likely to experience milder symptoms and a lower risk of complications.
As the number of cases continues to rise globally, vaccination has become a cornerstone of public health strategies aimed at controlling the mpox outbreak.
Types of Mpox Vaccines Available
Several vaccines have been developed and authorized for use in preventing mpox, most of which are derived from vaccines previously developed for smallpox. These vaccines provide cross-protection against both smallpox and mpox due to the genetic similarities between the two viruses.
1. JYNNEOS (also known as Imvamune or Imvanex)
JYNNEOS is a live-virus vaccine that was initially developed to protect against smallpox and is now authorized for use against mpox. It is a non-replicating vaccine, which means it does not replicate in the body, making it safer for individuals with weakened immune systems. The vaccine is administered in two doses, typically given four weeks apart, with full immunity developing within a few weeks of the second dose.
Effectiveness of JYNNEOS:
- Studies have shown that JYNNEOS provides strong protection against mpox, with an effectiveness rate of approximately 85% in preventing infection.
- The vaccine is especially recommended for individuals at higher risk, such as those who have been exposed to an infected person or have contact with animals in areas where mpox is endemic.
2. ACAM2000
ACAM2000 is another smallpox vaccine that provides protection against mpox due to the close relationship between the viruses. Unlike JYNNEOS, ACAM2000 is a live vaccine that can replicate in the body. This means that while it is effective in preventing infection, it may not be suitable for individuals with compromised immune systems or certain health conditions.
ACAM2000 is typically given as a single dose via a bifurcated needle, and it is more likely to cause side effects such as rash, swelling, and flu-like symptoms.
Effectiveness of ACAM2000:
- ACAM2000 has demonstrated high efficacy in preventing smallpox and is similarly effective against mpox.
- However, the risk of side effects means it is generally recommended for individuals who are not immunocompromised and who are at higher risk of exposure to the virus.
3. Older Smallpox Vaccines
Older smallpox vaccines, such as Dryvax, may also provide some protection against mpox, though they are not commonly used today. These vaccines are based on an older strain of the smallpox virus and have been largely replaced by newer, safer options like JYNNEOS and ACAM2000.
Effectiveness of Older Vaccines:
- While older smallpox vaccines do offer protection, they are not ideal for widespread use due to their higher likelihood of adverse reactions and complications.
How Mpox Vaccination Works
Mpox vaccination works by stimulating the immune system to recognize and fight the mpox virus if it enters the body. Both JYNNEOS and ACAM2000 vaccines contain viruses (modified to be less harmful) that resemble the mpox virus. Upon vaccination, the immune system produces antibodies, which are proteins that help fight off infections. If an individual is later exposed to mpox, these antibodies help prevent the virus from causing illness.
The Vaccine Schedule
- JYNNEOS: A two-dose regimen, with the second dose given four weeks after the first.
- ACAM2000: A single-dose vaccine administered via a bifurcated needle, often at a healthcare facility.
The exact schedule and recommendations may vary based on local health authorities and an individual’s specific risk factors.
Who Should Get Vaccinated?
While mpox vaccination is not recommended for the general population, certain groups of people are at higher risk of exposure and should consider getting vaccinated. These groups include:
1. Individuals in High-Risk Areas
People living in areas with active mpox outbreaks should get vaccinated to reduce the risk of contracting the virus.
2. Healthcare Workers
Healthcare workers who may come into contact with individuals infected with mpox should be vaccinated to protect themselves and prevent further transmission.
3. Close Contacts of Infected Individuals
Individuals who have had close contact with someone diagnosed with mpox, including sexual contacts or household members, should seek vaccination as soon as possible to prevent infection.
4. People with Specific Occupations
People who handle animals or have jobs in areas where mpox is more common, such as certain laboratory settings, should consider vaccination.
Potential Side Effects of Mpox Vaccination
Like any vaccine, mpox vaccines can cause side effects. However, the benefits of vaccination far outweigh the risks for most individuals. Common side effects include:
- Pain at the injection site
- Redness or swelling
- Fever
- Fatigue
- Headache
Serious side effects are rare but can include allergic reactions, skin rashes, or flu-like symptoms. Individuals with weakened immune systems or those who are pregnant should consult with their healthcare provider before getting vaccinated.
The Role of Mpox Vaccination in Preventing Outbreaks
Vaccination plays a crucial role in curbing mpox outbreaks by preventing further transmission of the virus. When a significant portion of the population is vaccinated, it creates herd immunity, reducing the overall spread of the virus and protecting those who may not be able to receive the vaccine due to health concerns.
Health authorities worldwide have emphasized vaccination as the most effective tool to stop the spread of mpox and prevent future outbreaks. As more vaccines become available and vaccination efforts intensify, we can expect a significant reduction in new cases.
Mpox vaccination is a vital tool in preventing the spread of the virus and ensuring the safety of individuals and communities. With vaccines like JYNNEOS and ACAM2000 offering robust protection against infection, vaccination is the best method to protect yourself from mpox, especially if you belong to a high-risk group.