Mouth irritation is a common issue that affects individuals of all ages, manifesting as discomfort, pain, or inflammation within the mouth. Whether caused by external factors such as infections or internal issues like allergies, mouth irritation can interfere with daily activities such as eating, speaking, and even sleeping. Understanding the various causes of mouth irritation and knowing how to treat and prevent it are essential steps in ensuring long-term oral health.
This guide will provide in-depth information on the most common causes of mouth irritation, ways to alleviate symptoms, and effective strategies to prevent its occurrence. If you’re struggling with sore gums, mouth sores, or other types of oral discomfort, the following tips can help restore your mouth’s health.
What is Mouth Irritation?
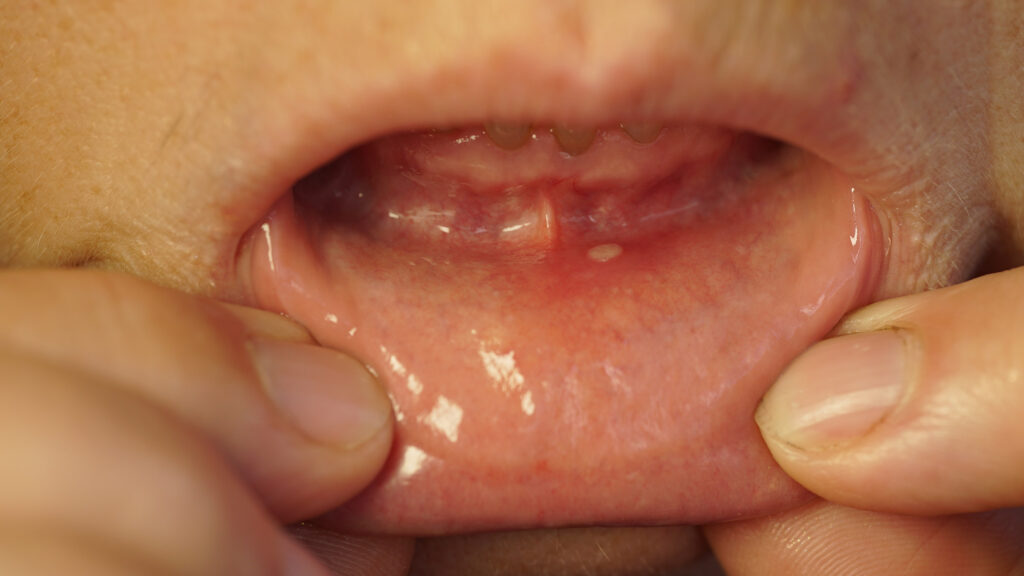
Mouth irritation refers to any discomfort, pain, or sensitivity within the oral cavity. It can affect various areas, including the gums, tongue, roof of the mouth, inner cheeks, and lips. The condition often results from irritation to the tissues in the mouth, which can lead to inflammation, redness, swelling, or the formation of sores.
There are numerous reasons why the mouth may become irritated, ranging from simple triggers such as spicy food to more complex conditions such as infections or autoimmune disorders. Depending on the underlying cause, mouth irritation can be temporary or chronic.
Common Causes of Mouth Irritation
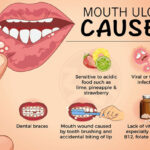
Understanding the causes of mouth irritation is crucial for determining the appropriate treatment and prevention methods. Below are the most frequent contributors to oral discomfort:
1. Infections
Infections are one of the leading causes of mouth irritation. These may be bacterial, viral, or fungal in nature and can lead to conditions such as:
- Canker Sores: These painful, shallow ulcers often appear on the inside of the lips, cheeks, or gums. They are typically caused by a combination of stress, injury, or a weakened immune system.
- Oral Thrush: This fungal infection, caused by the overgrowth of Candida, leads to white patches on the tongue, inner cheeks, and roof of the mouth.
- Cold Sores: Caused by the herpes simplex virus, cold sores usually appear on the lips or around the mouth, leading to irritation, itching, and discomfort.
2. Dry Mouth (Xerostomia)
Saliva plays a crucial role in maintaining the health of the oral tissues. When saliva production decreases due to dehydration, medications, or certain health conditions, the mouth becomes dry. This lack of moisture can lead to irritation, difficulty swallowing, and an increased risk of infections like cavities and gum disease.
3. Allergic Reactions
Allergies to certain foods, medications, or oral care products can cause irritation in the mouth. Common allergens include:
- Food Allergies: Certain foods like nuts, fruits, or spices can trigger allergic reactions that cause swelling, redness, and discomfort in the mouth.
- Medications: Some medications, especially antibiotics, can lead to oral reactions that cause irritation and sores.
- Dental Products: Toothpastes, mouthwashes, or chewing gums containing certain chemicals like sodium lauryl sulfate may cause sensitivity and irritation in some individuals.
4. Gum Disease (Gingivitis and Periodontitis)
Gum disease is a condition that causes inflammation and irritation of the gums, often due to the accumulation of plaque and tartar on the teeth. Gingivitis, the mildest form of gum disease, leads to redness, swelling, and bleeding of the gums, while periodontitis, a more severe form, can cause gum recession, tooth mobility, and other complications.
5. Dental Problems
Dental issues such as cavities, ill-fitting dentures, and damaged fillings can lead to mouth irritation. Cavities create holes in teeth, allowing bacteria to irritate the surrounding tissues. Poorly fitted dentures or braces may also rub against the gums, causing sores and pain.
6. Irritating Foods and Beverages
Certain foods and drinks are known to irritate the mouth’s tissues, especially when consumed in excess. Spicy, acidic, or salty foods can cause a burning sensation or discomfort, particularly for individuals with sensitive mouths.
7. Trauma or Injury
Physical trauma, such as biting the inside of your cheek, brushing too hard, or accidentally injuring the mouth while eating, can result in irritation or sores. These injuries often heal on their own, but they can cause temporary discomfort.
Prevention Strategies for Mouth Irritation
While it is not always possible to avoid mouth irritation completely, there are several effective strategies to minimize its occurrence:
1. Maintain Good Oral Hygiene
Good oral hygiene is essential for preventing many causes of mouth irritation. Brushing your teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste, flossing daily, and using an antimicrobial mouthwash can help keep bacteria at bay and reduce the risk of infections.
Additionally, regular dental checkups are important to catch any early signs of gum disease or other dental issues that may lead to irritation.
2. Stay Hydrated
Drinking plenty of water throughout the day helps prevent dry mouth and ensures that the mouth remains moist. Avoid beverages that can dry out the mouth, such as alcohol or caffeinated drinks, as they can exacerbate the symptoms of dry mouth.
3. Avoid Irritating Foods
Spicy, acidic, and salty foods can trigger mouth irritation, especially in individuals with sensitive mouths. If you are prone to irritation, limit your consumption of citrus fruits, hot peppers, and foods with strong spices.
4. Use Hypoallergenic Oral Products
Opt for toothpaste and mouthwash products that are free from harsh chemicals like sodium lauryl sulfate, which can irritate the soft tissues in the mouth. Look for options labeled as “gentle” or “hypoallergenic.”
5. Manage Stress
Stress can trigger mouth ulcers and other oral health issues. Incorporating stress management techniques, such as meditation, deep breathing, and regular physical activity, can help reduce the likelihood of stress-related mouth irritation.
6. Protect Your Mouth from Injury
If you play contact sports or engage in activities where injury to the mouth is possible, use a mouthguard to protect your teeth and gums from trauma. If you have braces or dentures, ensure that they fit properly to avoid irritation from rubbing.
Treatment Options for Mouth Irritation
When mouth irritation does occur, prompt treatment is essential to alleviate symptoms and prevent further discomfort. The treatment options vary depending on the cause of the irritation:
1. Topical Treatments
For mild irritation or mouth sores, over-the-counter topical gels or ointments can provide relief. Products containing benzocaine or hydrocortisone can numb the area and reduce inflammation.
2. Prescription Medications
If the irritation is caused by an infection or severe inflammation, a doctor or dentist may prescribe antibiotics, antifungals, or corticosteroids to reduce swelling and promote healing.
3. Home Remedies
Several home remedies can help soothe mild mouth irritation, including:
- Saltwater Rinses: A saline rinse can help reduce swelling and clean the mouth, especially after an injury or dental procedure.
- Aloe Vera: Applying aloe vera gel to the affected area can help soothe irritation and promote healing.
- Cold Compresses: For swollen gums or mouth sores, applying a cold compress can reduce pain and inflammation.
4. Professional Dental Care
For more severe cases of mouth irritation, professional dental care may be necessary. This includes treatment for gum disease, tooth infections, or other dental issues that require immediate attention.
Mouth irritation can be an uncomfortable and frustrating condition, but understanding its causes and prevention methods is the first step toward better oral health. By practicing good oral hygiene, staying hydrated, avoiding irritating foods, and seeking prompt treatment when necessary, you can reduce the risk of mouth irritation and maintain a healthy, pain-free mouth.